|
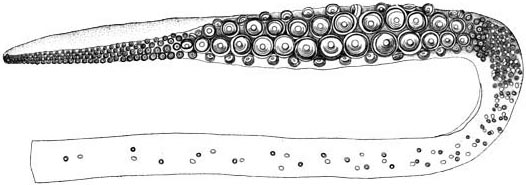
Teudopseina
The Teudopseina is a clade of stem- octopods that first evolved in the Toarcian,Fuchs, Dirk & Weis, Robert. (2010). Taxonomy, morphology and phylogeny of Lower Jurassic teudopseid coleoids (Cephalopoda). Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 257. 351-366. 10.1127/0077-7749/2010/0083. considered the largest clade of gladius-bearing coleoids in the Mesozoic. Up to five families are known, among which the Trachyteuthidae, '' Trachyteuthis'' in particular, were the most abundant.Tree of Life Project: Teudopseina ''Tree of Life Web Project''. Retrieved 2022-01-15. Description The Teudopseina can be united by five primary traits. These are the presence of a |
Gladius (cephalopod)
The gladius (plural: ''gladii''), or pen, is a hard internal bodypart found in many cephalopods of the superorder Decapodiformes (particularly squids) and in a single extant member of the Octopodiformes, the vampire squid (''Vampyroteuthis infernalis''). It is so named for its superficial resemblance to the Roman short sword of the same name, and is a vestige of the ancestral mollusc shell, which was external. The gladius is located dorsally within the mantle and usually extends for its entire length. Composed primarily of chitin, it lies within the shell sac, which is responsible for its secretion. Gladii are known from a number of extinct cephalopod groups, including teudopseids (''e.g.'' '' Actinosepia'', '' Glyphiteuthis'', '' Muensterella'', '' Palaeololigo'', '' Teudopsinia'', '' Teudopsis'', and '' Trachyteuthis''), loligosepiids (''e.g.'' '' Geopeltis'', '' Jeletzkyteuthis'', and '' Loligosepia''), and prototeuthids (''e.g.'' '' Dorateuthis'', '' Paraplesioteuthis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enchoteuthis
''Enchoteuthis'' (meaning "spear squid") is an extinct genus of large enchoteuthine cephalopod that lived during the Cretaceous. Although it and its relative '' Tusoteuthis'' are often compared to squid, both are now thought to be more closely related to modern octopuses. Examination of gladius remains initially yielded an estimated mantle length about based on specimen once described as ''Tusoteuthis longa'', close to or equal to that of the modern giant squid, although reclassification of this genus as a muensterelloid results in a much shorter total length, about . Three species are currently recognized as valid: ''E. melanae'', ''E. tonii'', and ''E. cobbani''. Etymology The generic name ''Enchoteuthis'' is derived from the Greek ''enchos'' ("spear") and ''teuthis'' ("squid"). The specific name ''melanae'' honors Melanie Bonner, who discovered the holotype. ''E. cobbani'' is named after William Cobban. Distribution ''E. melanae'' and ''E. cobbani'' are both known from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muensterelloidea
Muensterelloidea is a superfamily (or clade) of stem-octopod cephalopods from the Early Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. Two families are currently identified, Muensterellidae, and Patelloctopodidae. The clade is the ancestral group from which modern octopus arose. Description Overall Soft tissue anatomy within the Muensterelloidea is well-documented. Muenster (1842), who first recorded the holotype specimen of ''Muensterella'', noted its egg-shaped anatomy and apparent lack of swimming fins.Fuchs, D., Keupp, H., & Engeser, T. (2003). New records of soft parts of Muensterella scutellaris Muenster, 1842 (Coleoidea) from the Late Jurassic Plattenkalks of Eichstätt and their significance for octobrachian relationships. Berliner Paläobiologische Abhandlungen, 3, 101-111. Indeed, in all preserved specimens the same body structure is present, with all lacking a distinct swimming fin. Fuchs ''et al.'' (2003) suggested it possessed marginal fins, as a sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muensterellidae
Muensterellidae is a family of stem-octopod cephalopods from the Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. Phylogeny Muensterellidae is one of two families in the superfamily Muensterelloidea along with the Patelloctopodidae. The muensterelloids are characterized by having a roughly spoon-shaped end of the gladius ''Gladius'' () is a Latin word meaning "sword" (of any type), but in its narrow sense it refers to the sword of ancient Roman foot soldiers. Early ancient Roman swords were similar to those of the Greeks, called '' xiphe'' (plural; singular ''xi ... called the patella. This type of gladius is likely ancestral to the gladius remnants of modern octopuses. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q30434538 Octopuses Prehistoric cephalopod families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muensterella
Muensterella is a fossil stem-octopod known from a handful of specimens from German Solnhofen plattenkalk Plattenkalk is a very finely grained limestone chemically precipitated in a stratified water column under conditions where bioturbation does not occur. The reasons for the quiet depositional environment and the processes of sediment accumulation v ....Coleoid cephalopods through time (Warnke K., Keupp H., Boletzky S. v., eds) Berliner Paläobiol. Abh. 03 101-111 Berlin 2003 NEW RECORDS OF SOFT PARTS OF MUENSTERELLA SCUTELLARIS MUENSTER, 1842 (COLEOIDEA) FROM THE LATE JURASSIC PLATTENKALKS OF EICHSTÄTT AND THEIR SIGNIFICANCE FOR OCTOBRACHIAN RELATIONSHIPS D. Fuchs*, H. Keupp & Th. Engeser References Prehistoric cephalopod genera {{Paleo-cephalopod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Squids
The giant squid (''Architeuthis dux'') is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family (biology), family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of deep-sea gigantism, abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around Dianne Tracey, Tracey, D. M., O. F. Anderson & J. R. Naylor (2011)''A guide to common deepsea invertebrates in New Zealand waters. Third edition.''National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research, Wellington. 317 pp.Yukhov, V. L. (2014)Гигантские кальмары рода ''Architeuthis'' в Южном океане / Giant calmaries ''Аrchiteuthis'' in the Southern ocean [Gigantskiye kalmary roda ''Architeuthis'' v Yuzhnom okeane.] ''Ukrainian Antarctic Journal'' no. 13: 242–253. for females and for males, from the cephalopod fin, posterior fins to the tip of the two long cephalopod limb, tentacles (longer than the colossal squid at an estimated , but substantially lighter, due to the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopuses
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the center point of the eight limbs. The soft body can radically alter its shape, enabling octopuses to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their eight appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used both for respiration and for locomotion, by expelling a jet of water. Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse of all invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various regions of the ocean, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachyteuthis
''Trachyteuthis'' is a genus of fossil cephalopod, comprising five species: ''T. hastiformis'', ''T. latipinnis'', ''T. nusplingensis'', ''T. teudopsiformis'', ''T. covacevichi'' and ''T. chilensis''. Taxonomy The taxonomic placement of ''Trachyteuthis'' is uncertain. Though often assigned to the order Vampyromorphida, the discovery of fossilised ''Trachyteuthis'' beaks in the Upper Jurassic limestone of Germany suggests a close phylogenetic relation to the Octopoda. It is clear that it does at least belong in the Coleoidea. It is thought to be very closely related to '' Teudopsis''. Distribution Fossils are scarce but have been reported from the Kimmeridge clay of the UK; the Solnhofen Solnhofen is a municipality in the district of Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen in the region of Middle Franconia in the ' of Bavaria in Germany. It is in the Altmühl valley. The local area is famous in geology and palaeontology for Solnhofen limesto ... limestone of Germany, Jurassic deposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toarcian
The Toarcian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, an age and stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic. It spans the time between 182.7 Ma (million years ago) and 174.1 Ma. It follows the Pliensbachian and is followed by the Aalenian. The Toarcian Age began with the Toarcian turnover, the extinction event that sets its fossil faunas apart from the previous Pliensbachian age. It is believed to have ended with a global cooling event known as the Comptum Cooling Event, although whether it represented a worldwide event is controversial. Stratigraphic definitions The Toarcian takes its name from the city of Thouars, just south of Saumur in the Loire Valley of France. The stage was introduced by French palaeontologist Alcide d'Orbigny in 1842, after examining rock strata of this age in a quarry near Thouars. In Europe this period is represented by the upper part of the Lias. The base of the Toarcian is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where the ammonite genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleoids
Subclass Coleoidea, or Dibranchiata, is the grouping of cephalopods containing all the various taxa popularly thought of as "soft-bodied" or "shell-less" (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish). Unlike its extant sister group, Nautiloidea, whose members have a rigid outer shell for protection, the coleoids have at most an internal cuttlebone, gladius, or shell that is used for buoyancy or support. Some species have lost their cuttlebone altogether, while in some it has been replaced by a chitinous support structure. A unique trait of the group is the ability to edit their own RNA. The major divisions of Coleoidea are based upon the number of arms or tentacles and their structure. The extinct and most primitive form, the Belemnoidea, presumably had ten equally-sized arms in five pairs numbered dorsal to ventral as I, II, III, IV and V. More modern species either modified or lost a pair of arms. The superorder Decapodiformes has arm pair IV modified into long tentacles with sucker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |