|
Tegafur Uracil
Tegafur is a chemotherapeutic prodrug of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) used in the treatment of cancers. It is a component of the combination drug tegafur/uracil. When metabolised, it becomes 5-FU. It was patented in 1967 and approved for medical use in 1972. Medical uses As a prodrug to 5-FU it is used in the treatment of the following cancers: * Stomach (when combined with gimeracil and oteracil) * Breast (with uracil) * Gallbladder * Lung (specifically adenocarcinoma, typically with uracil) * Colorectal (usually when combined with gimeracil and oteracil) * Head and neck * Liver (with uracil) * Pancreatic It is often given in combination with drugs that alter its bioavailability and toxicity such as gimeracil, oteracil or uracil. These agents achieve this by inhibiting the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (uracil/gimeracil) or orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (oteracil). Adverse effects The major side effects of tegafur are similar to fluorouracil and include myelosuppression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapeutic
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms (palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidine Antagonists
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug, zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux reported the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodrugs
A prodrug is a medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted (ADME). Prodrugs are often designed to improve bioavailability when a drug itself is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. A prodrug may be used to improve how selectively the drug interacts with cells or processes that are not its intended target. This reduces adverse or unintended effects of a drug, especially important in treatments like chemotherapy, which can have severe unintended and undesirable side effects. History Many herbal extracts historically used in medicine contain glycosides (sugar derivatives) of the active agent, which are hydrolyzed in the intestines to release the active and more bioavailable aglycone. For example, salicin is a β-D-glucopyranosid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organofluorides
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from Lipophobicity, oil and hydrophobe, water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents. The carbon–fluorine bond Fluorine has several distinctive differences from all other substituents encountered in organic molecules. As a result, the physical and chemical properties of organofluorines can be distinctive in comparison to other organohalogens. # The carbon–fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry (an average bond energy around 480 kJ/molKirsch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tegafur/uracil
Tegafur/uracil is a chemotherapy drug combination used in the treatment of cancer, primarily bowel cancer. It is also called UFT or UFUR. Description UFT is a first generation dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) inhibitory fluoropyrimidine drug. It is an oral agent which combines uracil, a competitive inhibitor of DPD, with the 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) prodrug tegafur in a 4:1 molar ratio. Mechanism of action Excess uracil competes with 5-FU for DPD, thus inhibiting 5-FU catabolism. The tegafur is taken up by the cancer cells and breaks down into 5-FU, a substance that kills tumor cells. The uracil causes higher amounts of 5-FU to stay inside the cells and kill them. Tegafur is a type of antimetabolite. Uracil has also been stated to help protect the gastrointestinal tract from 5-FU toxicity and the related metabolites, with less side effects than 5-FU and other 5-FU related (pro)drugs. Tetrahydrofuran metabolites from the tegafur metabolism, unique among 5-FU based drugs, hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP2A6
Cytochrome P450 2A6 (abbreviated CYP2A6) is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and cotinine. It is also involved in the metabolism of several pharmaceuticals, carcinogens, and a number of coumarin-type alkaloids. CYP2A6 is the only enzyme in the human body that appreciably catalyzes the 7-hydroxylation of coumarin, such that the formation of the product of this reaction, 7-hydroxycoumarin, is used as a probe for CYP2A6 activity. The CYP2A6 gene is part of a large cluster of cytochrome P450 genes from the CYP2A, CYP2B and CYP2F subfamilies on chromosome 19q. The gene was formerly referred to as CYP2A3; however, it has been renamed CYP2A6. Interactive pathway map Distribution CYP2A6 localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and is found predominantly in the liver. Variability Significant interindividual variability in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymidylate Synthase
Thymidylate synthase (TS) () is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). Thymidine is one of the nucleotides in DNA. With inhibition of TS, an imbalance of deoxynucleotides and increased levels of dUMP arise. Both cause DNA damage. Function The following reaction is catalyzed by thymidylate synthase: : 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + dUMP \rightleftharpoons dihydrofolate + dTMP By means of reductive methylation, deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) and N5,N10-methylene tetrahydrofolate are together used to form dTMP, yielding dihydrofolate as a secondary product. This provides the sole de novo pathway for production of dTMP and is the only enzyme in folate metabolism in which the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is oxidised during one-carbon transfer. The enzyme is essential for regulating the balanced supply of the 4 DNA precursors in normal DNA replication: defects in the enzyme activity affectin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
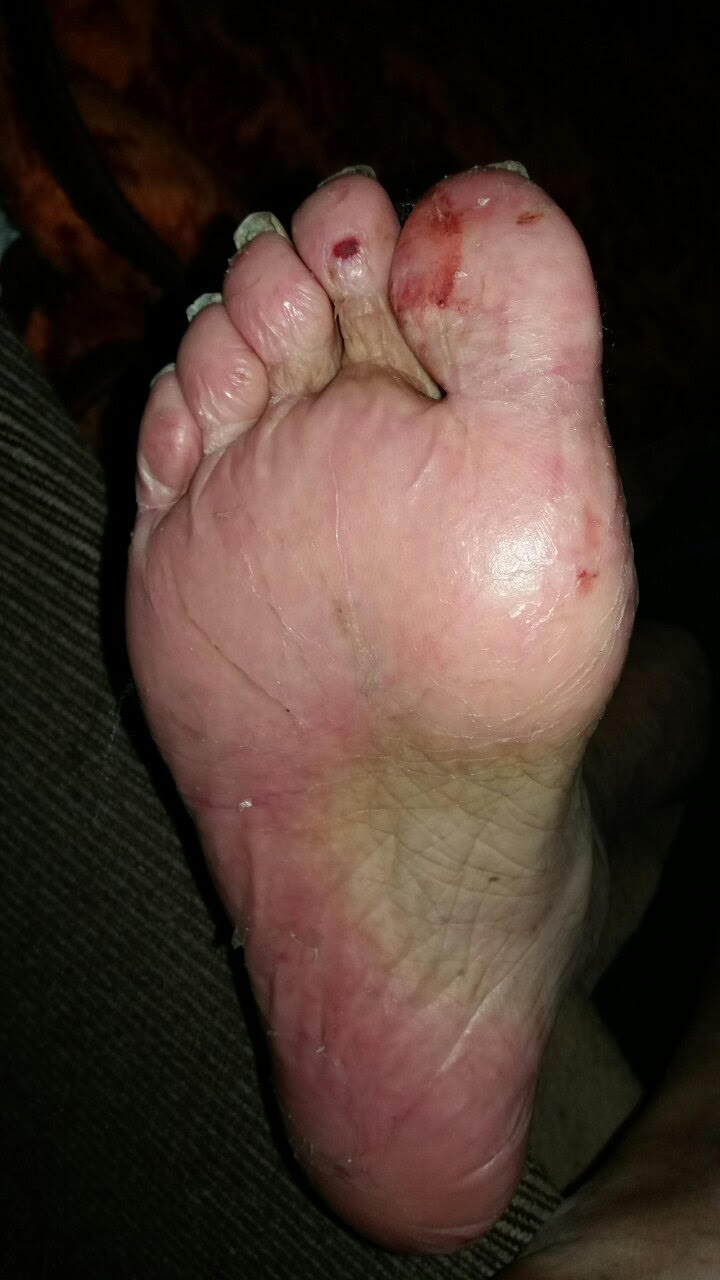
Hand-foot Syndrome
Chemotherapy-induced acral erythema, also known as palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia or hand-foot syndrome is reddening, swelling, numbness and desquamation (skin sloughing or peeling) on palms of the hands and soles of the feet (and, occasionally, on the knees, elbows, and elsewhere) that can occur after chemotherapy in patients with cancer. Hand-foot syndrome is also rarely seen in sickle-cell disease. These skin changes usually are well demarcated. Acral erythema typically disappears within a few weeks after discontinuation of the offending drug.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . Signs and symptoms The symptoms can occur anywhere between days to months after administration of the offending medication, depending on the dose and speed of administration. The patient first experiences tingling and/or numbness of the palms and soles. This is followed 2-4 days later by bright redness, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specifically, a neurotoxin or neurotoxicant– alters the normal activity of the nervous system in such a way as to cause permanent or reversible damage to nervous tissue. This can eventually disrupt or even kill neurons, which are cells that transmit and process signals in the brain and other parts of the nervous system. Neurotoxicity can result from organ transplants, radiation treatment, certain drug therapies, recreational drug use, and exposure to heavy metals, bites from certain species of venomous snakes, pesticides, certain industrial cleaning solvents, fuels and certain naturally occurring substances. Symptoms may appear immediately after exposure or be delayed. They may include limb weakness or numbness, loss of memory, vision, and/or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |