|
Tell Hassuna
Tell Hassuna is a tell, or settlement mound, in the Nineveh Province (Iraq), about 35km south-west of Nineveh. It is the type site for the Hassuna culture (early sixth millennium BCE). History of archaeological research Tell Hassuna was found in 1942 by Fuad Safar, and excavated in 1943 and 1944 by a team from the Iraqi Directorate General of Antiquities led by Seton Lloyd. Excavations revealed that there was once an advanced village culture that was spread throughout northern Mesopotamia. At Hassuna, six different layers of houses were uncovered, revealing various vessels and pottery that date ~5600-5350 BCE, with each layer becoming more substantial. Similar vessels were found throughout the Middle East, showing that there was an extensive trade network that was present as early as the 6th Millennium BCE. Tell Hassuna and its environment Tell Hassuna is located approximately southwest of modern Mosul, along the west bank of the Tigris River. It is a small site, roughly and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineveh Province
Nineveh Governorate ( ar, محافظة نينوى, syr, ܗܘܦܪܟܝܐ ܕܢܝܢܘܐ, Hoparkiya d’Ninwe, ckb, پارێزگای نەینەوا, Parêzgeha Neynewa), also known as Ninawa Governorate, is a Governorates of Iraq, governorate in northern Iraq. It has an area of and an estimated population of 2,453,000 people as of 2003. Its largest city and provincial capital is Mosul, which lies across the Tigris river from the ruins of ancient Nineveh. Before 1976, it was called ''Mosul Province'' and included the present-day Dohuk Governorate. The second largest city is Tal Afar, which has an almost exclusively Iraqi Turkmen, Turkmen population. An ethnically, religiously and culturally diverse region, it was partly conquered by Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIS in 2014. Iraqi government forces Battle of Mosul (2016–2017), retook the city of Mosul in 2017. Recent history and administration Its two cities endured the 2003 Invasion of Iraq, 2003 U.S.-led invasion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassuna Pottery Levels
Tell Hassuna is a tell, or settlement mound, in the Nineveh Province (Iraq), about 35km south-west of Nineveh. It is the type site for the Hassuna culture (early sixth millennium BCE). History of archaeological research Tell Hassuna was found in 1942 by Fuad Safar, and excavated in 1943 and 1944 by a team from the Iraqi Directorate General of Antiquities led by Seton Lloyd. Excavations revealed that there was once an advanced village culture that was spread throughout northern Mesopotamia. At Hassuna, six different layers of houses were uncovered, revealing various vessels and pottery that date ~5600-5350 BCE, with each layer becoming more substantial. Similar vessels were found throughout the Middle East, showing that there was an extensive trade network that was present as early as the 6th Millennium BCE. Tell Hassuna and its environment Tell Hassuna is located approximately southwest of modern Mosul, along the west bank of the Tigris River. It is a small site, roughly and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineveh Governorate
Nineveh Governorate ( ar, محافظة نينوى, syr, ܗܘܦܪܟܝܐ ܕܢܝܢܘܐ, Hoparkiya d’Ninwe, ckb, پارێزگای نەینەوا, Parêzgeha Neynewa), also known as Ninawa Governorate, is a governorate in northern Iraq. It has an area of and an estimated population of 2,453,000 people as of 2003. Its largest city and provincial capital is Mosul, which lies across the Tigris river from the ruins of ancient Nineveh. Before 1976, it was called ''Mosul Province'' and included the present-day Dohuk Governorate. The second largest city is Tal Afar, which has an almost exclusively Turkmen population. An ethnically, religiously and culturally diverse region, it was partly conquered by ISIS in 2014. Iraqi government forces retook the city of Mosul in 2017. Recent history and administration Its two cities endured the 2003 U.S.-led invasion of Iraq and emerged unscathed. In 2004, however, Mosul and Tal Afar were the scenes of fierce battles between US-led troops an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Iraq
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Iraq
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Type Sites
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1942 Archaeological Discoveries
Year 194 ( CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 947 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 194 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus and Decimus Clodius Septimius Albinus Caesar become Roman Consuls. * Battle of Issus: Septimius Severus marches with his army (12 legions) to Cilicia, and defeats Pescennius Niger, Roman governor of Syria. Pescennius retreats to Antioch, and is executed by Severus' troops. * Septimius Severus besieges Byzantium (194–196); the city walls suffer extensive damage. Asia * Battle of Yan Province: Warlords Cao Cao and Lü Bu fight for control over Yan Province; the battle lasts for over 100 days ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities Of The Ancient Near East
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC or with that by Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC. The largest cities of the Bronze Age Near East housed several tens of thousands of people. Memphis in the Early Bronze Age, with some 30,000 inhabitants, was the largest city of the time by far. Ebla is estimated to have had a population of 40,000 inhabitants in the Intermediate Bronze age. Ur in the Middle Bronze Age is estimated to have had some 65,000 inhabitants; Babylon in the Late Bronze Age similarly had a population of some 50,000–60,000. Niniveh had some 20,000–30,000, reaching 100,000 only in the Iron Age (around 700 BC). In Akkadian and Hittite orthography, URU became a determinative sign denoting a city, or combi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck Of A Painted Jar From Tell Hassuna, Iraq, Belonging To Samarra Culture
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles. In anatomy, the neck is also called by its Latin names, or , although when used alone, in context, the word ''cervix'' more often refers to the uterine cervix, the neck of the uterus. Thus the adjective ''cervical'' may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
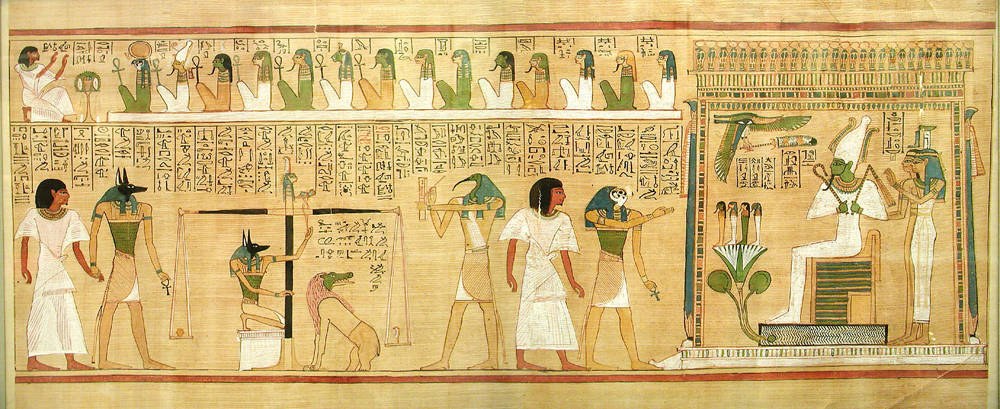
Afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary, nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into this world and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esotericism an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsidian
Obsidian () is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Obsidian is produced from felsic lava, rich in the lighter elements such as silicon, oxygen, aluminium, sodium, and potassium. It is commonly found within the margins of rhyolite, rhyolitic lava flows known as obsidian flows. These flows have a high content of silicon dioxide, silica, granting them a high viscosity. The high viscosity inhibits atomic diffusion, diffusion of atoms through the lava, which inhibits the first step (nucleation) in the formation of mineral crystals. Together with rapid cooling, this results in a natural glass forming from the lava. Obsidian is hard, Brittleness, brittle, and amorphous; it therefore Fracture (mineralogy)#Conchoidal fracture, fractures with sharp edges. In the past, it was used to manufacture cutting and piercing tools, and it has been used experimentally as surgic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fires. It occurs chiefly as nodules and masses in sedimentary rocks, such as chalks and limestones.''The Flints from Portsdown Hill'' Inside the nodule, flint is usually dark grey, black, green, white or brown in colour, and often has a glassy or waxy appearance. A thin layer on the outside of the nodules is usually different in colour, typically white and rough in texture. The nodules can often be found along s and |

%2C_(033)_der_geladene_Gastredner_Athiel_al-Nudschafi%2C_Gouverneur_von_Ninive.jpg)


.jpg)