|
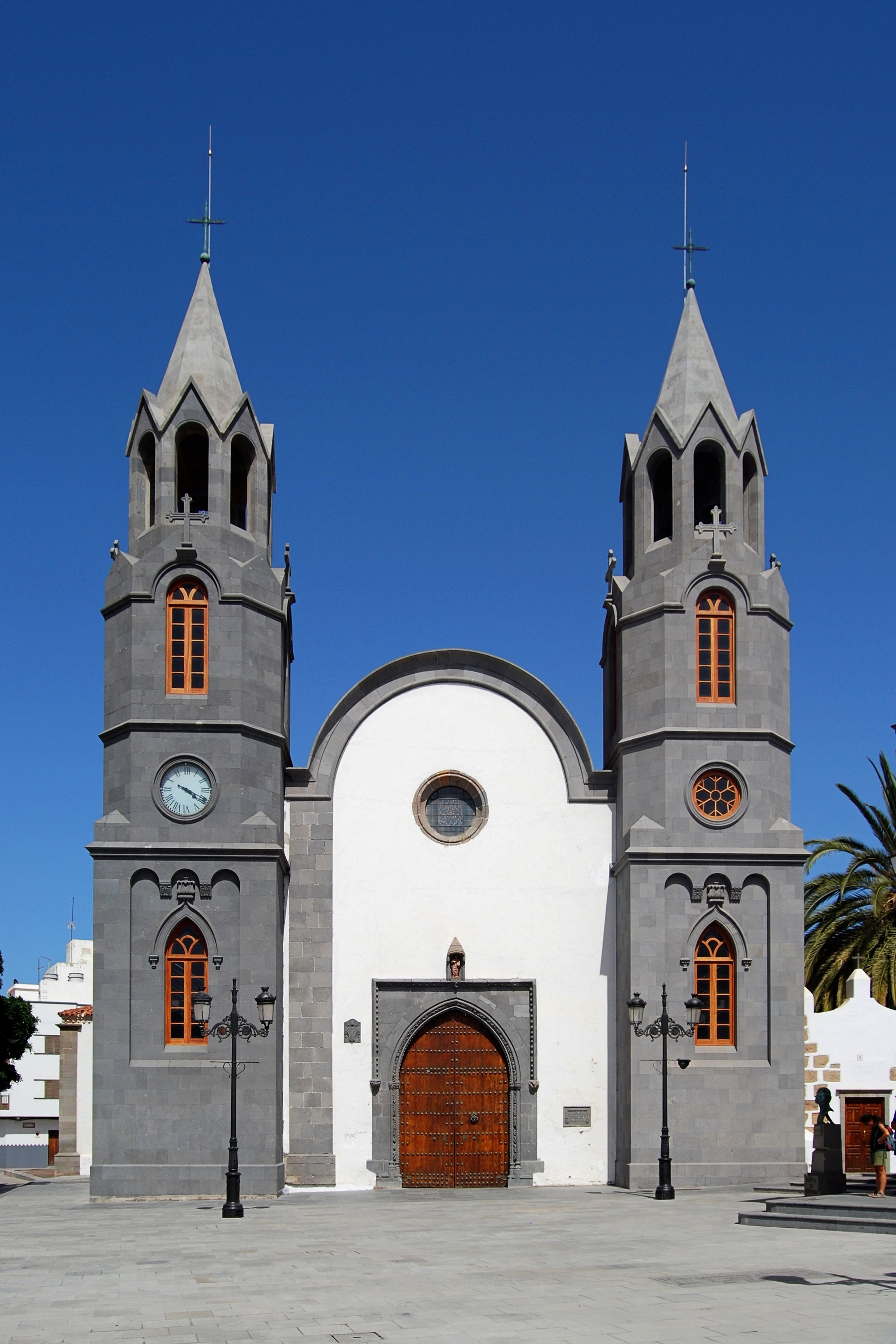
Telde, Las Palmas
Telde is a town and a municipality in the eastern part of the island of Gran Canaria, Canary Islands, overseas (Atlantic) insular Spain. It is the second most populous municipality on the island, with a population of (2013).Instituto Canario de Estadística , population Its area is . The city is the oldest and the first capital of the island of Gran Canaria, founded before 1351, a former medieval bishopric and present Catholic . The city Telde is located 4 km from the coast and 16 km south of the island capital |
Municipalities Of Spain
The municipality ( es, municipio, , ca, municipi, gl, concello, eu, udalerria, ast, conceyu)In other languages of Spain: * Catalan/Valencian (), sing. ''municipi''. * Galician () or (), sing. ''municipio''/''bisbarra''. *Basque (), sing. ''udalerria''. * Asturian (), sing. ''conceyu''. is the basic local administrative division in Spain together with the province. Organisation Each municipality forms part of a province which in turn forms part or the whole of an autonomous community (17 in total plus Ceuta and Melilla): some autonomous communities also group municipalities into entities known as ''comarcas'' (districts) or ''mancomunidades'' (commonwealths). There are a total of 8,131 municipalities in Spain, including the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla. In the Principality of Asturias, municipalities are officially named ''concejos'' (councils). The average population of a municipality is about 5,300, but this figure masks a huge range: the most populo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autopista GC-1
The GC-1 (also ''Autopista del Sur'', "Southern Highway") is a superhighway (or motorway) on the island of Gran Canaria. It links the capital Las Palmas in the north with Puerto de Mogán in the south. It is the fastest route from the north of the island to the south and vice versa with a top speed limit of 120 km/h (75 mph). It is approximately 75 km (47 miles) in length, and runs along the eastern and the southern coasts of this circular island and is also the second longest superhighway in the Canary Islands. The road provides easy access from the airport to the major cities and resorts. The resorts include Maspalomas and Playa del Inglés. The increase in tourism over the years has seen the GC1 route slowly being upgraded and widened to cope with extra traffic. GC-1 does not have motorway designation from Las Palmas to the airport, but has motorway designation from the airport to its southern end. Although the geographical name for the official name of the "Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostolic Nuncio
An apostolic nuncio ( la, nuntius apostolicus; also known as a papal nuncio or simply as a nuncio) is an ecclesiastical diplomat, serving as an envoy or a permanent diplomatic representative of the Holy See to a state or to an international organization. A nuncio is appointed by and represents the Holy See, and is the head of the diplomatic mission, called an Apostolic Nunciature, which is the equivalent of an embassy. The Holy See is legally distinct from the Vatican City or the Catholic Church. In modern times, a nuncio is usually an archbishop. An apostolic nuncio is generally equivalent in rank to that of ambassador extraordinary and plenipotentiary, although in Catholic countries the nuncio often ranks above ambassadors in diplomatic protocol. A nuncio performs the same functions as an ambassador and has the same diplomatic privileges. Under the 1961 Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, to which the Holy See is a party, a nuncio is an ambassador like those from any o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titular Bishopric
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbishop" (intermediary rank) or "titular bishop" (lowest rank), which normally goes by the status conferred on the titular see. Titular sees are dioceses that no longer functionally exist, often because the territory was conquered by Muslims or because it is schismatic. The Greek–Turkish population exchange of 1923 also contributed to titular sees. The see of Maximianoupolis along with the town that shared its name was destroyed by the Bulgarians under Emperor Kaloyan in 1207; the town and the see were under the control of the Latin Empire, which took Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade in 1204. Parthenia, in north Africa, was abandoned and swallowed by desert sand. Catholic Church During the Muslim conquests of the Middle Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
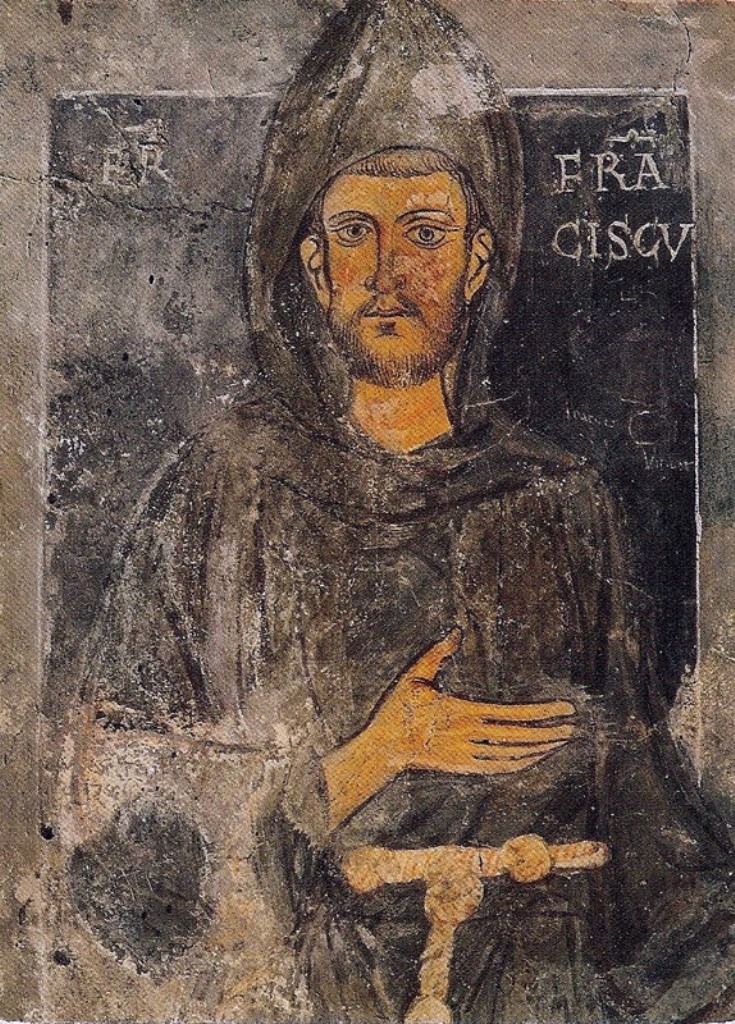
Friars Minor
The Order of Friars Minor (also called the Franciscans, the Franciscan Order, or the Seraphic Order; postnominal abbreviation OFM) is a mendicant Catholic religious order, founded in 1209 by Francis of Assisi. The order adheres to the teachings and spiritual disciplines of the founder and of his main associates and followers, such as Clare of Assisi, Anthony of Padua, and Elizabeth of Hungary, among many others. The Order of Friars Minor is the largest of the contemporary First Orders within the Franciscan movement. Francis began preaching around 1207 and traveled to Rome to seek approval of his order from Pope Innocent III in 1209. The original Rule of Saint Francis approved by the pope disallowed ownership of property, requiring members of the order to beg for food while preaching. The austerity was meant to emulate the life and ministry of Jesus Christ. Franciscans traveled and preached in the streets, while boarding in church properties. The extreme poverty required of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
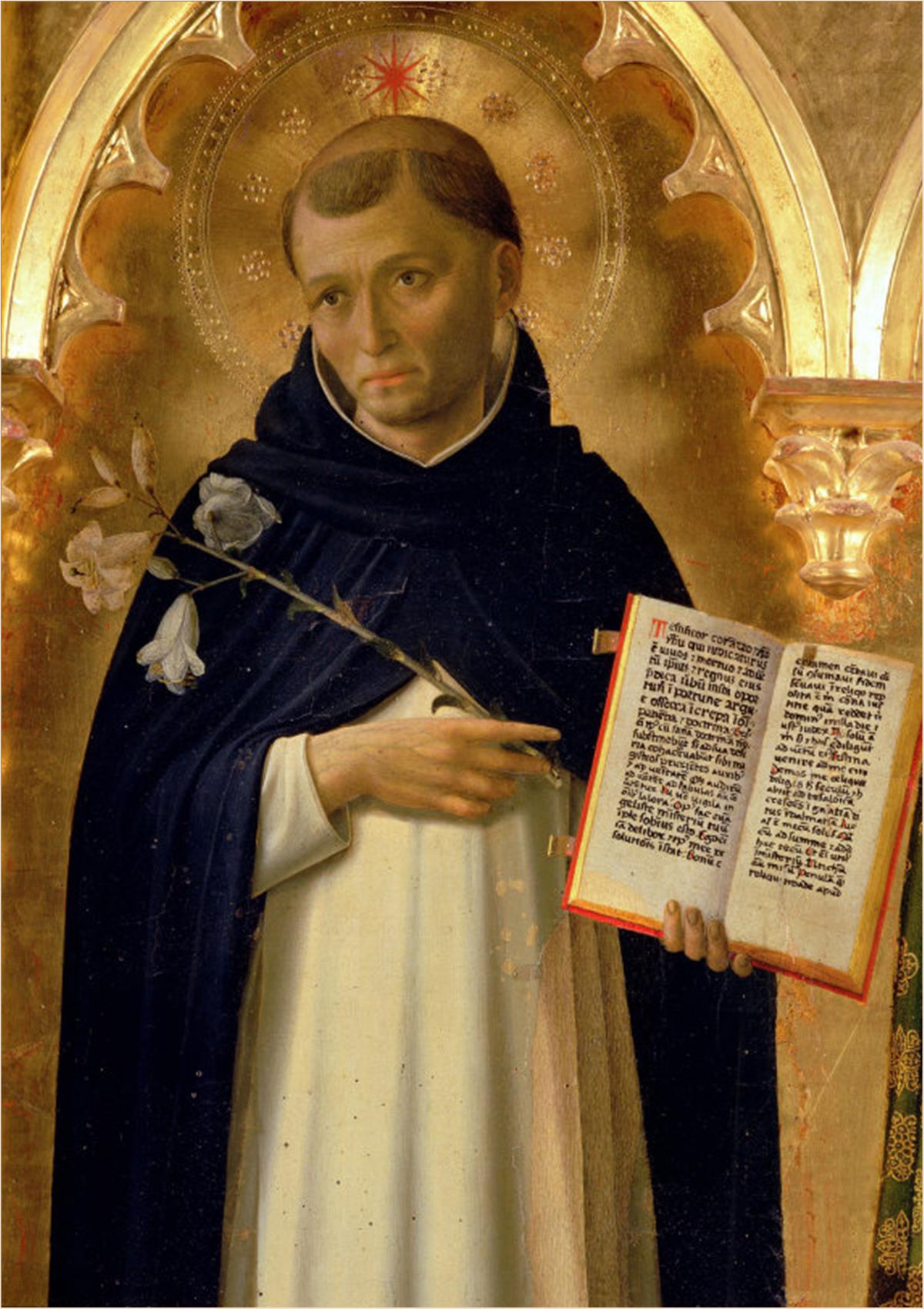
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of Caleruega. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull ''Religiosam vitam'' on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as ''Dominicans'', generally carry the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for ''Ordinis Praedicatorum'', meaning ''of the Order of Preachers''. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as tertiaries). More recently there has been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the Gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed the Preachers in the forefront of the intellectual life of the Middle Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Santa Giusta
The Diocese of Santa Giusta, formerly Othoca, was a Roman Catholic diocese in Santa Giusta, Sardinia. The bishop's seat was in the former Santa Giusta Cathedral, now a minor basilica. The diocese was established in 1119 and abolished in 1503, when it was absorbed into the Archdiocese of Oristano. Since 1969 Santa Giusta has been a titular bishopric A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbish .... SourcesCatholic Hierarchy: Titular See of Santa Giusta Former Roman Catholic dioceses in Italy [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carmelite Order
, image = , caption = Coat of arms of the Carmelites , abbreviation = OCarm , formation = Late 12th century , founder = Early hermits of Mount Carmel , founding_location = Mount Carmel , type = Mendicant order of pontifical right , status = Institute of Consecrated Life , membership = 1,979 (1,294 priests) as of 2017 , leader_title = Motto , leader_name = la, Zelo zelatus sum pro Domino Deo exercituumEnglish: ''With zeal have I been zealous for the Lord God of hosts'' , leader_title2 = General Headquarters , leader_name2 = Curia Generalizia dei CarmelitaniVia Giovanni Lanza, 138, 00184 Roma, Italia , leader_title3 = Prior General , leader_name3 = Mícéal O'Neill, OCarm , leader_title4 = Patron saints , leader_name4 = Our Lady of Mt. Carmel, Elijah , parent_organization = Catholic Church , website = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Rite
The Roman Rite ( la, Ritus Romanus) is the primary liturgical rite of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. It developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while distinct Latin liturgical rites such as the Ambrosian Rite remain, the Roman Rite has gradually been adopted almost everywhere in the Latin Church. In medieval times there were numerous local variants, even if all of them did not amount to distinct rites, yet uniformity increased as a result of the invention of printing and in obedience to the decrees of the Council of Trent of 1545–63 (see ''Quo primum''). Several Latin liturgical rites that survived into the 20th century were abandoned voluntarily after the Second Vatican Council. The Roman Rite is now the most widespread liturgical rite not only in the Catholic Church but in Christianity as a whole. The Roman Rite has been adapted through the centuries and the history of its Eucharistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Rubicon
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Canarias or Diocese Canariense-Rubicense ( la, Canarien(sis)) is a diocese located in the Canary Islands in the Ecclesiastical province of Seville in Spain. The dioceses includes the islands of Gran Canaria, Fuerteventura and Lanzarote (Oriental Province). However, it does not include the whole archipelago, since the Diocese of Tenerife (or Nivariense) includes the Province of Santa Cruz de Tenerife. For this reason, the use of the name of the archipelago is currently a very controversial topic in the Canary Islands. It has recently emerged between the society of Lanzarote the desire to recover the diocesan headquarters of San Marcial del Rubicón. History * 1351: Established as Diocese of Islas Canarias from the Diocese of Majorca * 1354: Suppressed * 1369: Restored as Diocese of Telde * 1393: Suppressed * 1406: Restored as Diocese of Rubicon * 1424: Established as Diocese of Fuerteventura * 1431: Suppressed * 1485: Renamed as Diocese of Canarias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archdiocese Of Seville
The Archdiocese of Seville is part of the Catholic Church in Seville, Spain. The Diocese of Seville was founded in the 3rd century. It was raised to the level of an archdiocese in the 4th century. The current archbishop is José Ángel Saiz Meneses. It has the suffragan dioceses of: * Cádiz y Ceuta * Córdoba *Huelva * Canaries *Jerez de la Frontera * San Cristóbal de La Laguna o Tenerife Early History of the Diocese During Roman times Seville was the capital of the Province of Baetica, and the origin of the diocese goes back to apostolic times, or at least to the 1st century. Saint Gerontius, Bishop of Italica, preached in Baetica, and without doubt must have left a pastor of its own to Seville. It is certain that in 303, when Saints Justa and Rufina were martyred for refusing to adore the idol Salambo, there was a Bishop of Seville named Sabinus, who assisted at the Council of Illiberis in 287. ''Zeno'' (472–486) was appointed vicar apostolic by Pope Simplicius, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffragan
A suffragan bishop is a type of bishop in some Christian denominations. In the Anglican Communion, a suffragan bishop is a bishop who is subordinate to a metropolitan bishop or diocesan bishop (bishop ordinary) and so is not normally jurisdictional in their role. Suffragan bishops may be charged by a metropolitan to oversee a suffragan diocese and may be assigned to areas which do not have a cathedral of their own. In the Catholic Church, a suffragan Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop instead leads a diocese within an ecclesiastical province other than the principal diocese, the Metropolitan bishop#Roman Catholic, metropolitan archdiocese; the diocese led by the suffragan is called a suffragan diocese. Anglican Communion In the Anglican churches, the term applies to a bishop who is assigned responsibilities to support a diocesan bishop. For example, the Bishop of Jarrow is a suffragan to the diocesan Bishop of Durham. Suffragan bishops in the Anglican Communion are nearly id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |