|
Termite Mounds
Mound-building termites are a group of termite species that live in mounds. These termites live in Africa, Australia and South America. The mounds sometimes have a diameter of . Most of the mounds are in well-drained areas. Termite mounds usually outlive the colonies themselves. If the inner tunnels of the nest are exposed it is usually dead. Sometimes other colonies, of the same or different species, occupy a mound after the original builders' deaths. Mound structure The structure of the mounds can be very complicated. Inside the mound is an extensive system of tunnels and conduits that serves as a ventilation system for the underground nest. In order to get good ventilation, the termites will construct several shafts leading down to the cellar located beneath the nest. The mound is built above the subterranean nest. The nest itself is a spheroidal structure consisting of numerous gallery chambers. They come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. Some, like ''Odontotermes'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litchfield National Park-03
Litchfield may refer to: Places Antarctica * Litchfield Island, Palmer Archipelago Australia * Litchfield Municipality, Northern Territory * Litchfield National Park, Northern Territory * Litchfield Station, Northern Territory Canada * Litchfield, Nova Scotia * Litchfield, Quebec United Kingdom * Litchfield, Hampshire, England * Litchfield Street, Westminster, London United States * Litchfield, California * Litchfield, Connecticut * Litchfield (borough), Connecticut * Litchfield County, Connecticut * Litchfield Hills, Connecticut * Litchfield, Illinois * Litchfield, Kansas * Litchfield, Maine * Litchfield, Michigan * Litchfield, Minnesota * Litchfield, Nebraska * Litchfield, New Hampshire * Litchfield, New York * Litchfield, Ohio * Litchfield Beach, South Carolina * Litchfield Plantation, South Carolina * Litchfield Township (other) Education * Litchfield Female Academy, in Litchfield, Connecticut; defunct * Litchfield High School (other) * Litchfield ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stack Effect
The stack effect or chimney effect is the movement of air into and out of buildings through unsealed openings, chimneys, flue-gas stacks, or other containers, resulting from air buoyancy. Buoyancy occurs due to a difference in indoor-to-outdoor air density resulting from temperature and moisture differences. The result is either a positive or negative buoyancy force. The greater the thermal difference and the height of the structure, the greater the buoyancy force, and thus the stack effect. The stack effect helps drive natural ventilation, air infiltration, and fires (e.g. the Kaprun tunnel fire, King's Cross underground station fire and the Grenfell Tower fire). Stack effect in buildings Since buildings are not totally sealed (at the very minimum, there is always a ground level entrance), the stack effect will cause air infiltration. During the heating season, the warmer indoor air rises up through the building and escapes at the top either through open windows, ventilatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amitermes Meridionalis
''Amitermes meridionalis'', commonly known as the magnetic termite or compass termite, is a species of eusocial insect in the family Termitidae. It is endemic to northern Australia and the common names derive from the fact that the wedge-shaped mound is aligned with its main axis running north and south. Description A large mound may house up to a million individual termites. Each is the nest of a colony of ''Amitermes meridionalis'' and houses the queen, king, reproductives, soldiers and workers. The outer surface of the mound is hard and durable whereas the material separating the chambers and galleries inside is more papery. The soldiers are long and their curved mandibles bear a single in-turned tooth. Many termites never leave the mound and as a result of this protected environment they have thin cuticles, colourless bodies, little sight and little ability to protect themselves. Distribution and habitat ''Amitermes meridionalis'' is native to the northern part of Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntermes
''Syntermes'' is a genus of large, hornless, open foraging Syntermitinae termites belonging to the family Termitidae Termitidae is the largest family of termites whose members are commonly known as the higher termites. They are evolutionarily the most specialised termite group, with their highly compartmentalized hindgut lacking the flagellated protozoans comm .... The genus is most recognized for the large mounds built from loose soil that some species construct, with some as old as 4,000 years. Species # '' Syntermes aculeosus'' # '' Syntermes barbatus'' # '' Syntermes bolivianus'' # '' Syntermes brevimalatus'' # '' Syntermes calvus'' # '' Syntermes cearensis'' # '' Syntermes chaquimayensis'' # '' Syntermes crassilabrum'' # '' Syntermes dirus'' # '' Syntermes grandis'' # '' Syntermes insidians'' # '' Syntermes longiceps'' # '' Syntermes magnoculus'' # '' Syntermes molestus'' # '' Syntermes nanus'' # '' Syntermes obtusus'' # '' Syntermes parallelus'' # '' Syntermes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caatinga
Caatinga (, ) is a type of semi-arid tropical vegetation, and an ecoregion characterized by this vegetation in interior northeastern Brazil. The name "Caatinga" is a Tupi word meaning "white forest" or "white vegetation" (''caa'' = forest, vegetation, ''tinga'' = white). The Caatinga is a xeric shrubland and thorn forest, which consists primarily of small, thorny trees that shed their leaves seasonally. Cacti, thick-stemmed plants, thorny brush, and arid-adapted grasses make up the ground layer. Most vegetation experiences a brief burst of activity during the three-month long rainy season. Caatinga falls entirely within earth's tropical zone and is one of 6 major ecoregions of Brazil. It covers 850,000 km², nearly 10% of Brazil's territory. It is home to 26 million people and over 2000 species of plants, fish, reptiles, amphibians, birds, and mammals. The Caatinga is the only exclusively Brazilian biome, which means that a large part of its biological heritage cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontotermes Obesus
''Odontotermes obesus'' is a species of termite in the family Termitidae. It is native to tropical southwestern Asia. This termite cultivates a symbiotic fungus in a special chamber in the nest. Workers gather vegetable detritus which they bring back to the colony, chewing up the material to make a suitable substrate on which the fungus will grow. The colony Termites of this species swarm from April and May onwards, before and during the wet season. After their nuptial flight, a pair of winged termites will search for a soil crevice or loose soil in which to establish their nest. The initial structure is a cone-shaped mound, with cone-shaped turrets; the fungus garden (sometimes called the comb) is at the centre of the cone with the royal chamber beneath. Galleries, runways and vaults are added as the colony expands, and the nest principally grows upwards. The fungus grown by the termites of this species is ''Macrolepiota albuminosa'', which exclusively grows in association with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrotermes Michaelseni
''Macrotermes michaelseni'' is a species of termite in the family Termitidae, found in sub-Saharan Africa. It is associated with the fungus ''Termitomyces schimperi''. Distribution and habitat ''M. michaelseni'' is one of a number of ''Macrotermes'' species occurring in savannahs in sub-Saharan Africa. These species vary in their different soil preferences, some preferring moist habitats, with ''M. michaelseni'' being tolerant of drier habitats than the others. It is common in the Okavango Delta in northern Botswana, an area that sees periodic flooding from summer rains in the catchment area; clay soils and high groundwater levels are favourable to it, and there are up to six mounds per hectare in the delta area. Colony structure A ''M. michaelseni'' nest initially consists of a number of chambers and tunnels completely underground. A mound is built above the ground only in a mature colony, and in time becomes an enormous structure, with ridges, pinnacles and chimneys, up to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontotermes Transvaalensis
''Odontotermes'', commonly known as the fungus-growing termites, is a termite genus belonging to family Termitidae, which is native to the Old World. They are most destructive in wooden homes, and are agricultural pests in the tropics and subtropics of Africa and Asia. It is the most diverse termite genus in Africa, with 78 species recorded (as of 2002). Nests Their underground nests form a slight mound above ground, which may be covered in grass. In large colonies, the mounds may be up to in diameter, and may be covered by shrubs and trees. Some species construct open chimneys or vent holes that descend into the mound. The fungal garden is enveloped by a thick layer of clay. Castes The queen is imprisoned in a clay cell in the midst of the fungal garden at the center of the hive. The African species have a single soldier cast, unlike the related genus ''Macrotermes''. Food Their only food is the fungus grown in the fungal garden at the center of the nest. The fungus is cultiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venturi Effect
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section (or choke) of a pipe. The Venturi effect is named after its discoverer, the 18th century Italian physicist, Giovanni Battista Venturi. Background In inviscid fluid dynamics, an incompressible fluid's velocity must ''increase'' as it passes through a constriction in accord with the principle of mass continuity, while its static pressure must ''decrease'' in accord with the principle of conservation of mechanical energy (Bernoulli's principle). Thus, any gain in kinetic energy a fluid may attain by its increased velocity through a constriction is balanced by a drop in pressure. By measuring pressure, the flow rate can be determined, as in various flow measurement devices such as Venturi meters, Venturi nozzles and orifice plates. Referring to the adjacent diagram, using Bernoulli's equation in the special case of steady, incompressible, inviscid flows (such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrotermes Natalensis
''Macrotermes natalensis'' is a fungus-growing termite species that belongs to the genus ''Macrotermes.'' This species is associated with the ''Termitomyces'' fungal genus. ''M. natalensis'' has domesticated ''Termitomyces'' to produce food for the colony. Both termite species- fungal genus- are obligate and mutually beneficial where termite relies on the fungus to break down for plant materiel and nutrient resource. In contrast, the fungal species obtain plant material and optimal conditions for growth. This is relationship also inhibits competitors and antagonistic fungi to termites mounds. Habitat: This fungal-termite species reported in South Africa. Genome data size: ''M. natalensis'' has become a well-studied fungus-growing termite species, and its genomic sequence reads generate 1.3 gigabytes of data, making it the largest termite genome to date. Colony caste system All the fungus-growing termite colonies similar caste systems. Each caste plays a different roles i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Termite Mound On Cape York
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes (eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blattodea (along with cockroaches). Termites were once classified in a separate order from cockroaches, but recent phylogenetic studies indicate that they evolved from cockroaches, as they are deeply nested within the group, and the sister group to wood eating cockroaches of the genus ''Cryptocercus''. Previous estimates suggested the divergence took place during the Jurassic or Triassic. More recent estimates suggest that they have an origin during the Late Jurassic, with the first fossil records in the Early Cretaceous. About 3,106 species are currently described, with a few hundred more left to be described. Although these insects are often called "white ants", they are not ants, and are not closely related to ants. Like ants and some bees and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
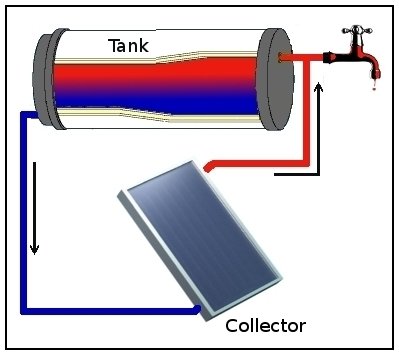
Thermosiphon
Thermosiphon (or thermosyphon) is a method of passive heat exchange, based on natural convection, which circulates a fluid without the necessity of a mechanical pump. Thermosiphoning is used for circulation of liquids and volatile gases in heating and cooling applications such as heat pumps, water heaters, boilers and furnaces. Thermosiphoning also occurs across air temperature gradients such as those utilized in a wood fire chimney or solar chimney. This circulation can either be open-loop, as when the substance in a holding tank is passed in one direction via a heated transfer tube mounted at the bottom of the tank to a distribution point—even one mounted above the originating tank—or it can be a vertical closed-loop circuit with return to the original container. Its purpose is to simplify the transfer of liquid or gas while avoiding the cost and complexity of a conventional pump. Simple thermosiphon Natural convection of the liquid starts when heat transfer to the liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
.jpg)