|
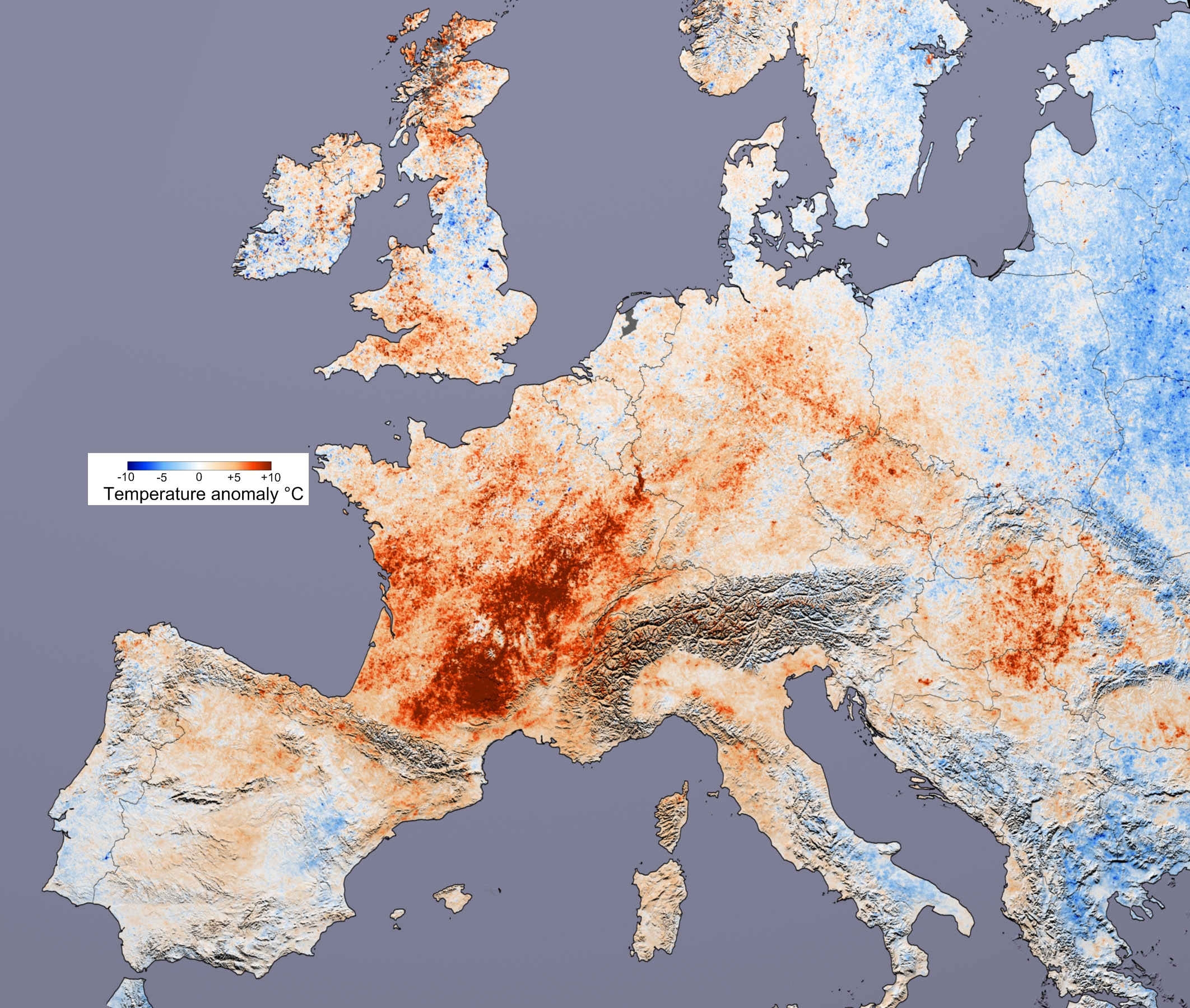
Temperature Anomaly
Temperature anomaly is the difference, positive or negative, of a temperature from a base or reference value, normally chosen as an average of temperatures over a certain reference or base period. In atmospheric sciences, the average temperature is commonly calculated over a period of at least 30 years over a homogeneous geographic region, or globally over the entire planet. Temperatures are obtained from surface and offshore weather stations or inferred from meteorological satellite data. Temperature anomalies can be calculated based on datasets of near-surface and upper-air atmospheric temperatures or sea surface temperatures. Description Temperature anomalies are a measure of temperature compared to a reference temperature, which is often calculated as an average of temperatures over a reference period, often called a base period. Publication datePrecursor webpagewas archived as early as December 2013. Records of global average surface temperature are usually presented as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20200324 Global Average Temperature - NASA-GISS HadCrut NOAA Japan BerkeleyE
3 (three) is a number, numeral (linguistics), numeral and numerical digit, digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic numerals, Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. The standard deviation is commonly used in the determination of what constitutes an outlier and what does not. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD or std dev, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lowercase Greek alphabet, Greek letter Sigma, σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin script, Latin letter ''s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, Sample (statistics), sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. (For a finite population, v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Heatwave
A marine heatwave is a period of abnormally high sea surface temperatures compared to the typical temperatures in the past for a particular season and region. Marine heatwaves are caused by a variety of drivers. These include shorter term weather events such as fronts, intraseasonal events (30 to 90 days) , annual, and decadal (10-year) modes like El Niño events, and human-caused climate change. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License/ref> Marine heatwaves affect ecosystems in the oceans. For example, marine heatwaves can lead to severe biodiversity changes such as coral bleaching, sea star wasting disease, harmful algal blooms, and mass mortality of benthic communities. Unlike heatwaves on land, marine heatwaves can extend over vast areas, persist for weeks to months or even years, and occur at subsurface levels. Major marine heatwaves have occurred for example in the Great Barrier Reef in 2002, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Wave
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather generally considered to be at least ''five consecutive days''. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and to normal temperatures for the season. The main difficulties with this broad definition emerge when one must quantify what the 'normal' temperature state is, and what the spatial extent of the event may or must be. Temperatures that humans from a hotter climate consider normal can be regarded as a heat wave in a cooler area. This would be the case if the warm temperatures are outside the normal climate pattern for that area. Heat waves have become more frequent, and more intense over land, across almost every area on Earth since the 1950s, the increase in frequency and duration being caused by climate change. Heat waves form when a high-pressure area in the upper atmosphere strengthens and remains over a region for several days up to seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Weather
Extreme weather includes unexpected, unusual, severe weather, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Extreme events are based on a location's recorded weather history. The main types of extreme weather include heat waves, cold waves, droughts, and heavy precipitation or storm events, such as tropical cyclones. Extreme weather can have various effects, from natural hazards such as floods and landslides to social costs on human health and the economy. Severe weather is a particular type of extreme weather which poses risks to life and property. Weather patterns in a given region vary with time, and so extreme weather can be attributed, at least in part, to the natural Climate variability and change, climate variability that exists on Earth. For example, the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) or the North Atlantic oscillation (NAO) are climate phenomena that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment And Climate Change Canada
Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC; )Environment and Climate Change Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of the Environment (). is the department of the Government of Canada responsible for coordinating environmental policies and programs, as well as preserving and enhancing the natural environment and renewable resources. It is also colloquially known by its former name, Environment Canada (EC; ). The minister of environment and climate change has been Julie Dabrusin since May 13, 2025; Environment and Climate Change Canada supports the minister's mandate to: "preserve and enhance the quality of the natural environment, including water, air, soil, flora and fauna; conserve Canada's renewable resources; conserve and protect Canada's water resources; forecast daily weather conditions and warnings, and provide detailed meteorological information to all of Canada; enforce rules relating to boundary waters; and coord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorological Service Of Canada
The Meteorological Service of Canada (MSC; ) is a branch of Environment and Climate Change Canada, which primarily provides public meteorological information and weather forecasts and warnings of severe weather and other environmental hazards. MSC also monitors and conducts research on the climate, atmospheric science, air quality, water quantities, ice and other environmental issues. MSC operates a network of radio stations throughout Canada transmitting weather and environmental information 24 hours a day called Weatheradio Canada. History Private Observations Prior to 1840, meteorological observations in Canada were made by private individuals, other entities (like HBC), and explorers, but this information was not provided to the general public. Her Majesty's Magnetic and Meteorological Observatory In 1840, British officials ( British Ordnance Department) and the Royal Society established an observatory in Toronto, Canada West, one of a few across the British Empire and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Assimilation
Data assimilation refers to a large group of methods that update information from numerical computer models with information from observations. Data assimilation is used to update model states, model trajectories over time, model parameters, and combinations thereof. What distinguishes data assimilation from other estimation methods is that the computer model is a dynamical model, i.e. the model describes how model variables change over time, and its firm mathematical foundation in Bayesian Inference. As such, it generalizes inverse methods and has close connections with machine learning. Data assimilation initially developed in the field of numerical weather prediction. Numerical weather prediction models are equations describing the evolution of the atmosphere, typically coded into a computer program. When these models are used for forecasting the model output quickly deviates from the real atmosphere. Hence, we use observations of the atmosphere to keep the model on track. Data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Weather Prediction
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to weather forecasting, predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs. Mathematical models based on the same physical principles can be used to generate either short-term weather forecasts or longer-term climate predictions; the latter are widely applied for understanding and projecting climate change. The improvements made to regional models have allowed significant improvements in Tropical cyclone track forecasting, tropical cyclone track and air quality forecasts; however, atmospheric models perform poorly at han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20200509 Emergence Of Temperatures From Range Of Normal Historical Variability - Tropical Vs Northern Americas (Hawkins)
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. Humans, and many other animals, have 5 digits on their limbs. Mathematics 5 is a Fermat prime, a Mersenne prime exponent, as well as a Fibonacci number. 5 is the first congruent number, as well as the length of the hypotenuse of the smallest integer-sided right triangle, making part of the smallest Pythagorean triple ( 3, 4, 5). 5 is the first safe prime and the first good prime. 11 forms the first pair of sexy primes with 5. 5 is the second Fermat prime, of a total of five known Fermat primes. 5 is also the first of three known Wilson primes (5, 13, 563). Geometry A shape with five sides is called a pentagon. The pentagon is the first regular polygon that does not tile the plane with copies of itself. It is the largest face any of the five regular three-dimensional regular Platonic solid can have. A conic is determined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |