|
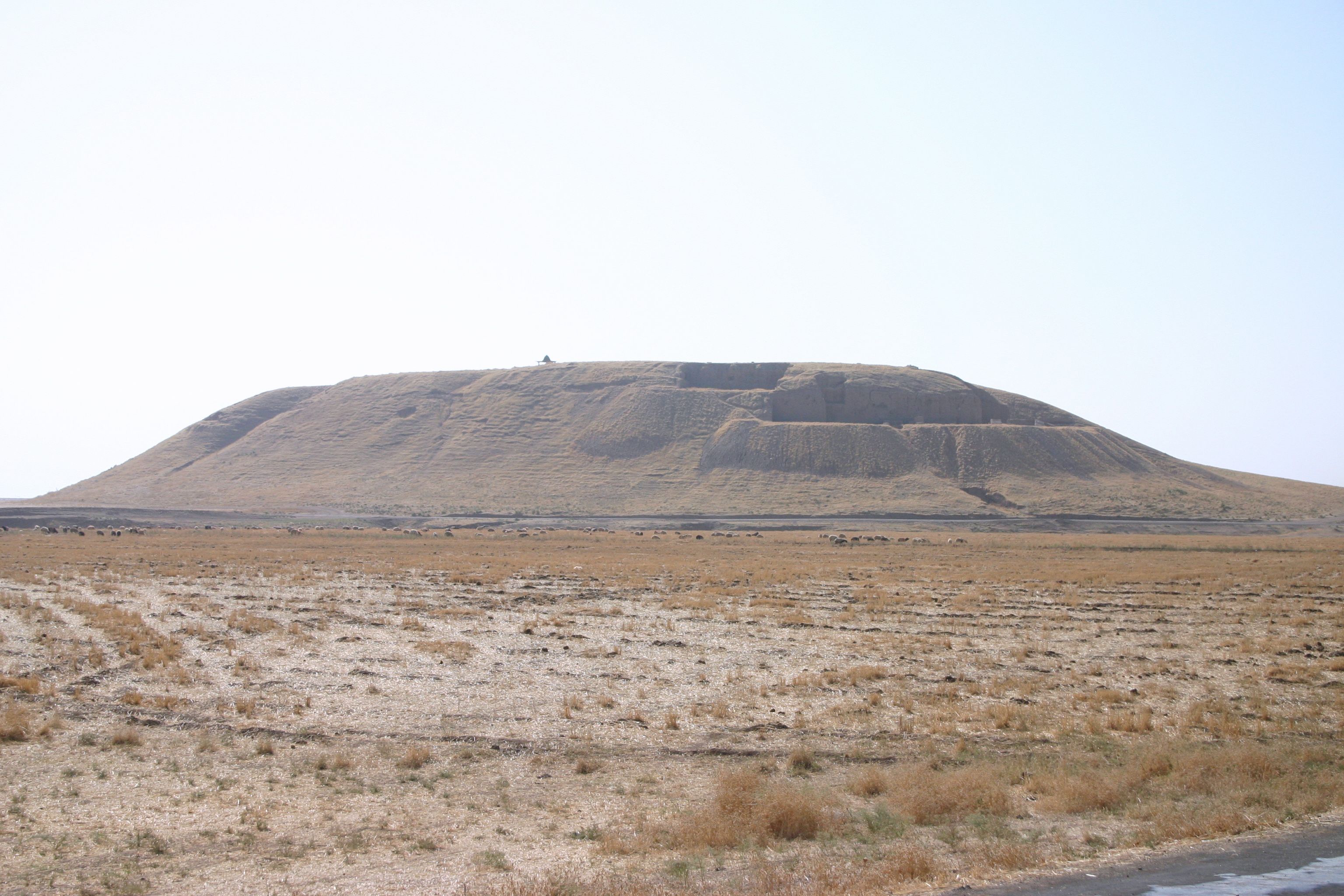
Tel Heror
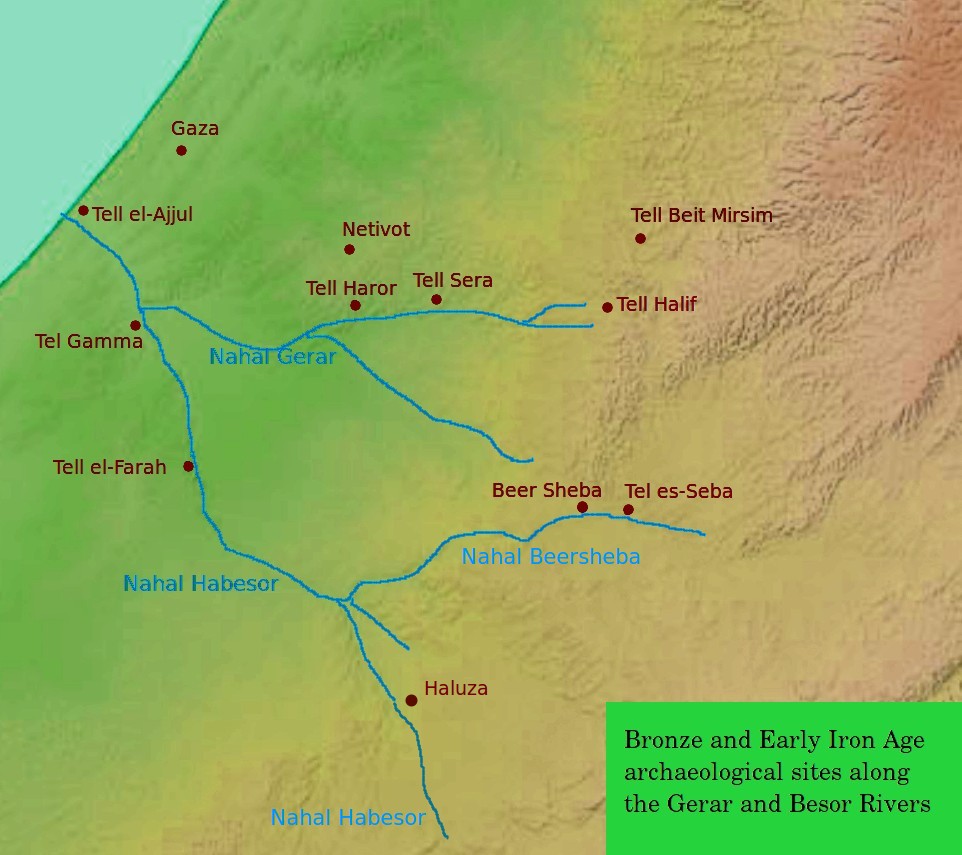
Tel Haror (Hebrew name) or Tell Abu Hureyra (Arabic name; also spelled Hureira and Hareira), also known as ''Tel Heror'', is an archaeological site in the western Negev Desert, Israel, northwest of Beersheba, about 20 km east of the Mediterranean Sea, situated on the north bank of Wadi Gerar, a wadi known in Arabic as Wadi esh-Sheri'a. During the Middle Bronze Age II it was one of the largest urban centres in the area, occupying about 40 acres. The city contains substantial remains of Middle Bronze Age II through to Persian-period settlement strata. Excavations W.F. Albright suggested as early as 1924 that there was a Cushite colony here founded in the tenth century BCE. In 1956 Yohanan Aharoni identified biblical Gerar with the site of Tell Abu Hureira (Tel Haror). Tel Haror was excavated by Eliezer Oren of the Ben Gurion University of the Negev between 1982 and 1992. In 2010, there were also further explorations by Oren with P. Nahshoni and G. Bar-Oz. Substantia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerar
Gerar ( ''Gərār'', "lodging-place") was a Philistine town and district in what is today south central Israel, mentioned in the Book of Genesis and in the Second Book of Chronicles of the Hebrew Bible. Identification According to the International Standard Bible Encyclopedia, the biblical ''valley of Gerar'' () was probably located in the area of a valley known in Arabic as Wady Sheri'a, and in Modern Hebrew as Nahal Gerar. Most commentators see the mound of Tel Haror (Hebrew) or Tell Abu Hureyra (Arabic) as representing the ancient Gerar. Some older commentaries, such as Smith's Bible Dictionary, stated simply that Gerar was located "south of Gaza". Also, a ninth century rabbinical source (Saadia Gaon) identified Gerar with Haluza, located along the Besor River in the Negev.Rabbi Saadia Gaon's Judeo-Arabic Translation of the word Gerar (Judeo-Arabic: אלכ'לוץ = ''al-Khalūṣ'') in the Pentateuch (''Tafsir''), s.v. Genesis 10:19, Genesis 20:2, Genesis 26:17, 20. On Haluza' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minoan Civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450BC until it ended around 1100BC, during the early Greek Dark Ages, part of a wider bronze age collapse around the Mediterranean. It represents the first advanced civilization in Europe, leaving behind a number of massive building complexes, Minoan art, sophisticated art, and writing systems. Its economy benefited from a network of trade around much of the Mediterranean. The civilization was rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century through the work of British archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans. The name "Minoan" derives from the mythical Minos, King Minos and was coined by Evans, who identified the site at Knossos with the labyrinth of the Minotaur. The Minoan civilization has been described as the earliest of its kind in Europe, and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tze'elim
Tze'elim ( he, צֶאֱלִים) is a kibbutz in southern Israel. Located in the Negev desert, it falls under the jurisdiction of Eshkol Regional Council. In it had a population of . A military training base of the ground forces of the IDF (often named "Tze'elim Base") is located nearby. History The kibbutz was founded in January 1947 by gar'in from Jewish youth movements in Eastern Europe and North Africa, and was named for the abundant acacia trees in the area, which were mistakenly identified as the biblical ''Tze'elim'' trees. During the 1948 Arab–Israeli War the kibbutz was used as a military base. Many of the Selvino children were settled in the kibbutz. Economy Today the kibbutz markets itself as a tourist destination, with a natural hot springs spa and accommodation. Other economic activities are agriculture and farming. A 120 MW solar power plant, Israel's largest to date, opened in the kibbutz in 2020. The production plant for cleantech materials made out of uns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Et-Tuwail
Tell may refer to: *Tell (archaeology), a type of archaeological site *Tell (name), a name used as a given name and a surname *Tell (poker), a subconscious behavior that can betray information to an observant opponent Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Tell'' (2012 film), a short psychological horror film by Ryan Connolly * ''Tell'' (2014 film), a crime thriller starring Katee Sackhoff, Jason Lee and Milo Ventimiglia * '' Tell Magazine'', a Nigerian newsweekly * " The Tell", an episode of ''NCIS'' * "The Tell" (''Teen Wolf''), a television episode * ''The Tell'', a photomural, part of the Laguna Canyon Project Places Middle East *Tel Aviv, Israel *Et-Tell, an archaeological site identified with Bethsaida *Tell, West Bank, a Palestinian village near Nablus *Ancient Tell, Beirut, Lebanon; the Canaanite pre-Phoenician era of Beirut and archaeological site United States *Tell, Texas, unincorporated community in the United States *Tell, Wisconsin, town in the United States *Tell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Esh-Sharia
Tell may refer to: *Tell (archaeology), a type of archaeological site *Tell (name), a name used as a given name and a surname *Tell (poker), a subconscious behavior that can betray information to an observant opponent Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Tell'' (2012 film), a short psychological horror film by Ryan Connolly * ''Tell'' (2014 film), a crime thriller starring Katee Sackhoff, Jason Lee and Milo Ventimiglia * '' Tell Magazine'', a Nigerian newsweekly * " The Tell", an episode of ''NCIS'' * "The Tell" (''Teen Wolf''), a television episode * ''The Tell'', a photomural, part of the Laguna Canyon Project Places Middle East *Tel Aviv, Israel *Et-Tell, an archaeological site identified with Bethsaida *Tell, West Bank, a Palestinian village near Nablus *Ancient Tell, Beirut, Lebanon; the Canaanite pre-Phoenician era of Beirut and archaeological site United States *Tell, Texas, unincorporated community in the United States *Tell, Wisconsin, town in the United States *Tell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Jemmeh
Tell Jemmeh ( ar, تل جمه), also known in Hebrew as Tel Gamma (תל גמה) or Tel Re'im (תל רעים), is a prominent mound, or tell (archaeology), tell, located in the region of the northwestern Negev and the southern Israeli coastal plain, coastal plain of Israel, about 12 km south of Gaza City, Gaza, bounded by the kibbutz of Re'im 2 km to the east, and the kibbutz of Kisufim 6 km to the west, and is 9 km east of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast. The site is located at the confluence of two streams, Nahal Besor and Nahal Gerar. Both have changed their course in this area many times throughout history. Re'im is a modern secular kibbutz town located to the east nearby. Tell Jemmeh is one of three major sites along the Besor Stream along with Tell el-Far'ah (South), Tell el-Far'ah and Tell el-Ajjul. Some archaeologists identify the Besor Stream with the "Brook of Egypt" found in the Hebrew Bible (Torah). There are also a number of ancient sites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaza City
Gaza (;''The New Oxford Dictionary of English'' (1998), , p. 761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory in Palestine, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza...". ar, غَزَّة ', ), also referred to as Gaza City, is a Palestinian city in the Gaza Strip, with a population of 590,481 (in 2017), making it the largest city in the State of Palestine. Inhabited since at least the 15th century BCE, Gaza has been dominated by several different peoples and empires throughout its history. The Philistines made it a part of their pentapolis after the Ancient Egyptians had ruled it for nearly 350 years. Under the Roman Empire Gaza experienced relative peace and its port flourished. In 635 CE, it became the first city in Palestine to be conquered by the Muslim Rashidun army and quickly developed into a center of Islamic law. However, by the time the Crusaders invaded the country starting in 1099, Gaza was in ruins. In later centuries, Gaza experienced several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell (archaeology)
In archaeology, a tell or tel (borrowed into English from ar, تَلّ, ', 'mound' or 'small hill'), is an artificial topographical feature, a species of mound consisting of the accumulated and stratified debris of a succession of consecutive settlements at the same site, the refuse of generations of people who built and inhabited them, and of natural sediment. (Very limited snippet view).Matthews (2020)Introduction and Definition/ref> Tells are most commonly associated with the ancient Near East, but they are also found elsewhere, such as Southern and parts of Central Europe, from Greece and Bulgaria to Hungary and SpainBlanco-González & Kienlin, eds (2020), 6th page of chapter 1, see map. and in North Africa. Within the Near East, they are concentrated in less arid regions, including Upper Mesopotamia, the Southern Levant, Anatolia and Iran, which had more continuous settlement. Eurasian tells date to the Neolithic,Blanco-González & Kienlin, eds (2020), 2nd page of chapter 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Redford
Donald Bruce Redford (born September 2, 1934) is a Canadian Egyptologist and archaeologist, currently Professor of Classics and Ancient Mediterranean Studies at Pennsylvania State University. He is married to Susan Redford, who is also an Egyptologist currently teaching classes at the university. Professor Redford has directed a number of important excavations in Egypt, notably at Karnak and Mendes. Biography Redford received his B.A., M.A. and Ph.D from McGill University and the University of Toronto, and was an Assistant/Associate Professor (1962–1969) and full Professor (1969–1998) at the latter. He moved to Pennsylvania State University in 1998. Redford was the winner of the 1993 "''Best Scholarly Book in Archaeology''" awarded by the Biblical Archaeology Society for his work ''Egypt, Canaan, and Israel in Ancient Times''. In the book he argues that the experiences of the Hyksos in Egypt became a central foundation of myths in Canaanite culture, leading to the story of Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharuhen
Sharuhen ( he, שָׁרוּחֶן) was an ancient town in the Negev Desert or perhaps in Gaza. Following the expulsion of the Hyksos from Egypt in the second half of the 16th century BCE, they fled to Sharuhen and fortified it. The armies of Pharaoh Ahmose I seized and razed the town after a three-year siege. History The destruction of Sharuhen was merely the first stage of a new policy of pre-emptive warfare waged by the Egyptians. Because the Egyptians of the 17th Dynasty felt deeply humiliated by the 15th and 16th Dynasty rule of the Hyksos (ca. 1650 BCE – ca. 1540 BCE), the Theban dynasty launched an ambitious war, led by Seqenenre Tao, against the foreign king, Apepi, to reclaim lost territory. Though his own campaign to expel the Hyksos from Egypt failed, and he himself was killed in battle, his son, Kamose, launched an attack on the Hyksos capital of Avaris. It was his much younger brother, Ahmose I, however, who finally succeeded in capturing Avaris, razing it, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anson Rainey
Anson Frank Rainey (January 11, 1930 – February 19, 2011) was professor emeritus of ancient Near Eastern cultures and Semitic linguistics at Tel Aviv University. He is known in particular for contributions to the study of the Amarna tablets, the noted administrative letters from the period of Pharaoh Akhenaten's rule during the 18th Dynasty of Egypt.Rollston, C. (2011)Among the last of the titans: Aspects of Professor Anson Rainey's life and legacy (1930–2011)(February 20, 2011); retrieved May 22, 2017 He authored and edited books and articles on the cultures, languages and geography of the Biblical lands. Early life Anson Rainey was born in Dallas, Texas, in 1930. Upon the death of his father that same year, he was left with his maternal grandparents. He attended Brown Military Academy in San Diego, California, from 1943 to 1946. After one semester of study there – as a cadet battalion commander – he served as assistant commandant at Southern California Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)





