|
Tellimagrandin I
Tellimagrandin I is an ellagitannin found in plants, such as ''Cornus canadensis'', ''Eucalyptus globulus'', ''Melaleuca styphelioides'', ''Rosa rugosa'', and walnut. It is composed of two galloyl and one hexahydroxydiphenyl groups bound to a glucose residue. It differs from Tellimagrandin II only by a hydroxyl group instead of a third galloyl group. It is also structurally similar to punigluconin and pedunculagin, two more ellagitannin monomers. Tellimagrandin I has been shown to restore antioxidant enzyme activity in glucose- and oxalate-challenged rat cells and affects Cu(II)- and Fe(II)-dependent DNA strand breaks. It has hepatoprotective effects on carbon tetrachloride- and d-galactosamine-stressed HepG2 cells and enhances peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation in liver, increasing mRNA expression of PPAR alpha, ACOX1, and CPT1A. It enhances gap junction communication and reduces tumor phenotype in HeLa cells and inhibits invasion of HSV-1 and HCV similar to eugenii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellagitannin
The ellagitannins are a diverse class of hydrolyzable tannins, a type of polyphenol formed primarily from the oxidative linkage of galloyl groups in 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl glucose. Ellagitannins differ from gallotannins, in that their galloyl groups are linked through C-C bonds, whereas the galloyl groups in gallotannins are linked by depside bonds. Ellagitannins contain various numbers of hexahydroxydiphenoyl units, as well as galloyl units and/or sanguisorboyl units bounded to sugar moiety. In order to determine the quantity of every individual unit, the hydrolysis of the extracts with trifluoroacetic acid in methanol/water system is performed. Hexahydroxydiphenic acid, created after hydrolysis, spontaneously lactonized to ellagic acid, and sanguisorbic acid to sanguisorbic acid dilactone, while gallic acid remains intact. Ellagitannins generally form macrocycles, whereas gallotannins do not. Examples * Castalagin * Castalin * Casuarictin * Grandinin * Oenothein B from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-oxidation
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH2, which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport chain. It is named as such because the beta carbon of the fatty acid undergoes oxidation to a carbonyl group. Beta-oxidation is primarily facilitated by the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, an enzyme complex associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane, although very long chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes. The overall reaction for one cycle of beta oxidation is: :C''n''-acyl-CoA + FAD + + + CoA → C''n''-2-acyl-CoA + + NADH + + acetyl-CoA Activation and membrane transport Free fatty acids cannot penetrate any biological membrane due to their negative charge. Free fatty acids must cross the cell membrane through specific transport proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punigluconin
Punigluconin is an ellagitannin, a polyphenol compound. It is found in the bark of ''Punica granatum'' (pomegranate) and in ''Emblica officinalis''. It is a molecule having a hexahydroxydiphenic acid group and two gallic acids attached to a gluconic acid Gluconic acid is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H12O7 and condensed structural formula HOCH2(CHOH)4COOH. It is one of the 16 stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoic acid. In aqueous solution at neutral pH, gluconic acid f ... core. References Pomegranate ellagitannins {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedunculagin
Pedunculagin is an ellagitannin. It is formed from casuarictin via the loss of a gallate group. Natural occurrence Pedunculagin is found in plants in orders in the clade Rosidae. It can be found the pericarp of pomegranates (''Punica granatum''), in the family Lythraceae, in the order Myrtales. It is also found in plants in the order Fagales such as walnuts (''Juglans regia'') in the family Juglandaceae, in ''Alnus sieboldiana'' and in the Manchurian alder ('' Alnus hirsuta var. microphylla''), both species in the family Betulaceae and it is one of the main oak wood ellagitannins along with castalagin, vescalagin, grandinin and roburins A-E (genus ''Quercus'', in the family Fagaceae). It is also found in the Indian gooseberry (''Phyllanthus emblica''), a plant in the family Phyllanthaceae, in the order Malpighiales. Galloyl pedunculagin can be found in ''Platycarya strobilacea''. Research Pedunculagin is a highly active carbonic anhydrase inhibitor ''in vitro''. Chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellagitannin
The ellagitannins are a diverse class of hydrolyzable tannins, a type of polyphenol formed primarily from the oxidative linkage of galloyl groups in 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl glucose. Ellagitannins differ from gallotannins, in that their galloyl groups are linked through C-C bonds, whereas the galloyl groups in gallotannins are linked by depside bonds. Ellagitannins contain various numbers of hexahydroxydiphenoyl units, as well as galloyl units and/or sanguisorboyl units bounded to sugar moiety. In order to determine the quantity of every individual unit, the hydrolysis of the extracts with trifluoroacetic acid in methanol/water system is performed. Hexahydroxydiphenic acid, created after hydrolysis, spontaneously lactonized to ellagic acid, and sanguisorbic acid to sanguisorbic acid dilactone, while gallic acid remains intact. Ellagitannins generally form macrocycles, whereas gallotannins do not. Examples * Castalagin * Castalin * Casuarictin * Grandinin * Oenothein B from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casuarictin
Casuarictin is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolysable tannin. It can be found in ''Casuarina'' and ''Stachyurus'' species.Tannins of Casuarina and Stachyurus species. I: Structures of pendunculagin, casuarictin, strictinin, casuarinin, casuariin, and stachyurin. Okuda T., Yoshida T., Ashida M. and Yazaki K., Journal of the Chemical Society, 1983, number 8, pages 1765-1772, It is formed from two hexahydroxydiphenic acid units and one gallic acid unit linked to a glucose molecule. The molecule is formed from tellimagrandin II, itself formed from pentagalloyl glucose via oxidation. Casuarictin is transformed into pedunculagin via loss of a gallate group, and further into castalagin Castalagin is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolyzable tannin, found in oak and chestnut wood and in the stem barks of '' Anogeissus leiocarpus'' and ''Terminalia avicennoides''. Castalagin is the diastereomer of vescalagin in C-1 of the glycosidi ... via glucose pyranose ring opening. Oligomers Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugeniin
Tellimagrandin II is the first of the ellagitannins formed from 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl-glucose. It can be found in '' Geum japonicum'' and ''Syzygium aromaticum'' (clove).Purification and Characterization of Eugeniin as an Anti-herpesvirus Compound from Geum japonicum and Syzygium aromaticum. Masahiko Kurokawa, Toyoharu Hozumi, Purusotam Basnet, Michio Nakano, Shigetoshi Kadota, Tuneo Namba, Takashi Kawana and Kimiyasu Shiraki, JPET, February 1, 1998 vol. 284 no. 2, pages 728-735article Tellimagrandin II is an isomer of punicafolin or nupharin A, but the hexahydroxydiphenoyl group is not attached to the same hydroxyl groups in the glucose molecule. The compound shows anti-herpesvirus properties. Metabolism It is formed by oxidation of pentagalloyl glucose in '' Tellima grandiflora'' by the enzyme pentagalloylglucose: O(2) oxidoreductase, a laccase-type phenol oxidase. It is further oxidized to casuarictin, a molecule formed via oxidative dehydrogenation of 2 other galloyl g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
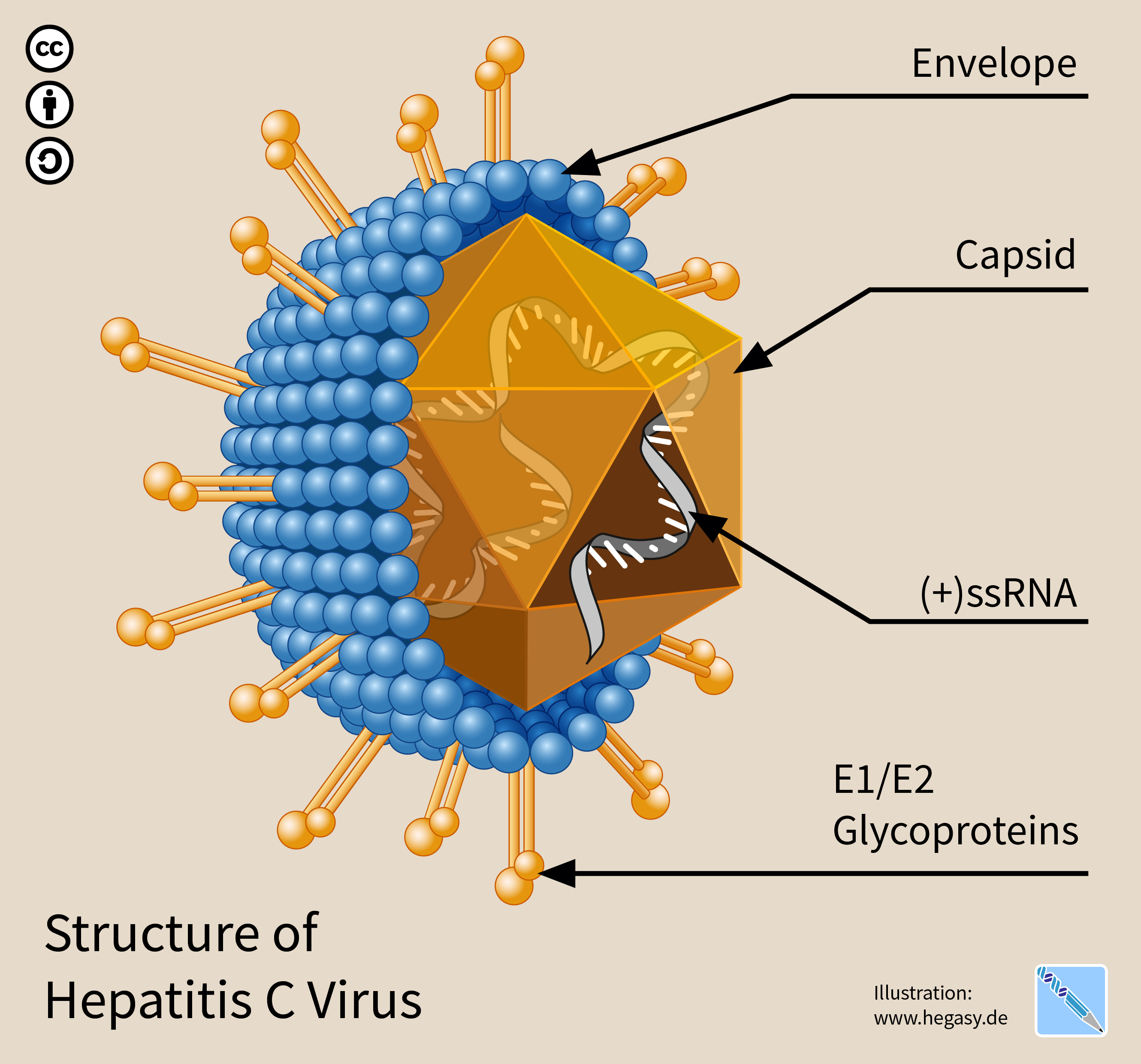
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus ''Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the envel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HSV-1
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 are very common and contagious. They can be spread when an infected person begins shedding the virus. As of 2016, about 67% of the world population under the age of 50 had HSV-1. In the United States, about 47.8% and 11.9% are estimated to have HSV-1 and HSV-2, respectively, though actual prevalence may be much higher. Because it can be transmitted through any intimate contact, it is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Symptoms Many of those who are infected ''never'' develop symptoms. Symptoms, when they occur, may include watery blisters in the skin or mucous membranes of the mouth, lips, nose, genitals, or eyes (herpes simplex keratitis). Lesions heal wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HeLa Cells
HeLa (; also Hela or hela) is an immortalized cell line used in scientific research. It is the oldest and most commonly used human cell line. The line is derived from cervical cancer cells taken on February 8, 1951, named after Henrietta Lacks, a 31-year-old African-American mother of five, who died of cancer on October 4, 1951. The cell line was found to be remarkably durable and prolific, which allows it to be used extensively in scientific study. The cells from Lacks's cancerous cervical tumor were taken without her knowledge or consent, which was common practice in the United States at the time. Cell biologist George Otto Gey found that they could be kept alive, and developed a cell line. Previously, cells cultured from other human cells would only survive for a few days. Cells from Lacks's tumor behaved differently. History Origin In 1951, a patient named Henrietta Lacks was admitted to the Johns Hopkins Hospital with symptoms of irregular vaginal bleeding, and was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gap Junction
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections between a multitude of animal cell-types. They directly connect the cytoplasm of two cells, which allows various molecules, ions and electrical impulses to directly pass through a regulated gate between cells. One gap junction channel is composed of two protein hexamers (or hemichannels) called connexons in vertebrates and innexons in invertebrates. The hemichannel pair connect across the intercellular space bridging the gap between two cells. Gap junctions are analogous to the plasmodesmata that join plant cells. Gap junctions occur in virtually all tissues of the body, with the exception of adult fully developed skeletal muscle and mobile cell types such as sperm or erythrocytes. Gap junctions are not found in simpler organisms such as sponges and slime molds. A gap junction may also be called a ''nexus'' or ''macula communicans''. While an ephapse has some similarities to a gap junction, by modern definition the two a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPT1A
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1) also known as carnitine acyltransferase I, CPTI, CAT1, CoA:carnitine acyl transferase (CCAT), or palmitoylCoA transferase I, is a mitochondrial enzyme responsible for the formation of acyl carnitines by catalyzing the transfer of the acyl group of a long-chain fatty acyl-CoA from coenzyme A to l-carnitine. The product is often Palmitoylcarnitine (thus the name), but other fatty acids may also be substrates. It is part of a family of enzymes called carnitine acyltransferases. This "preparation" allows for subsequent movement of the acyl carnitine from the cytosol into the intermembrane space of mitochondria. Three isoforms of CPT1 are currently known: CPT1A, CPT1B, and CPT1C. CPT1 is associated with the outer mitochondrial membrane. This enzyme can be inhibited by malonyl CoA, the first committed intermediate produced during fatty acid synthesis. Its role in fatty acid metabolism makes CPT1 important in many metabolic disorders such as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |