|
Telegrafenberg
The Einstein Tower (German: ''Einsteinturm'') is an astrophysical observatory in the Albert Einstein Science Park in Potsdam, Germany built by architect Erich Mendelsohn. It was built on the summit of the Potsdam '' Telegraphenberg'' to house a solar telescope designed by the astronomer Erwin Finlay-Freundlich. The telescope supports experiments and observations to validate (or disprove) Albert Einstein's relativity theory. The building was first conceived around 1917, built from 1919 to 1921 after a fund-raising drive, and became operational in 1924. Although Einstein never worked there, he supported the construction and operation of the telescope. It is still a working solar observatory today as part of the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam. Light from the telescope is directed down through the shaft to the basement where the instruments and laboratory are located. There were more than half a dozen telescopes in the laboratory. This was one of Mendelsohn's first m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysical Institute Potsdam
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP) is a German research institute. It is the successor of the Berlin Observatory founded in 1700 and of the Astrophysical Observatory Potsdam (AOP) founded in 1874. The latter was the world's first observatory to emphasize explicitly the research area of astrophysics. The AIP was founded in 1992, in a re-structuring following the German reunification. The AIP is privately funded and member of the Leibniz Association. It is located in Babelsberg in the state of Brandenburg, just west of Berlin, though the Einstein Tower solar observatory and the great refractor telescopeGreat Refractor telescope at Telegrafenberg on Telegrafenberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Einstein Science Park
The Albert Einstein Science Park is located on the Telegrafenberg hill in Potsdam, Germany. The park was named after the physicist Albert Einstein. The best known buildings in the park are the Einstein Tower, an astrophysical observatory that was built to perform checks of Einstein's theory of General Relativity; and the Great Refractor of Potsdam,Great Refractor telescope at Telegrafenberg which today belong to the . These buildings, along with various astronomical, meteorological, and geophysical |
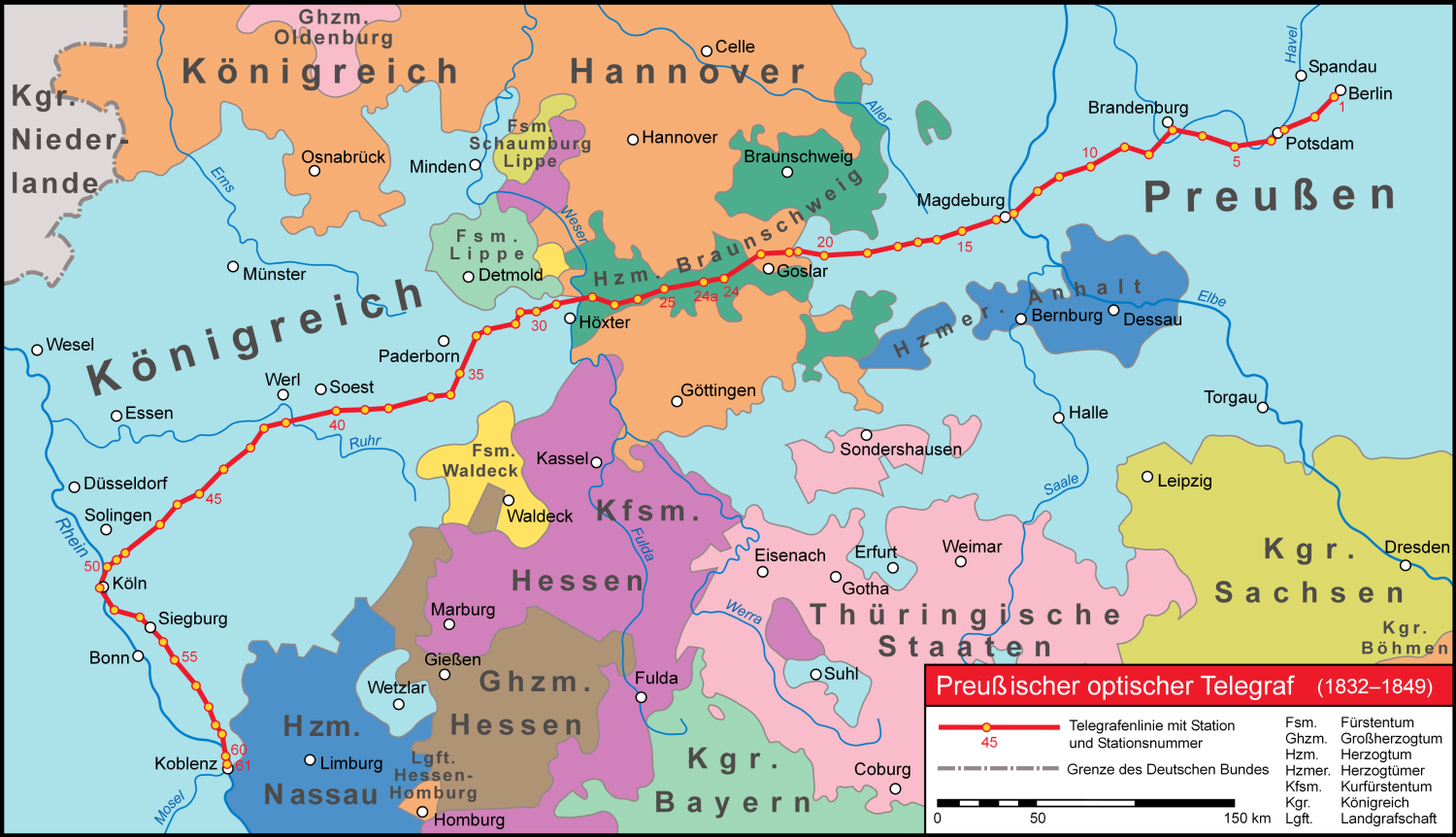
Prussian Semaphore System
The Prussian Semaphore System was a telegraphic communications system used between Berlin and the Rhine Province from 1832 to 1849. It could transmit administrative and military messages by optical signal over a distance of nearly . The telegraph line comprised 62 stations each furnished with a signal mast with six cable-operated arms. The stations were equipped with telescopes that operators used to copy coded messages and forward them to the next station. Three dispatch departments (telegraphische Expeditionen) located in Berlin, Cologne and Koblenz handled the coding and decoding of official telegrams. Although electric telegraphy made the system obsolete for military use, simplified semaphores were still used for railway signals. Historical background At the time of construction of the Prussian semaphore system, the technology had already been known for thirty years. It was based on earlier designs by Claude Chappe and his brother which were in use in France on many te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenerife
Tenerife (; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands. It is home to 43% of the total population of the Archipelago, archipelago. With a land area of and a population of 978,100 inhabitants as of January 2022, it is also the most populous island of Spain and of Macaronesia. Approximately five million tourists visit Tenerife each year; it is the most visited island in the archipelago. It is one of the most important tourist destinations in Spain and the world, hosting one of the world's largest carnivals, the Carnival of Santa Cruz de Tenerife. The capital of the island, , is also the seat of the island council (). That city and are the co-capitals of the autonomous community of the Canary Islands The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a unit directly proportional to the photon energy, such as reciprocal centimeters or electron volts, which has a reciprocal relationship to wavelength. A spectrometer is used in spectroscopy for producing spectral lines and measuring their wavelengths and intensities. Spectrometers may operate over a wide range of non-optical wavelengths, from gamma rays and X-rays into the far infrared. If the instrument is designed to measure the spectrum on an absolute scale rather than a relative one, then it is typically called a spectrophotometer. The majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Turbulence
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation to produce ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, the solar wind, and cosmic rays to protect organisms from genetic damage. The current com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Physics
Solar physics is the branch of astrophysics that specializes in the study of the Sun. It deals with detailed measurements that are possible only for our closest star. It intersects with many disciplines of pure physics, astrophysics, and computer science, including fluid dynamics, plasma physics including magnetohydrodynamics, seismology, particle physics, atomic physics, nuclear physics, stellar evolution, space physics, spectroscopy, radiative transfer, applied optics, signal processing, computer vision, computational physics, stellar physics and solar astronomy. Because the Sun is uniquely situated for close-range observing (other stars cannot be resolved with anything like the spatial or temporal resolution that the Sun can), there is a split between the related discipline of observational astrophysics (of distant stars) and observational solar physics. The study of solar physics is also important as it provides a "physical laboratory" for the study of plasma ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. The term itself is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos, photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it being a spherical surface that is perceived to emit light. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered. A photosphere is the deepest region of a luminous object, usually a star, that is transparent to photons of certain wavelengths. Temperature The surface of a star is defined to have a temperature given by the effective temperature in the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Stars, except neutron stars, have no solid or liquid surface. Therefore, the photosphere is typically used to describe the Sun's or another star's visual surface. Composition of the Sun The Sun is composed primari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. Historically, observatories were as simple as containing an astronomical sextant (for measuring the distance between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are used to make observations in the radio and visible light portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Most optical telescopes are housed within a dome or similar structure, to protect the delicate instruments from the elements. Telescope domes have a slit or other opening in the roof that can be opened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volker März
{{disambiguation ...
Volker may refer to: * Volker (name), including a list of people with the given name or surname * Volker, Kansas City, a historic neighborhood in Kansas City * Volker Boulevard, Kansas City * ''Alien Nations'' (German: ''Die Völker''), a real-time strategy video game released in 1999 See also * VolkerWessels, a Dutch construction company ** VolkerRail, a railway infrastructure services company based in Doncaster, England, owned by VolkerWessels * Voelcker (other) * Voelker (other) Voelker is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Joe Voelker (Born 1987), and Mike Voelker (Born 1982), Famous brothers from Florida * Bobby Voelker (born 1979), American mixed martial artist * Christopher Voelker (born 1961), Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
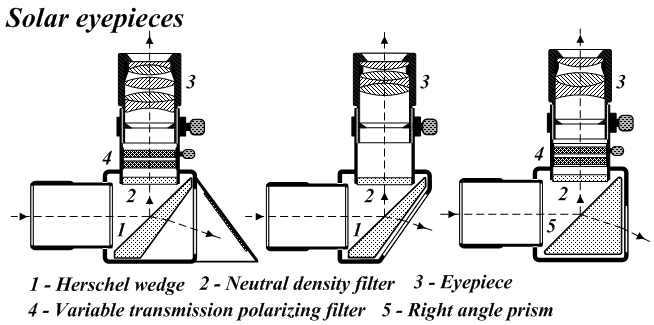
Coelostat
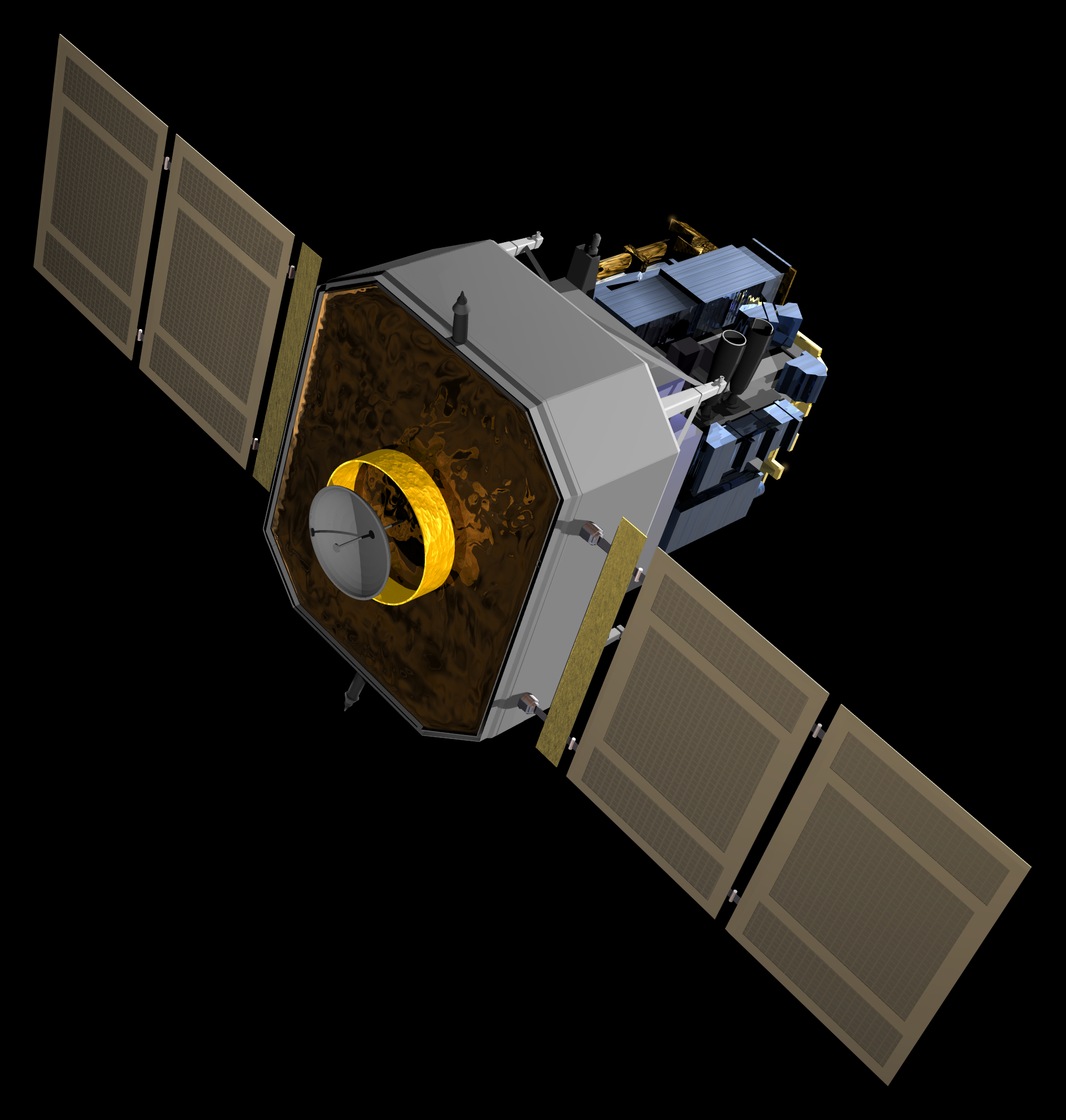
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Pöppel
Ernst Pöppel (born 29 April 1940) is a German psychologist and neuroscientist. He is the father of Dr. David Poeppel. Education and research Pöppel was born in Świeszyno, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, Schwessin, Farther Pomerania. He studied psychology and biology in Freiburg and Munich, before finishing his academic education with PhD in 1968 in Innsbruck, Austria. He did research on temporal perception and circadian rhythms between 1964 and 1968, in the Max-Planck-Institute of Behavioral Physiology, and on neurophysiology of vision in 1969 and 1970 in Max-Planck-Institute of Psychiatry, Munich. From 1971 to 1973, he did research on neuropsychology of vision at the Department of Psychology and Brain Science at MIT, Cambridge, USA. At the same time, he was staff scientist at the Neuroscience Research Program (NRP). At this time, he described together with Richard Held and Douglas Frost a phenomenon of residual vision, which became known as blindsight. After his first habil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |