|
Tendu Gewog
Tendu or Tendruk Gewog ( dz, 1=བསྟང་འབྲུག་, translit=bstang 'brug) is a gewog (village block) of Samtse District, Bhutan. The Tendruk Gewog comprises part of Sipsu Dungkhag (sub-district), together with Bara, Biru, Lehereni, and Sipsu Gewogs. The Tendruk village is on a ridge near the confluence of the Bindu River with the Dichu (or Jaldhaka) River. The Indo-Bhutan border meets the Dichu near this point, with the west bank of Dichu being in India (Kalimpong district Kalimpong district is a district in the state of West Bengal, India. Originally known as Dalingkot tehsil, the region was alternatively under the control of Sikkim and Bhutan. In 1865, it was annexed from Bhutan by British India under the Treaty ...) and the east bank being in Bhutan. Thus, part of the Tendruk gewog lies on the border with India. A little below the confluence is the Bindu Dam over Dichu, which is said to be the second oldest dam in the Indian subcontinent. There is a bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gewogs Of Bhutan
A gewog ( dz, རྒེད་འོག ''geok'', block), in the past also spelled as geog, is a group of villages in Bhutan. The head of a ''gewog'' is called a ''gup'' ( ''gepo''). Gewogs form a geographic administrative unit below dzongkhag districts (and dungkhag subdistricts, where they exist), and above Dzongkhag Thromde class B and Yenlag Thromde municipalities. Dzongkhag Thromde class A municipalities have their own independent local government body. Bhutan comprises 205 gewogs, which average in area. The gewogs in turn are divided into chewogs for elections and thromdes "municipalities" for administration. The Parliament of Bhutan passed legislation in 2002 and 2007 on the status, structure, and leadership of local governments, including gewogs. The most recent legislation by parliament regarding gewogs is the Local Government Act of Bhutan 2009. In July 2011, the government slated 11 gewogs across Bhutan for reorganization, including both mergers and bifurcations, to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Bhutan
The Kingdom of Bhutan is divided into 20 districts ( Dzongkha: ). Bhutan is located between the Tibet Autonomous Region of China and India on the eastern slopes of the Himalayas in South Asia. are the primary subdivisions of Bhutan. They possess a number of powers and rights under the Constitution of Bhutan, such as regulating commerce, running elections, and creating local governments. The Local Government Act of 2009 established local governments in each of the 20 overseen by the Ministry of Home and Cultural Affairs. Each has its own elected government with non-legislative executive powers, called a (district council). The is assisted by the administration headed by a (royal appointees who are the chief executive officer of each ). Each also has a court presided over by a (judge), who is appointed by the Chief Justice of Bhutan on the advice of Royal Judicial Service Council. The , and their residents, are represented in the Parliament of Bhutan, a bicameral l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
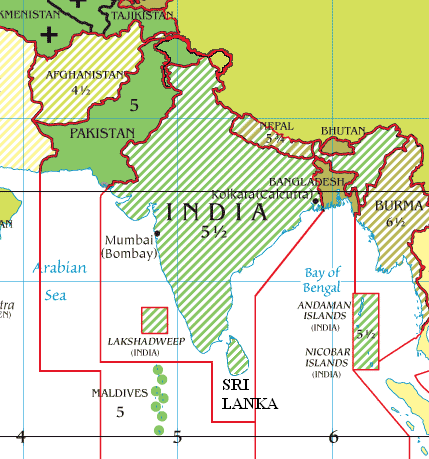
Samtse District
Samtse District ( Dzongkha: བསམ་རྩེ་རྫོང་ཁག་; Wylie: ''Bsam-rtse rdzong-khag''; older spelling "Samchi") is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It comprises two subdistricts (''dungkhags''): Tashicholing and Dophuchen. They are further subdivided into 15 gewogs (village blocks). The Samtse district covers a total area of 1304 sq km. History and culture Historically, Samtse was sparsely populated as the mountain-dwelling Bhutanese considered the low-lying district to be prone to tropical disease. During the early 20th century, the district experienced a large influx of Nepali people who were invited to the area to assist in forest-clearing. Overall, the district population has been increasing, and there have been housing shortages in Samtse as reported by Kuensel. Samtse is also home to the Lhop (Doya) people, a little-studied ethnic group of approximately 2,500 persons. The Bhutanese believe them to be the aboriginals who p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhutan Time
Bhutan Time (BTT) is the time zone of Bhutan. It is six hours ahead of UTC ( UTC+06:00). Bhutan does not observe Daylight saving time. IANA time zone database The IANA time zone database contains one zone for Bhutan in the file zone.tab, which is named Asia/Thimphu. See also *Bangladesh Standard Time Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million pe ... References Geography of Bhutan Time zones {{Standard-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous country, Bhutan is known as "Druk Yul," or "Land of the Thunder Dragon". Nepal and Bangladesh are located near Bhutan but do not share a land border. The country has a population of over 727,145 and territory of and ranks 133rd in terms of land area and 160th in population. Bhutan is a Constitutional Democratic Monarchy with King as head of state and Prime Minister as head of government. Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhism is the state religion and the Je Khenpo is the head of state religion. The subalpine Himalayan mountains in the north rise from the country's lush subtropical plains in the south. In the Bhutanese Himalayas, there are peaks higher than above sea level. Gangkhar Puensum is Bhutan's highest peak and is the highest uncl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Bhutan
The Government of Bhutan has been a constitutional monarchy since 18 July 2008. The King of Bhutan is the head of state. The executive power is exercised by the Lhengye Zhungtshog, or council of ministers, headed by the Prime Minister. Legislative power is vested in the bicameral Parliament, both the upper house, National Council, and the lower house, National Assembly. A royal edict issued on April 22, 2007 lifted the previous ban on political parties in anticipation of the National Assembly elections in the following year. In 2008, Bhutan adopted its first modern Constitution, codifying the institutions of government and the legal framework for a democratic multi-party system. Sovereignty Bhutanese external relations and foreign policies were put under British control following the 1910 Treaty of Punakha. However, due to the policy of self-imposed isolationism, the effect of the treaty was limited to an extent. After Indian independence in 1949, Bhutan and India agreed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dungkhag
A dungkhag ( dz, དྲུང་ཁག་ ''drungkhak'') is a sub-district of a dzongkhag (district) of Bhutan. The head of a dungkhag is a ''Dungpa''. As of 2007, nine of the twenty dzongkhags had from one to three dungkhags, with sixteen dungkhags in total. History Under Bhutan's first government Act of decentralization, the Dzongkhag Yargay Tshogdu Chathrim of 2002 Dungpas were given a non-voting seat on the Dzongkhag Yargay Tshogdu. Under the Local Government Act of 2007, dungkhags provided general administration and coordination for two or more gewogs. As a result, some gewogs within a given district were directly subordinate to dungkhags while others are directly subordinate to dzongkhags. Dungkhag Administrations guided and supported their constituent Gewog Administrations and implemented the decisions of the Dzongkhag Tshogdu. Dungpas were administrative executives that reported directly to the Dzongkhag administration. The Dungpa was empowered to attend the meetings of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bara Gewog
Bara Gewog is a former gewog (village block) of Samtse District, Bhutan. The gewog has an area of 186 square kilometres and contains 474 households. Bara Gewog comprises part of Sipsu Dungkhag (sub-district), together with Tendu, Biru, Lehereni, and Sipsu Gewog Tashicholing ( dz, བཀྲིས་ཙོས་གླིང་, translit=bkris tsos gling ) or Sipsu Gewog is a gewog (village block) of the Samtse District, Bhutan. Geography The gewog is to the south of Pemaling gewog and southwest of ... Gewogs. References Former gewogs of Bhutan Samtse District {{coord missing, Bhutan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biru Gewog
Biru Gewog is a former gewog (village block) of Samtse District, Bhutan. The gewog has an area of 49.04 square kilometres and contains 15 '' chewogs'' with 46 villages and 448 households. Biru Gewog comprises part of Sipsu Dungkhag (sub-district), together with Tendu, Bara, Lehereni, and Sipsu Gewog Tashicholing ( dz, བཀྲིས་ཙོས་གླིང་, translit=bkris tsos gling ) or Sipsu Gewog is a gewog (village block) of the Samtse District, Bhutan. Geography The gewog is to the south of Pemaling gewog and southwest of ...s. References Former gewogs of Bhutan Samtse District {{coord missing, Bhutan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lehereni Gewog
Lehereni Gewog is a former gewog (village block) of Samtse District, Bhutan. Lehereni Gewog comprises part of Sipsu Dungkhag A dungkhag ( dz, དྲུང་ཁག་ ''drungkhak'') is a sub-district of a dzongkhag (district) of Bhutan. The head of a dungkhag is a ''Dungpa''. As of 2007, nine of the twenty dzongkhags had from one to three dungkhags, with sixteen dungkh ... (sub-district), together with Tendu, Biru, Bara, and Sipsu Gewogs. References Former gewogs of Bhutan Samtse District {{coord missing, Bhutan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sipsu Gewog
Tashicholing ( dz, བཀྲིས་ཙོས་གླིང་, translit=bkris tsos gling ) or Sipsu Gewog is a gewog (village block) of the Samtse District, Bhutan. Geography The gewog is to the south of Pemaling gewog and southwest of Namgaychhoeling gewog. It is bordered by India's West Bengal state in the west and the south (Kalimpong and Jalpaiguri districts). The Dichu (or Jaldhaka) River forms the western border of the gewog, and the rivers Sipsu Jhora and Sati Khola flow through it before joining Dichu at the southwestern corner. The Tashichholing Gewog occupies an area of . It has 11 villages in 4 chiwogs. In 2012, it had a population of 4,087. History The village of Sipsu (also spelt Sibsu, Sibsoo and Sipchoo) had some encounters in history, as it appears to have been the seat of administration of the surrounding Dichu basin. In the 19th century, it was governed by deputy Dzongpön, perhaps under the control of a main Dzongpön at Dalingkot to the west. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |