|
Temple (Greek)
Greek temples ( grc, ναός, naós, dwelling, semantically distinct from Latin , "temple") were structures built to house deity statues within Greek sanctuaries in ancient Greek religion. The temple interiors did not serve as meeting places, since the sacrifices and rituals dedicated to the respective ouranic (a god or goddess that does not reside on the Earth) deity took place outside them, within the wider precinct of the sanctuary, which might be large. Temples were frequently used to store votive offerings. They are the most important and most widespread building type in Greek architecture. In the Hellenistic kingdoms of Southwest Asia and of North Africa, buildings erected to fulfill the functions of a temple often continued to follow the local traditions. Even where a Greek influence is visible, such structures are not normally considered as Greek temples. This applies, for example, to the Graeco-Parthian and Bactrian temples, or to the Ptolemaic examples, which follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attica 06-13 Athens 50 View From Philopappos - Acropolis Hill
Attica ( el, Αττική, Ancient Greek ''Attikḗ'' or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the city of Athens, the capital of Greece and its countryside. It is a peninsula projecting into the Aegean Sea, bordering on Boeotia to the north and Megaris to the west. The southern tip of the peninsula, known as Laurion, was an important mining region. The history of Attica is tightly linked with that of Athens, and specifically the Golden Age of Athens during the classical period. Ancient Attica ( Athens city-state) was divided into demoi or municipalities from the reform of Cleisthenes in 508/7 BC, grouped into three zones: urban (''astu'') in the region of Athens main city and Piraeus (port of Athens), coastal (''paralia'') along the coastline and inland (''mesogeia'') in the interior. The modern administrative region of Attica is more extensive than the historical region and includes Megaris as part of the regional unit West Attica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Temple Of Aphaia Glyptothek Munich
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the Plan_(drawing), plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure. Models can be divided into physical models (e.g. a model plane) and abstract models (e.g. mathematical expressions describing behavioural patterns). Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science, as almost every scientific theory effectively embeds some kind of model of the universe, physical or human condition, human sphere. In commerce, "model" can refer to a specific design of a product as displayed in a catalogue or show room (e.g. Ford Model T), and by extension to the sold product itself. Types of models include: Physical model A physical model (most commonly referred to simply as a model but in this context distinguished from a conceptual model) is a smaller or larger physical copy of an physical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
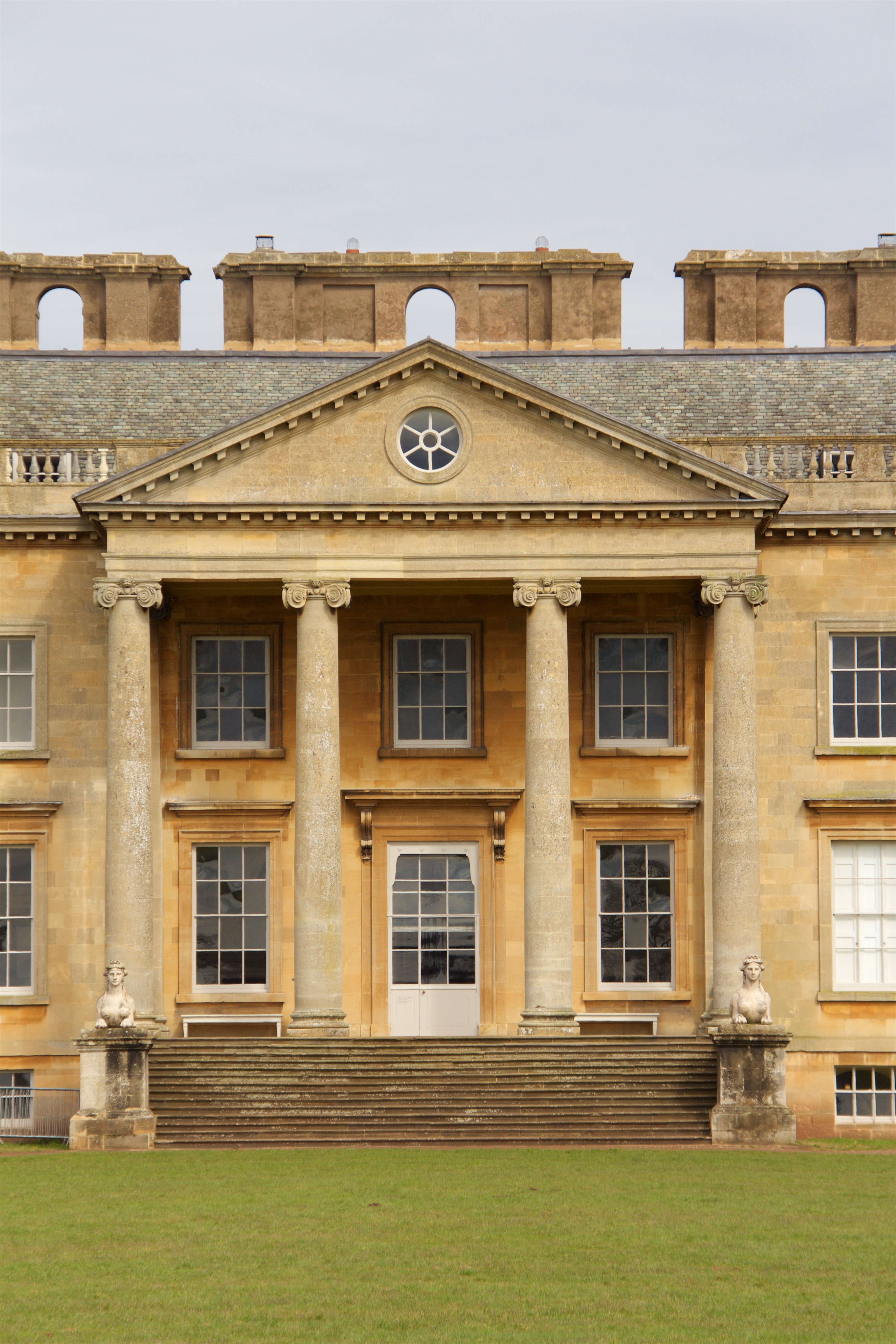
Pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds. A pediment is sometimes the top element of a portico. For symmetric designs, it provides a center point and is often used to add grandness to entrances. The tympanum, the triangular area within the pediment, is often decorated with a pedimental sculpture which may be freestanding or a relief sculpture. The tympanum may hold an inscription, or in modern times, a clock face. Pediments are found in ancient Greek architecture as early as 600 BC (e.g. the archaic Temple of Artemis). Variations of the pediment occur in later architectural styles such as Classical, Neoclassical and Baroque. Gable roofs were common in ancient Greek temples with a low pitch (angle of 12.5° to 16°). History The pediment is found in classical Greek temples, Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane. When a relief is carved into a flat surface of stone (relief sculpture) or wood (relief carving), the field is actually lowered, leaving the unsculpted areas seeming higher. The approach requires a lot of chiselling away of the background, which takes a long time. On the other hand, a relief saves forming the rear of a subject, and is less fragile and more securely fixed than a sculpture in the round, especially one of a standing figure where the ankles are a potential weak point, particularly in stone. In other materials such as metal, clay, plaster stucco, ceramics or papier-mâché the form can be simply added to or raised up from the background. Monumental bronze reliefs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture. Stucco can be applied on construction materials such as metal, expanded metal lath, concrete, cinder block, or clay brick and adobe for decorative and structural purposes. In English, "stucco" sometimes refers to a coating for the outside of a building and "plaster" to a coating for interiors; as described below, however, the materials themselves often have little to no differences. Other European languages, notably Italian, do not have the same distinction; ''stucco'' means ''plaster'' in Italian and serves for both. Composition The basic composition of stucco is cement, water, and sand. The difference in nomenclature between stucco, plaster, and mortar is based more on use than composition. Until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term ''column'' applies especially to a large round support (the shaft of the column) with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a ''post''. Supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called ''piers''. For the purpose of wind or earthquake engineering, columns may be designed to resist lateral forces. Other compression members are often termed "columns" because of the similar stress conditions. Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest. In architecture, "column" refers to such a structural element that also has certain proportional and decorative featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
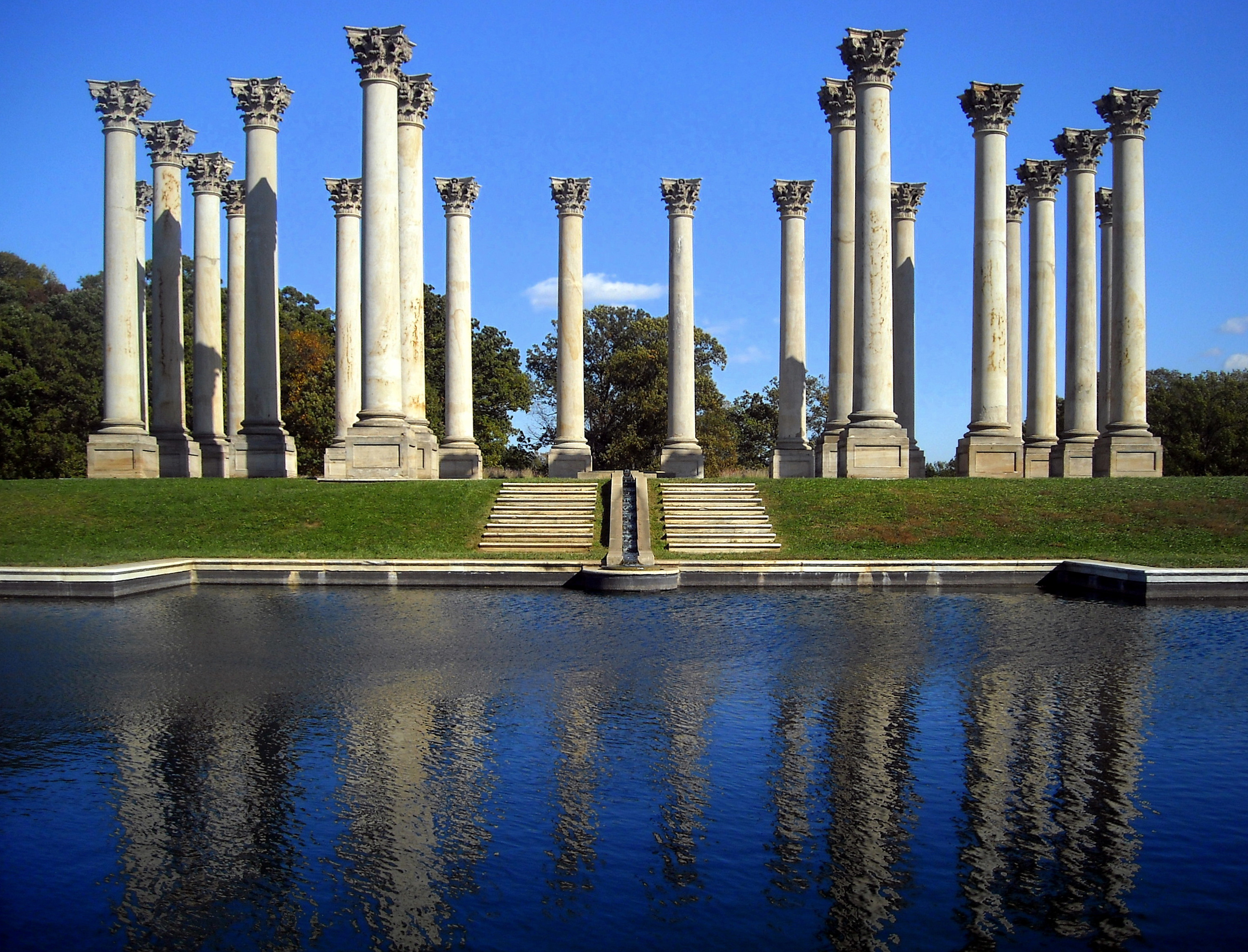
Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects other than the capitals of the columns. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon: the Tuscan order and the Composite order. The Corinthian, with its offshoot the Composite, is the most ornate of the orders. This architectural style is characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls. There are many variations. The name ''Corinthian'' is derived from the ancient Greek city of Corinth, although the style had its own model in Roman practice, following precedents set by the Tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
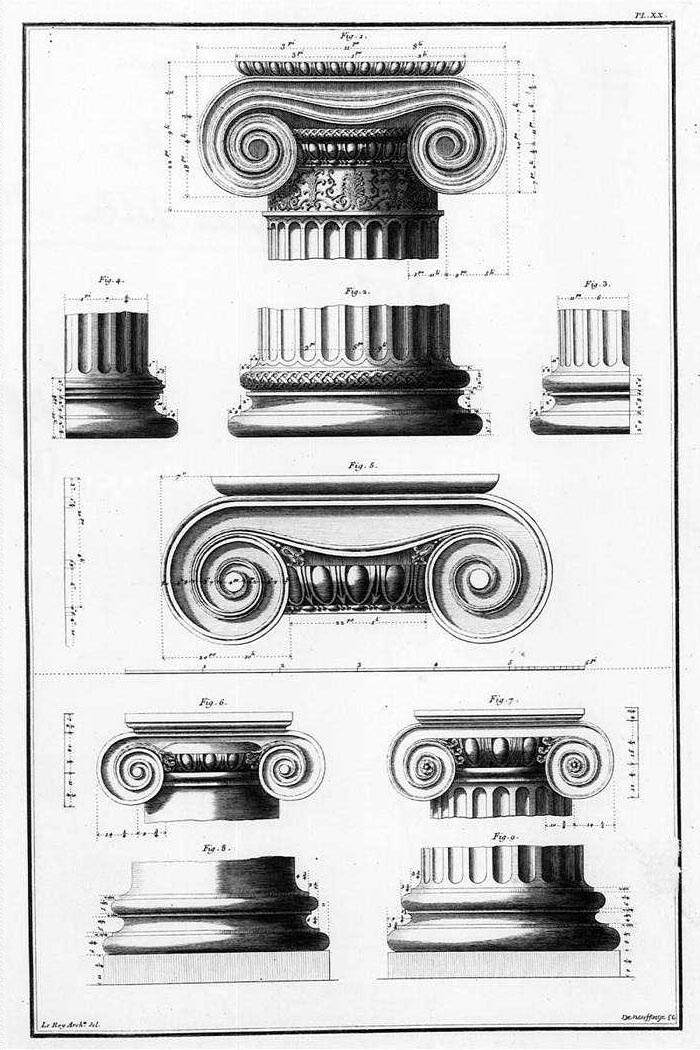
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Orders
An order in architecture is a certain assemblage of parts subject to uniform established proportions, regulated by the office that each part has to perform. Coming down to the present from Ancient Greek and Ancient Roman civilization, the architectural orders are the styles of classical architecture, each distinguished by its proportions and characteristic profiles and details, and most readily recognizable by the type of column employed. The three orders of architecture—the Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian—originated in Greece. To these the Romans added, in practice if not in name, the Tuscan, which they made simpler than Doric, and the Composite, which was more ornamental than the Corinthian. The architectural order of a classical building is akin to the mode or key of classical music; the grammar or rhetoric of a written composition. It is established by certain ''modules'' like the intervals of music, and it raises certain expectations in an audience attuned to its languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or curved. The space enclosed may be covered or open. In St. Peter's Square in Rome, Bernini's great colonnade encloses a vast open elliptical space. When in front of a building, screening the door (Latin ''porta''), it is called a portico. When enclosing an open court, a peristyle. A portico may be more than one rank of columns deep, as at the Pantheon in Rome or the stoae of Ancient Greece. When the intercolumniation is alternately wide and narrow, a colonnade may be termed "araeosystyle" (Gr. αραιος, "widely spaced", and συστυλος, "with columns set close together"), as in the case of the western porch of St Paul's Cathedral and the east front of the Louvre. History Colonnades have been built since ancient times and inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Some noteworthy examples of porticos are the East Portico of the United States Capitol, the portico adorning the Pantheon in Rome and the portico of University College London. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the ''cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)