|
Tequatrovirus
''Tequatrovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the order ''Caudovirales'', in the family ''Myoviridae'', in the subfamily '' Tevenvirinae''. Gram-negative bacteria serve as the natural host, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are 75 species in this genus. Taxonomy The following species are assigned to the genus: *'' Citrobacter virus CrRp10'' *'' Citrobacter virus PhiZZ6'' *'' Citrobacter virus PhiZZ23'' *'' Enterobacteria virus Aplg8'' *'' Enterobacteria virus GiZh'' *'' Enterobacteria virus IME340'' *'' Enterobacteria virus Kha5h'' *'' Enterobacteria virus RB18'' *'' Enterobacteria virus RB27'' *'' Enterobacteria virus T6'' *'' Escherichia virus AR1'' *'' Escherichia virus AREG1'' *'' Escherichia virus C40'' *'' Escherichia virus CF2'' *'' Escherichia virus DalCa'' *'' Escherichia virus E112'' *'' Escherichia virus EC121'' *'' Escherichia virus ECML134'' *'' Escherichia virus EcNP1'' *'' Escherichia virus ECO4'' *'' Escherichia virus EcoMF1'' *'' Escheric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tevenvirinae
''Tevenvirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses in the order ''Caudovirales'', in the family ''Myoviridae''. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There are 135 species in this subfamily, most included in 12 genera. Taxonomy The following genera are recognized: * '' Dhakavirus'' * '' Gaprivervirus'' * '' Gelderlandvirus'' * '' Jiaodavirus'' * '' Karamvirus'' * '' Krischvirus'' * '' Moonvirus'' * '' Mosigvirus'' * '' Pseudotevenvirus'' * '' Schizotequatrovirus'' * '' Slopekvirus'' * ''Tequatrovirus ''Tequatrovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the order ''Caudovirales'', in the family ''Myoviridae'', in the subfamily '' Tevenvirinae''. Gram-negative bacteria serve as the natural host, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. Ther ...'' The following species are unassigned to a genus: ** '' Acinetobacter virus 133'' ** '' Aeromonas virus Aeh1'' Structure Viruses in ''Tevenvirinae'' are non-enveloped, with head-tail geometries. These viruses are about 70 nm wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoviridae
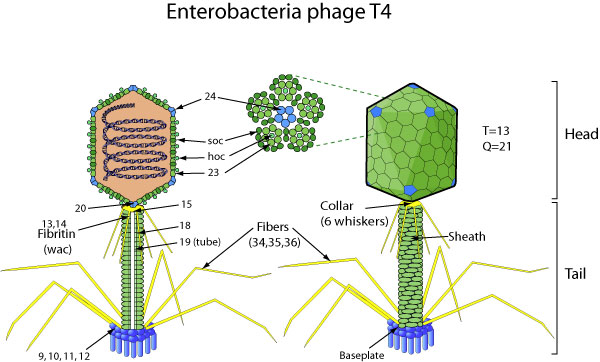
''Myoviridae'' is a family of bacteriophages in the order ''Caudovirales''. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There are 625 species in this family, assigned to eight subfamilies and 217 genera. Subdivisions The subfamily ''Tevenvirinae'' (synonym: ''Tequatrovirinae'') is named after its type species ''Enterobacteria phage T4''. Members of this subfamily are morphologically indistinguishable and have moderately elongated heads of about 110 nanometers (nm) in length, 114 nm long tails with a collar, base plates with short spikes and six long kinked tail fibers. The genera within this subfamily are divided on the basis of head morphology with the genus ''Tequatrovirus'' (Provisional name: ''T4virus'') having a head length of 137 nm and those in the genus ''Schizot4virus'' being 111 nm in length. Within the genera on the basis of protein homology the species have been divided into a number of groups. The subfamily ''Peduovirinae'' have virions with heads of 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Virus CF2
''Escherichia'' () is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, ''Escherichia'' species provide a portion of the microbially derived vitamin K for their host. A number of the species of ''Escherichia'' are pathogenic. The genus is named after Theodor Escherich, the discoverer of ''Escherichia coli''. ''Escherichia'' are facultative aerobes, with both aerobic and anaerobic growth, and an optimum temperature of 37 °C. ''Escherichia'' are usually motile by flagella, produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine or hydrolyze arginine. Species include '' E. albertii'', '' E. fergusonii'', '' E. hermannii'', '' E. marmotae'' and most notably, the model organism and clinically relevant ''E. coli''. ''Shimwellia blattae'' was formerly classified in this genus. Pathogenesis While man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Virus G50
''Escherichia'' () is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, ''Escherichia'' species provide a portion of the microbially derived vitamin K for their host. A number of the species of ''Escherichia'' are pathogenic. The genus is named after Theodor Escherich, the discoverer of ''Escherichia coli''. ''Escherichia'' are facultative aerobes, with both aerobic and anaerobic growth, and an optimum temperature of 37 °C. ''Escherichia'' are usually motile by flagella, produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine or hydrolyze arginine. Species include '' E. albertii'', '' E. fergusonii'', '' E. hermannii'', '' E. marmotae'' and most notably, the model organism and clinically relevant ''E. coli''. ''Shimwellia blattae'' was formerly classified in this genus. Pathogenesis While man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Virus G28
''Escherichia'' () is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, ''Escherichia'' species provide a portion of the microbially derived vitamin K for their host. A number of the species of ''Escherichia'' are pathogenic. The genus is named after Theodor Escherich, the discoverer of ''Escherichia coli''. ''Escherichia'' are facultative aerobes, with both aerobic and anaerobic growth, and an optimum temperature of 37 °C. ''Escherichia'' are usually motile by flagella, produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine or hydrolyze arginine. Species include '' E. albertii'', '' E. fergusonii'', '' E. hermannii'', '' E. marmotae'' and most notably, the model organism and clinically relevant ''E. coli''. ''Shimwellia blattae'' was formerly classified in this genus. Pathogenesis While man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Virus G8
''Escherichia'' () is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, ''Escherichia'' species provide a portion of the microbially derived vitamin K for their host. A number of the species of ''Escherichia'' are pathogenic. The genus is named after Theodor Escherich, the discoverer of ''Escherichia coli''. ''Escherichia'' are facultative aerobes, with both aerobic and anaerobic growth, and an optimum temperature of 37 °C. ''Escherichia'' are usually motile by flagella, produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine or hydrolyze arginine. Species include '' E. albertii'', '' E. fergusonii'', '' E. hermannii'', '' E. marmotae'' and most notably, the model organism and clinically relevant ''E. coli''. ''Shimwellia blattae'' was formerly classified in this genus. Pathogenesis While man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Virus FFiEco06
''Escherichia'' () is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, ''Escherichia'' species provide a portion of the microbially derived vitamin K for their host. A number of the species of ''Escherichia'' are pathogenic. The genus is named after Theodor Escherich, the discoverer of ''Escherichia coli''. ''Escherichia'' are facultative aerobes, with both aerobic and anaerobic growth, and an optimum temperature of 37 °C. ''Escherichia'' are usually motile by flagella, produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine or hydrolyze arginine. Species include '' E. albertii'', '' E. fergusonii'', '' E. hermannii'', '' E. marmotae'' and most notably, the model organism and clinically relevant ''E. coli''. ''Shimwellia blattae'' was formerly classified in this genus. Pathogenesis While man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Virus F2
''Escherichia'' () is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, ''Escherichia'' species provide a portion of the microbially derived vitamin K for their host. A number of the species of ''Escherichia'' are pathogenic. The genus is named after Theodor Escherich, the discoverer of ''Escherichia coli''. ''Escherichia'' are facultative aerobes, with both aerobic and anaerobic growth, and an optimum temperature of 37 °C. ''Escherichia'' are usually motile by flagella, produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine or hydrolyze arginine. Species include '' E. albertii'', '' E. fergusonii'', '' E. hermannii'', '' E. marmotae'' and most notably, the model organism and clinically relevant ''E. coli''. ''Shimwellia blattae'' was formerly classified in this genus. Pathogenesis While man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Virus EcoMF1
''Escherichia'' () is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, ''Escherichia'' species provide a portion of the microbially derived vitamin K for their host. A number of the species of ''Escherichia'' are pathogenic. The genus is named after Theodor Escherich, the discoverer of ''Escherichia coli''. ''Escherichia'' are facultative aerobes, with both aerobic and anaerobic growth, and an optimum temperature of 37 °C. ''Escherichia'' are usually motile by flagella, produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine or hydrolyze arginine. Species include '' E. albertii'', '' E. fergusonii'', '' E. hermannii'', '' E. marmotae'' and most notably, the model organism and clinically relevant ''E. coli''. ''Shimwellia blattae'' was formerly classified in this genus. Pathogenesis While man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Virus ECO4
''Escherichia'' () is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, ''Escherichia'' species provide a portion of the microbially derived vitamin K for their host. A number of the species of ''Escherichia'' are pathogenic. The genus is named after Theodor Escherich, the discoverer of ''Escherichia coli''. ''Escherichia'' are facultative aerobes, with both aerobic and anaerobic growth, and an optimum temperature of 37 °C. ''Escherichia'' are usually motile by flagella, produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine or hydrolyze arginine. Species include '' E. albertii'', '' E. fergusonii'', '' E. hermannii'', '' E. marmotae'' and most notably, the model organism and clinically relevant ''E. coli''. ''Shimwellia blattae'' was formerly classified in this genus. Pathogenesis While man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Virus EcNP1
''Escherichia'' () is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, ''Escherichia'' species provide a portion of the microbially derived vitamin K for their host. A number of the species of ''Escherichia'' are pathogenic. The genus is named after Theodor Escherich, the discoverer of ''Escherichia coli''. ''Escherichia'' are facultative aerobes, with both aerobic and anaerobic growth, and an optimum temperature of 37 °C. ''Escherichia'' are usually motile by flagella, produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine or hydrolyze arginine. Species include '' E. albertii'', '' E. fergusonii'', '' E. hermannii'', '' E. marmotae'' and most notably, the model organism and clinically relevant ''E. coli''. ''Shimwellia blattae'' was formerly classified in this genus. Pathogenesis While man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |