|
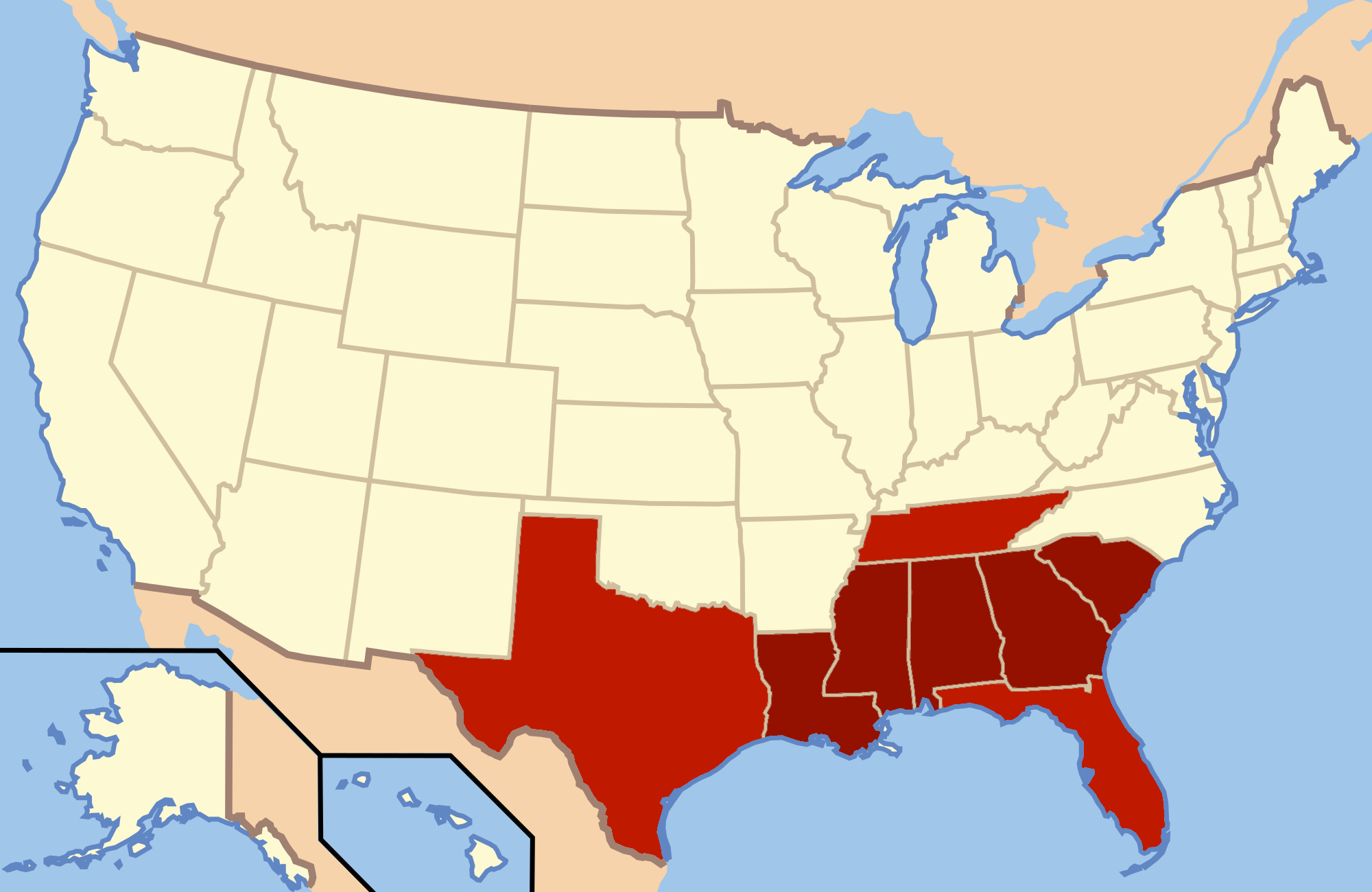
Texas Regulars
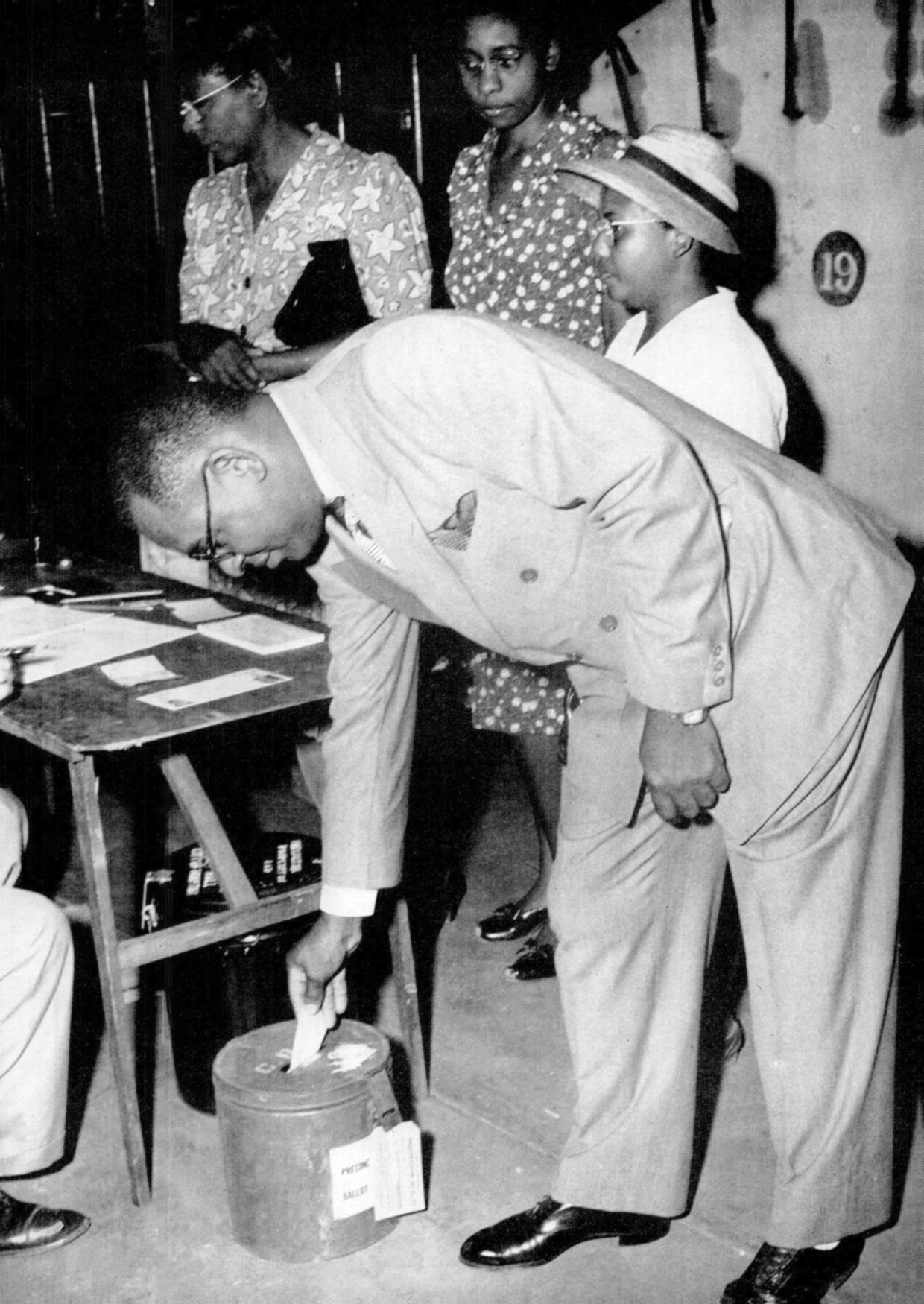
The Texas Regulars was a group based in Texas which was formed in 1944 to deny Franklin D. Roosevelt a majority of the Electoral College in the 1944 presidential election. Background By the 1940s, conservative Democrats in Texas had become increasingly disenchanted with Roosevelt and his New Deal. They were also unhappy that the US Supreme Court, in ''Smith v. Allwright'' (1944), had disallowed the segregated primaries used by the Democratic Party in Texas and some other states. History Attempt at taking over the Texas Democratic Party The Texas Regulars tried to gain control of the state nominating convention and select a slate of presidential electors who would not vote for Roosevelt. The group's supporters included US Representative Martin Dies Jr., former Texas governor Dan Moody, and Senator W. Lee O'Daniel. The Texas Regulars won the first convention, but lost the second convention. Unpledged electors This defeat led them to form their own ticket of unple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both List of U.S. states and territories by area, area (after Alaska) and List of U.S. states and territories by population, population (after California). Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Houston is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas and the List of United States cities by population, fourth-largest in the U.S., while San Antonio is the second most pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidney Hillman
Sidney Hillman (March 23, 1887 – July 10, 1946) was an American labor leader. He was the head of the Amalgamated Clothing Workers of America and was a key figure in the founding of the Congress of Industrial Organizations and in marshaling labor's support for President Franklin D. Roosevelt and the New Deal coalition of the Democratic Party. Early life Sidney Hillman was born in Žagarė, Lithuania, then part of the Russian Empire, on March 23, 1887, the son of Lithuanian Jewish parents. Sidney's maternal grandfather was a small-scale merchant; his paternal grandfather was a rabbi known for his piety and lack of concern for material possessions.Steven Fraser, ''Labor Will Rule: Sidney Hillman and the Rise of American Labor.'' New York: The Free Press, 1991; pp. 3-4. Hillman's father was himself an impoverished merchant, more concerned with reading and prayer than with his faltering business. From a young age Sidney had shown great academic promise, mastering the rote memorizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unpledged Elector
In United States presidential elections, an unpledged elector is a person nominated to stand as an elector but who has not pledged to support any particular presidential or vice presidential candidate, and is free to vote for any candidate when elected a member of the Electoral College. Presidential elections are indirect, with voters in each state choosing electors on Election Day in November, and these electors choosing the president and vice president of the United States in December. Electors in practice have since the 19th century almost always agreed in advance to vote for a particular candidate — that is, they are said to have been ''pledged'' to that candidate. In several elections in the 20th century, however, competitive campaigns were mounted by candidates who made no pledge to any presidential nominee before the election. These anomalies largely arose from fissures within the Democratic Party over the issues of civil rights and segregation. No serious general elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Democrat
In American politics, a conservative Democrat is a member of the Democratic Party with conservative political views, or with views that are conservative compared to the positions taken by other members of the Democratic Party. Traditionally, conservative Democrats have been elected to office from the Southern states, rural areas, the Rust Belt, and the Midwest. In 2019, the Pew Research Center found that 14% of Democratic and Democratic-leaning registered voters identify as conservative or very conservative, 38% identify as moderate, and 47% identify as liberal or very liberal. 21st century conservative Democrats are similar to liberal Republican counterparts, in that both became political minorities after their respective political parties underwent a major political realignment, which began to gain speed in 1964. Prior to 1964, both parties had their liberal, moderate, and conservative wings, each of them influential in both parties. During this period, conservative Democra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party, also referred to as the GOP ("Grand Old Party"), is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States. The GOP was founded in 1854 by anti-slavery activists who opposed the Kansas–Nebraska Act, which allowed for the potential expansion of chattel slavery into the western territories. Since Ronald Reagan's presidency in the 1980s, conservatism has been the dominant ideology of the GOP. It has been the main political rival of the Democratic Party since the mid-1850s. The Republican Party's intellectual predecessor is considered to be Northern members of the Whig Party, with Republican presidents Abraham Lincoln, Rutherford B. Hayes, Chester A. Arthur, and Benjamin Harrison all being Whigs before switching to the party, from which they were elected. The collapse of the Whigs, which had previously been one of the two major parties in the country, strengthened the party's electoral success. Upon its founding, it supported c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwight D
Dwight may refer to: People * Dwight (given name) * Dwight D. Eisenhower (1890–1969), 34th president of the United States and former military officer *New England Dwight family of American educators, military and political leaders, and authors * Ed Dwight (born 1933), American test pilot, participated in astronaut training program * Mabel Dwight (1875–1955), American artist * Elton John (born Reginald Dwight in 1947), English singer, songwriter and musician Places Canada * Dwight, Ontario, village in the township of Lake of Bays, Ontario United States * Dwight (neighborhood), part of an historic district in New Haven, Connecticut * Dwight, Illinois, village in Livingston and Grundy counties * Dwight, Kansas, city in Morris County * Dwight, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Dwight, Nebraska, village in Butler County * Dwight, North Dakota, city in Richland County * Dwight Township, Livingston County, Illinois * Dwight Township, Michigan Institutions * Dwight Correctional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1948 United States Presidential Election
The 1948 United States presidential election was the 41st quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 2, 1948. In one of the greatest election upsets in American history, incumbent President Harry S. Truman, the Democratic nominee, defeated Republican Governor Thomas E. Dewey. Truman had ascended to the presidency in April 1945 after the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt. Defeating attempts to drop him from the ticket, Truman won the presidential nomination at the 1948 Democratic National Convention. The Democratic convention's civil rights plank caused a walk-out by several Southern delegates, who launched a third-party " Dixiecrat" ticket led by Governor Strom Thurmond of South Carolina. The Dixiecrats hoped to win enough electoral votes to force a contingent election in the House of Representatives, where they could extract concessions from either Dewey or Truman in exchange for their support. Truman also faced a challenge from his party in the form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strom Thurmond
James Strom Thurmond Sr. (December 5, 1902June 26, 2003) was an American politician who represented South Carolina in the United States Senate from 1954 to 2003. Prior to his 48 years as a senator, he served as the 103rd governor of South Carolina from 1947 to 1951. Thurmond was a member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party until 1964, when he joined the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party for the remainder of his legislative career. He also 1948 United States presidential election, ran for president in 1948 as the Dixiecrat candidate, receiving over a million votes and winning four states. A staunch opponent of civil rights legislation in the 1950s and 1960s, Thurmond Strom Thurmond filibuster of the Civil Rights Act of 1957, conducted the longest speaking filibuster ever by a lone senator, at 24 hours and 18 minutes in length, in opposition to the Civil Rights Act of 1957. In the 1960s, he voted against the Civil Rights Act of 1964, 1964 Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dixiecrat
The States' Rights Democratic Party (whose members are often called the Dixiecrats) was a short-lived segregationist political party in the United States, active primarily in the South. It arose due to a Southern regional split in opposition to the Democratic Party. After President Harry S. Truman, a member of the Democratic Party, ordered integration of the military in 1948 and other actions to address civil rights of African Americans, many Southern conservative white politicians who objected to this course organized themselves as a breakaway faction. The Dixiecrats wished to protect Southern states' rights to maintain racial segregation. Supporters assumed control of the state Democratic parties in part or in full in several Southern states. The Party opposed racial integration and wanted to retain Jim Crow laws and white supremacy in the face of possible federal intervention. Its members were referred to as "Dixiecrats", a portmanteau of "Dixie", referring to the Souther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Bill Of Rights
The United States Bill of Rights comprises the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. Proposed following the often bitter 1787–88 debate over the ratification of the Constitution and written to address the objections raised by Anti-Federalists, the Bill of Rights amendments add to the Constitution specific guarantees of personal freedoms and rights, clear limitations on the government's power in judicial and other proceedings, and explicit declarations that all powers not specifically granted to the federal government by the Constitution are reserved to the states or the people. The concepts codified in these amendments are built upon those in earlier documents, especially the Virginia Declaration of Rights (1776), as well as the Northwest Ordinance (1787), the English Bill of Rights (1689), and Magna Carta (1215). Largely because of the efforts of Representative James Madison, who studied the deficiencies of the Constitution pointed out by anti-feder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Supremacy
White supremacy or white supremacism is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races and thus should dominate them. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine of scientific racism and was a key justification for European colonialism. As a political ideology, it imposes and maintains cultural, social, political, historical, and/or institutional domination by white people and non-white supporters. In the past, this ideology had been put into effect through socioeconomic and legal structures such as the Atlantic slave trade, Jim Crow laws in the United States, the White Australia policies from the 1890s to the mid-1970s, and apartheid in South Africa. This ideology is also today present among neo-Confederates. White supremacy underlies a spectrum of contemporary movements including white nationalism, white separatism, neo-Nazism, and the Christ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom Of Education
Freedom of education is the right for parents to have their children educated in accordance with their religious and other views, allowing groups to be able to educate children without being impeded by the nation state. Freedom of education is a constitutional (legal) concept that has been included in the European Convention on Human Rights, Protocol 1, Article 2, International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights Article 13 and several national constitutions, e.g. the Belgian constitution (former article 17, now article 24) and the Dutch constitution (article 23). Europe The European forum for freedom in education was formed in 1989 and has 69 members across 13 countries. Their official demands include a need for autonomy to students and teachers. It also establishes the importance of diversity in education, to allow parents the choice of sending their child to a school that aligns with their views. The Netherlands In the Netherlands, a political battle raged t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |