|
Terezín Ghetto Museum
Terezín (; german: Theresienstadt) is a town in Litoměřice District in the Ústí nad Labem Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 2,800 inhabitants. It is a former military fortress composed of the citadel and adjacent walled garrison town. The town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument reservation. Terezin is most infamously the location of the Nazis' notorious Theresienstadt Ghetto. Administrative parts Villages of České Kopisty, Nové Kopisty and Počaply are administrative parts of Terezín. Geography Terezín is located about south of Litoměřice and southeast of Ústí nad Labem. It lies in a flat landscape of the Lower Eger Table. It is situated on both banks of the Ohře River, near its confluence with the Elbe. The Elbe forms the northern municipal border. History On 10 January 1780, the Habsburg emperor Joseph II ordered the erection of the fortress, named ''Theresienstadt'' after his mother Empress Maria Theresa. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obec
Obec (plural: ''obce'') is the Czech language, Czech and Slovak language, Slovak word for a municipality (in the Czech Republic, in Slovakia and abroad). The literal meaning of the word is "Intentional community, commune" or "community". It is the smallest administrative unit that is governed by elected representatives. Cities and towns are also municipalities. Definition Legal definition (according to the Czech code of law with similar definition in the Slovak code of law) is: ''"The municipality is a basic territorial self-governing community of citizens; it forms a territorial unit, which is defined by the boundary of the municipality."'' Every municipality is composed of one or more cadastre, cadastral areas. Every municipality is composed of one or more administrative parts, usually called town parts or villages. A municipality can have its own flag and coat of arms. Czech Republic Almost whole area of the republic is divided into municipalities, with the only exception be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, northwest of Hamburg. Its total length is . The Elbe's major tributaries include the rivers Vltava, Saale, Havel, Mulde, Schwarze Elster, and Ohře. The Elbe river basin, comprising the Elbe and its tributaries, has a catchment area of , the twelfth largest in Europe. The basin spans four countries, however it lies almost entirely just in two of them, Germany (65.5%) and the Czech Republic (33.7%, covering about two thirds of the state's territory). Marginally, the basin stretches also to Austria (0.6%) and Poland (0.2%). The Elbe catchment area is inhabited by 24.4 million people, the biggest cities within are Berlin, Hamburg, Prague, Dresden and Leipzig. Etymology Firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neratovice
Neratovice (; german: Neratowitz) is a town in Mělník District in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 16,000 inhabitants. It is an industrial town. Administrative parts Villages of Byškovice, Horňátky, Korycany, Lobkovice and Mlékojedy are administrative parts of Neratovice. Geography Neratovice is located about north of Prague. It lies in a flat landscape in the Central Elbe Table. The highest point is at above sea level. The Elbe River flows through the town. A notable body of water is the flooded sandstone quarry Mlékojedy. History The first written mention of Neratovice is from 1227, at that time known as Neradice. It was a serf village of Chapter of St. Wenceslaus at the Prague Castle and of St. George's Convent, Prague, St. George's Convent in Prague. In the second half of the 14th century, it became a property of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Prague, Archbishopric of Prague. At the beginning of the 15th century, Neratovice was purc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 1866 between the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia, with each also being aided by various allies within the German Confederation. Prussia had also allied with the Kingdom of Italy, linking this conflict to the Third Italian War of Independence, Third Independence War of Italian unification. The Austro-Prussian War was part of the wider Austria-Prussia rivalry, rivalry between Austria and Prussia, and resulted in Prussian dominance over the German states. The major result of the war was a shift in power among the German states away from Austrian and towards Prussian hegemony. It resulted in the abolition of the German Confederation and its partial replacement by the unification of Germany, unification of all of the northern German sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
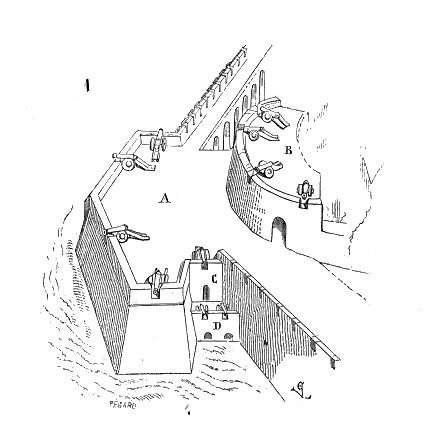
Cavalier (fortification)
A cavalier is a fortification which is built within a larger fortification, and which is higher than the rest of the work. It usually consists of a raised platform within a fort or bastion, so as to be able to fire over the main parapet without interfering with the fire of the latter. Through the use of cavaliers, a greater volume of fire can be obtained, but its great height also makes it an easy target for a besieger's guns. There are two types of cavaliers: *Common cavalier – a raised gun platform without any additional defensive features *Defensible cavalier – a raised gun platform surrounded by a ditch. If the ditch cuts across the bastion's terreplein and is supported by cuts, the cavalier can also be considered as a retrenchment. Gallery Malta - Birgu - Ix-Xatt tal-Birgu - Fort Saint Angelo (MSTHC) 02 ies.jpg, Ferramolino's Cavalier, Fort St. Angelo, Birgu, Malta Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaroměř
Jaroměř (; german: Jermer) is a town in Náchod District in the Hradec Králové Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 12,000 inhabitants. It is known for the Josefov Fortress. Josefov is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument reservation, the town centre of Jaroměř is proceted as an urban monument zone. Administrative parts Town parts of Cihelny, Jakubské Předměstí, Josefov and Pražské Předměstí, and villages of Dolní Dolce, Jezbiny, Semonice and Starý Ples are administrative parts of Jaroměř. Geography Jaroměř is located about northeast of Hradec Králové. It lies mostly in a flat agricultural landscape of the East Elbe Table. The eastern tip of the municipal territory extends into the Orlice Table. The town lies at the confluence of the rivers Úpa, Metuje and Elbe. There is also the confluence of Metuje and Stará Metuje, which flows through the eastern part of the territory. There are several ponds in the municipal territory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josefov Fortress
Josefov Fortress ( cs, Pevnost Josefov, german: Josefstadt or ) is a large historic defence complex of 18th-century military architecture in Jaroměř in the Hradec Králové Region of the Czech Republic. It was built between 1780 and 1787. Together with Terezín fortress, it was built for protection against attacks from Prussia, but its military importance, like other such fortresses built across Europe, was minimal as decisive battles were often fought elsewhere. In 1948 it became part of the town of Jaroměř. Design After the coronation of Emperor Joseph II, new fortifications began to be built for the defence of the northern border of the Empire. The defence of Moravia was entrusted to Olomouc, which was fortified by powerful forts. When the work was completed, the fortification of Hradec Králové commenced between 1766-88. The Emperor Joseph II himself had the Josefov Fortress built around the area of Plesy, near the town of Jaroměř. Designed by the French arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electorate Of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz. In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles IV designated the Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg an electorate, a territory whose ruler was one of the prince-electors who chose the Holy Roman emperor. After the extinction of the male Saxe-Wittenberg line of the House of Ascania in 1422, the duchy and the electorate passed to the House of Wettin. The electoral privilege was tied only to the Electoral Circle, specifically the territory of the former Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg. In the 1485 Treaty of Leipzig, the Wettin noble house was divided between the sons of Elector Frederick II into the Ernestine and Albertine lines, with the electoral district going to the Ernestines. In 1547, when the Ernestine elector John Frederick I was defeated in the Schmalkaldic War, the electoral district and el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia ( cs, České království),; la, link=no, Regnum Bohemiae sometimes in English literature referred to as the Czech Kingdom, was a medieval and early modern monarchy in Central Europe, the predecessor of the modern Czech Republic. It was an Imperial State in the Holy Roman Empire, and the Bohemian king was a prince-elector of the empire. The kings of Bohemia, besides the region of Bohemia proper itself, also ruled other lands belonging to the Bohemian Crown, which at various times included Moravia, Silesia, Lusatia, and parts of Saxony, Brandenburg, and Bavaria. The kingdom was established by the Přemyslid dynasty in the 12th century from the Duchy of Bohemia, later ruled by the House of Luxembourg, the Jagiellonian dynasty, and from 1526 the House of Habsburg and its successor, the House of Habsburg-Lorraine. Numerous kings of Bohemia were also elected Holy Roman Emperors, and the capital, Prague, was the imperial seat in the late 14th century, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II, more commonly known as Frederick the Great, who was the third son of Frederick William I.Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position ''suo jure'' (in her own right). She was the sovereign of Austria, Hungary, Croatia, Bohemia, Transylvania, Mantua, Milan, Lodomeria and Galicia, the Austrian Netherlands, and Parma. By marriage, she was Duchess of Lorraine, Grand Duchess of Tuscany and Holy Roman Empress. Maria Theresa started her 40-year reign when her father, Emperor Charles VI, died on 20 October 1740. Charles VI paved the way for her accession with the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713 and spent his entire reign securing it. He neglected the advice of Prince Eugene of Savoy, who believed that a strong military and a rich treasury were more important than mere signatures. Eventually, Charles VI left behind a weakened and impoverished state, particularly due to the War of the Polish Succession and the Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_Tafel_03.png)
