|
Tell Maghzaliyah
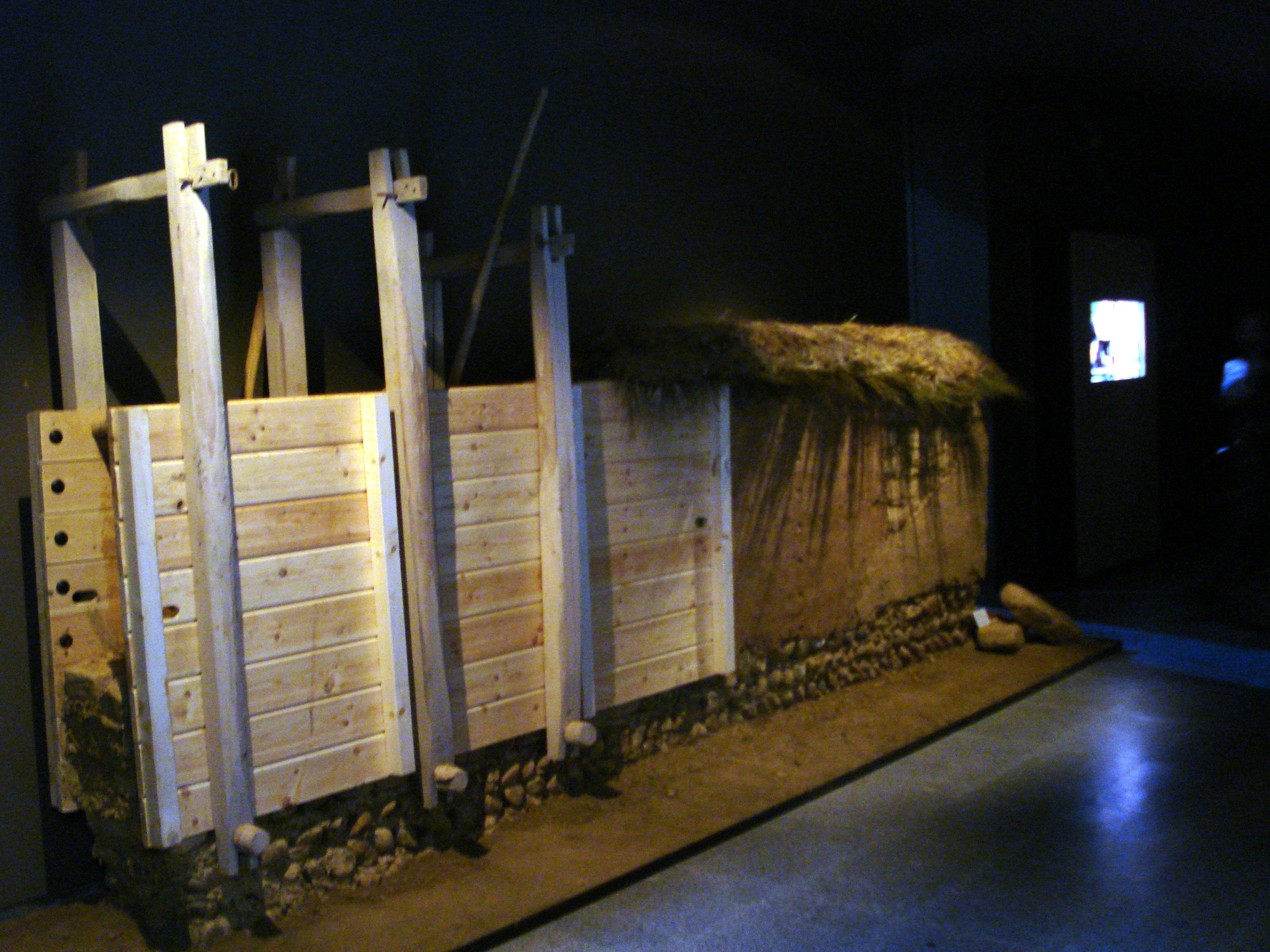
Tell Maghzaliyah (Tell Maghzalia), in Nineveh Governorate, Iraq, is a prehistoric fortified aceramic Mesolithic and Neolithic site located approximately 7.5 km northwest of Yarim Tepe, with which it shows some similarities. It is situated near the Abra River, a tributary of the Habur River, which eventually drains into the Euphrates River. Tell Maghzaliyah shows the development of pre-Hassuna culture. There are also numerous connections to the Jarmo culture going back to 7000 BCE. Archaeology The site is approximately 4500 square meters in area, and the depth of deposit is approximately 8 meters. It was excavated during 12 seasons between 1969 and 1980 on the Sinjar Plain, by a Soviet team from the Institute of Archaeology, Academy of Sciences led by R. M. Munchaev and N. Ya. Merpert with N.O. Bader. The original village housed approximately 150 people. It was more suited to hunting and gathering, than to long-standing agriculture. Archeological evidence includes flint flak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisé
Rammed earth is a technique for constructing foundations, floors, and walls using compacted natural raw materials such as earth, chalk, lime, or gravel. It is an ancient method that has been revived recently as a sustainable building method. Under its French name of pisé it is also a material for sculptures, usually small and made in molds. It has been especially used in Central Asia and Tibetan art, and sometimes in China. Edifices formed of rammed earth are on every continent except Antarctica, in a range of environments including temperate, wet, semiarid desert, montane, and tropical regions. The availability of suitable soil and a building design appropriate for local climatic conditions are the factors that favour its use. The French term "pisé de terre" or "terre pisé" was sometimes used in English for architectural uses, especially in the 19th century. The process Making rammed earth involves compacting a damp mixture of subsoil that has suitable proportions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolithic Sites Of Asia
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in the Levant and Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and Western Asia, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 BP; in Southwest Asia (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, but it is associated with a decline in the group hunting of large animals in favour of a broader hunter-gathere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Sites Of Asia
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities Of The Ancient Near East
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC or with that by Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC. The largest cities of the Bronze Age Near East housed several tens of thousands of people. Memphis in the Early Bronze Age, with some 30,000 inhabitants, was the largest city of the time by far. Ebla is estimated to have had a population of 40,000 inhabitants in the Intermediate Bronze age. Ur in the Middle Bronze Age is estimated to have had some 65,000 inhabitants; Babylon in the Late Bronze Age similarly had a population of some 50,000–60,000. Niniveh had some 20,000–30,000, reaching 100,000 only in the Iron Age (around 700 BC). In Akkadian and Hittite orthography, URU became a determinative sign denoting a city, or combi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marvdasht
Marvdasht ( fa, مرودشت, also romanized as Marv Dasht) is a city and the capital of Marvdasht County, Fars Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 123,858, in 29,134 families. Name Some historians hold that Marvdasht was originally the name of one of the neighborhoods of the ancient city of Estakhr, until gradually the whole area was called Marvdasht. Others have argued that ''marv'' was the name of a plant which grew in the area and the suffix ''dasht'' (meaning plain in the Persian language) was added to form a descriptive placename. History Marvdasht is as ancient as the history of Iran and the Persian Empire. Its former capital Persepolis is in the vicinity of the city, and few kilometers farther Naqsh-e-Rostam, Naqsh-e Rajab and the ruins of the ancient city of Estakhr are reminiscent of the region's importance in historic times. Archaeological excavations have shown that civilized people had already been living in the Marvdasht Plains for millennia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgros'' ''کویا زاگرس'') are a long mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. This mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros mountain range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of southeastern Turkey and northeastern Iraq. From this border region, the range continues to the southeast under also the waters of the Persian Gulf. It spans the southern parts of the Armenian highland, the whole length of the western and southwestern Iranian plateau, ending at the Strait of Hormuz. The highest point is Mount Dena, at . Geology The Zagros fold and thrust belt was mainly formed by the collision of two tectonic plates, the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tepe Sialk
Tepe Sialk ( fa, تپه سیلک) is a large ancient archeological site (a ''tepe'', "hill, tell (archaeology), tell") in a suburb of the city of Kashan, Isfahan Province, in central Iran, close to Fin Garden. The culture that inhabited this area has been linked to the Zayandeh River Culture. History A joint study between Iran's Cultural Heritage Organization, the Louvre, and the Institut Francais de Recherche en Iran also verifies the oldest settlements in Sialk to date to around 6000–5500 BC. The Sialk ziggurat was built around 3000 BC. Sialk, and the entire area around it, is thought to have originated as a result of the pristine large water sources nearby that still run today. The Cheshmeh ye Soleiman ("Solomon's Spring") has been bringing water to this area from nearby mountains for thousands of years. The Fin garden, built in its present form in the 17th century, is a popular tourist attraction. It is here that the kings of the Safavid dynasty would spend their vacations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Kosh
Ali Kosh is a small Tell of the Early Neolithic period located in Ilam Province in west Iran, in the Zagros Mountains. It was excavated by Frank Hole and Kent Flannery in the 1960s. Site The site is about 135 m in diameter. Research has found three phases of occupation of the site. The exact length of the occupation is debated; earlier authors saw the site as inhabited over an almost 2,000 year period, starting from about 9,500 years ago (7500 BCE). But recent (2018) analysis indicates only a 1000 year occupation. The site was occupied originally by pre-pottery peoples. Pottery was introduced to Ali Kosh during the third phase of its occupation. Nearby Chogha Sefid has only one pre-pottery phase, after which the occupation extended into the Chalcolithic period. Occupational phases Three phases of occupations have been identified. Bus Mordeh phase Bus Mordeh phase started around 7500 BC. The settlement began as a group of small, rectangular houses with several rooms mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundation (engineering)
In engineering, a foundation is the element of a structure which connects it to the ground, transferring loads from the structure to the ground. Foundations are generally considered either shallow or deep. Foundation engineering is the application of soil mechanics and rock mechanics (geotechnical engineering) in the design of foundation elements of structures. Purpose Foundations provide the structure's stability from the ground: * To distribute the weight of the structure over a large area in order to avoid overloading the underlying soil (possibly causing unequal settlement). * To anchor the structure against natural forces including earthquakes, floods, droughts, frost heaves, tornadoes and wind. * To provide a level surface for construction. * To anchor the structure deeply into the ground, increasing its stability and preventing overloading. * To prevent lateral movements of the supported structure (in some cases). Requirements of a good foundation The design and the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |