|
Tebuthiuron
Tebuthiuron is a nonselective broad spectrum herbicide of the urea class. It is used to control weeds, woody and herbaceous plants, and sugar cane. It is absorbed by the roots and transported to the leaves, where it inhibits photosynthesis. The ingredient was discovered by Air Products and Chemicals, but was registered by Elanco in the United States in 1974, and later sold to Dow AgroSciences. Environmental impacts The Environmental Protection Agency considers tebuthiuron to have a great potential for groundwater contamination, due to its high water solubility, low adsorption to soil particles, and high persistence in soil (its soil half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay. Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to: Film * Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang * ''Half Life: ... is 360 days). In Europe, tebuthiuron has been banned since November 2002. Applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auburn Tigers
The Auburn Tigers are the athletic teams representing Auburn University, a public four-year university located in Auburn, Alabama, United States. The Auburn Tigers compete in Division I of the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) as a member of the Southeastern Conference (SEC). Sports sponsored Auburn sponsors 21 varsity teams in 15 sports and competes in the Southeastern Conference. Football Auburn claims five national championships: 1913 (chosen by one selector in 1999), 1957, 1983, 1993 (one of four co-champions by one selector), and 2010. Three Auburn players, Pat Sullivan in 1971, Bo Jackson in 1985, and Cam Newton in 2010 have won the Heisman Trophy. The Trophy's namesake, John Heisman, coached at Auburn from 1895 until 1899. Auburn is the only school that Heisman coached at (among others, Georgia Tech and Clemson) that has produced a Heisman Trophy winner. Auburn's Jordan–Hare Stadium has a capacity of 87,451 ranking as the tenth-largest on-camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society and professional association in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 49,000 in the world. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing and Shanghai, People' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid (the ''absorbate'') is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid (the ''absorbent''). While adsorption does often precede absorption, which involves the transfer of the absorbate into the volume of the absorbent material, alternatively, adsorption is distinctly a surface phenomenon, wherein the adsorbate does not penetrate through the material surface and into the bulk of the adsorbent. The term '' sorption'' encompasses both adsorption and absorption, and ''desorption'' is the reverse of sorption. Like surface tension, adsorption is a consequence of surface energy. In a bulk material, all the bonding requirements (be they ionic, covalent or metallic) of the constituent atoms of the material are fulfilled by other atoms in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureas
image:Biotin_structure.svg, 220 px, Biotin, a water-soluble B vitamins, B vitamin, is a bicyclic urea. In chemistry, ureas are a class of organic compounds with the formula (R2N)2CO where R = H, alkyl, aryl, etc. Thus, in addition to describing the specific chemical compound urea ((H2N)2CO), urea is the name of a functional group that is found in many compounds and materials of both practical and theoretical interest. Generally ureas are colorless crystalline solids, which, owing to the presence of fewer hydrogen bonds, exhibit melting points lower than that of urea itself. Synthesis Ureas can be prepared many methods, but rarely by direct carbonation, which is the route to urea itself. Instead, methods can be classified according those that assemble the urea functionality and those that start with preformed urea. Assembly of N-substituted urea functionality Phosgenation entails the reaction of amines with phosgene, proceeding via the isocyanate (or carbamoyl chloride) as an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiadiazoles
In chemistry, thiadiazoles are a sub-family of azole compounds, with the name ''thiadiazole'' originating from the Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature. Structurally, they are five-membered heterocyclic compounds containing one sulfur and two nitrogen atoms. The ring is Aromaticity, aromatic by virtue of the two double bonds and one of the lone pairs of electrons of sulfur. Four constitutional isomers are possible, differing by the relative positions of the sulfur and nitrogen atoms. The nomenclature thus includes the locations of each of those three atoms, with the first of the three numbers referring to the sulfur. The parent compounds are rarely synthesized and possess no particular application, however, compounds bearing them as a structural motif are fairly common in pharmacology. Of them, 1,3,4-thiadiazole is the most common, appearing in such medications as cephazolin and acetazolamide. 3,4-Dichloro-1,2,5-thiadiazole arises readily from cyanogen. In the Hurd–Mori reaction, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicides
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page for EPA reports on pesticide use ihere Selective herbicides control specific weed species while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides (sometimes called "total weed killers") kill plants indiscriminately. The combined effects of herbicides, nitrogen fertilizer, and improved cultivars has increased yields (per acre) of major crops by three to six times from 1900 to 2000. In the United States in 2012, about 91% of all herbicide usage, was determined by weight applied, in agriculture. In 2012, world pesticide expenditures totaled nearly US$24.7 billion; herbicides were about 44% of those sales and constituted the biggest portion, followed by insecticides, fungicides, and fumigants. Herbicide is also used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camden, Maine
Camden is a town in Knox County, Maine, United States. The population was 5,232 at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census. The population of the town more than triples during the summer months, due to tourists and summer residents. Camden is a summer colony in the Mid-Coast region of Maine. Similar to Bar Harbor, Nantucket and North Haven, Maine, North Haven, Camden is well known for its summer community of wealthy Northeastern United States, Northeasterners, mostly from Boston, New York City, and Philadelphia. History Penobscot people, The Penobscot Nation have lived in the area for thousands of years. They called it Megunticook, meaning "great swells of the sea", a reference to the silhouette of the Camden Hills (more visibly seen on a bright night). Although part of the Waldo Patent, Europeans did not attempt to colonize it until after the French and Indian War, around 1771–1772. They were led by James Richards, who built a home at the mouth of the Megunticook River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Bowl
The Alabama–Auburn football rivalry, better known as the Iron Bowl, is an American college football rivalry game between the University of Alabama Crimson Tide and the Auburn University Tigers, both charter members of the Southeastern Conference (SEC) and both teams are located in the state of Alabama. The series is considered one of the most important rivalries in American sports. The rivalry, which started in 1893 and has been renewed annually since 1948, was played for many years at Legion Field in Birmingham, Alabama. In the early 20th Century, Birmingham was the leading industrial city of the South, rivaling Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, in the production of pig iron, coke, coal and the manufacture of steel. Thus, the term "Iron Bowl" came to represent the rivalry. Auburn Coach Ralph "Shug" Jordan is credited with actually coining it—when asked by reporters in 1964 how he would deal with the disappointment of not taking his team to a bowl game, he responded, "We've ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Group 5 Herbicides
Group 5 is a category of the HRAC classification system by herbicidal mode of action In pharmacology and biochemistry, mode of action (MoA) describes a functional or anatomical change, resulting from the exposure of a living organism to a substance. In comparison, a mechanism of action (MOA) describes such changes at the molecul .... It is equivalent to Group C (Australia) and Groups C1 and C2 (Global). Note, the classification was changed slightly. Group C (Aus) and Group C2 (Global) herbicides may actually be Group 7. Herbicides by numeric HRAC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HRAC Classification
The Herbicide Resistance Action Committee (HRAC) classifies herbicides by their mode of action (MoA) to provide a uniform way for farmers and growers to identify the agents they use and better manage pesticide resistance around the world. It is run by CropLife International in conjunction with the Weed Science Society of America (WSSA). Resistance overview A weed that develops resistance to one herbicide typically has resistance to other herbicides with the same mode of action (MoA), so herbicides with different MoAs, or different resistance groups, are needed. Preventative weed resistance management rotates herbicide types to prevent selective breeding of resistance to the same mode of action. By rotating MoAs, successive generations gain no advantage from any resistant mutations of the last generation. ''Cross-resistant'' and ''multiply resistant'' weeds resist multiple MoAs, and are particularly difficult to control. There is limited evidence of resistance undoing other res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
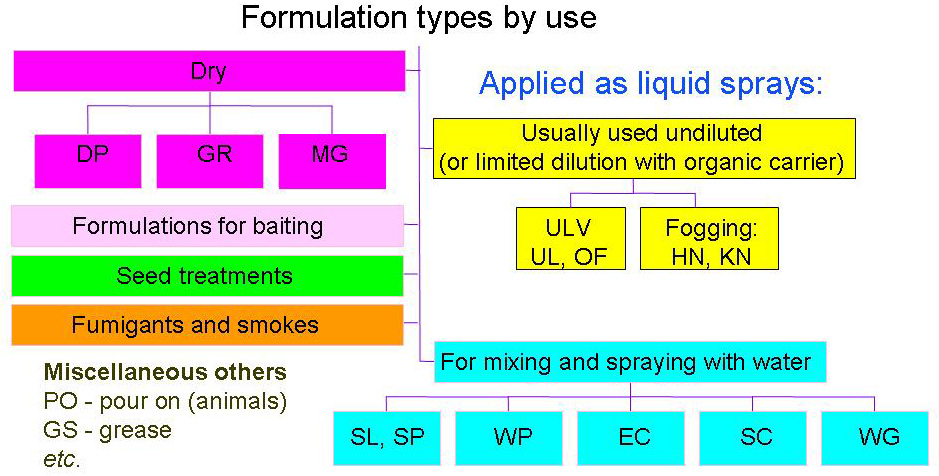
Pesticide Formulation
The biological activity of a pesticide, be it chemical or biological in nature, is determined by its active ingredient (AI - also called the ''active substance''). Pesticide products very rarely consist of the pure active ingredient. The AI is usually formulated with other materials (adjuvents and co-formulants) and this is the product as sold, but it may be further diluted in use. Formulations improve the properties of a chemical for handling, storage, application and may substantially influence effectiveness and safety. Formulation terminology follows a 2-letter convention: (''e.g.'' GR: granules) listed by CropLife International (formerly GIFAP then GCPF) in the ''Catalogue of Pesticide Formulation Types'' (Monograph 2); see download page Some manufacturers do not follow these industry standards, which can cause confusion for users. Water-miscible formulations By far the most frequently used products are formulations for mixing with water then applying as sprays. Water miscibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Half-life
Biological half-life (elimination half-life, pharmacological half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a drug, biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration (chemistry), concentration (Cmax (pharmacology), Cmax) to half of Cmax in the blood plasma. It is denoted by the abbreviation t_. This is used to measure the removal of things such as metabolites, drugs, and signalling molecules from the body. Typically, the biological half-life refers to the body's natural detoxification (cleansing) through liver metabolism and through the excretion of the measured substance through the kidneys and intestines. This concept is used when the rate of removal is roughly Exponential function, exponential. In a medical context, half-life explicitly describes the time it takes for the blood plasma concentration of a substance to halve (''plasma half-life'') its steady-state when circulating in the full blood of an organism. This measurement is usefu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |