|
Tear-drop Hull
A teardrop hull is a submarine hull design which emphasizes submerged performance over surfaced performance. It was somewhat commonly used in the early stages of submarine development, but was gradually abandoned in the early 20th century in favour of designs optimized for high performance on the surface as a result of changes in operational doctrine. Although naval doctrine changed, design practices remained until the later parts of World War II when the German Kriegsmarine suffered ever-growing losses of submarines in the Battle of the Atlantic. In an attempt to combat the growing threat of allied anti-submarine efforts, experimental design concepts dating back to the late interbellum were shoehorned into the existing submarine design process, resulting in a small number of hydrogen peroxide-powered submarines as well as the Elektroboot family of diesel-electric submarine classes. Although too late and too few to turn the war around, examination of these boats in the immedia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Hull
A submarine hull has two major components, the ''light hull'' and the ''pressure hull''. The light hull (''casing'' in British usage) of a submarine is the outer non-watertight hull which provides a hydrodynamically efficient shape. The pressure hull is the inner hull of a submarine that maintains structural integrity with the difference between outside and inside pressure at depth. Shapes Modern submarines are usually cigar-shaped. This design, already visible on very early submarines, is called a "teardrop hull". It is structurally efficient for withstanding external pressure, and significantly reduces the hydrodynamic drag on the sub when submerged, but decreases the sea-keeping capabilities and increases drag while surfaced. History The concept of an outer hydrodynamically streamlined light hull separated from the inner pressure hull was first introduced in the early pioneering submarine Ictineo I designed by the Spanish inventor Narcís Monturiol in 1859. However, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Submarine V-80
The V-80 (german: Versuchs-U-Boot V 80) was a 76-ton experimental submarine and the only representative of the German Type V design produced for Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine''. The prototype was completed in 1940 in Friedrich Krupp Germaniawerft in Kiel. The four-man vessel was designed to test the Walter hydrogen peroxide-based turbine propulsion system. Its range was at . The only earlier attempt to use a chemical reaction based air-independent propulsion system was in the Spanish submarine the '' Ictineo II''. This midget submarine led to the design of the German Type XVII submarine. Gallery File:German_v80_midget_submarine1.jpg, ''V-80'' midget submarine during sea trials, World War II File:German_v80_midget_submarine2.jpg, ''V-80'' schematic See also * History of submarines * List of U-boat types List of U-boat types contains lists of the German U-boat types ( submarine classes) used in World War I and World War II. The anglicized word ''U-boat'' is usually only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whiskey-class Submarine
Whiskey-class submarines (known in the Soviet Union as List of ships of Russia by project number, Projects 613, 640, 644, and 665) are a class of diesel-electric attack submarines that the Soviet Union built in the early Cold War period. Design The initial design was developed in the early 1940s as a sea-going follow on to the Soviet S-class submarine, S-class submarine. As a result of war experience and the capture of German technology at the end of the war, the Soviets issued a new design requirement in 1946. The revised design was developed by the Lazurit Design Bureau based in Gorkiy. Like most conventional submarines designed 1946–1960, the design was heavily influenced by the Type XXI submarine, Type XXI U-boat. Patrol variants Between 1949 and 1958 a total of 236 of an envisaged 340 submarines of this type were commissioned into the Soviet Navy. The vessels were initially designed as coastal patrol submarines. These patrol variants are known in the west as Whiskey I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
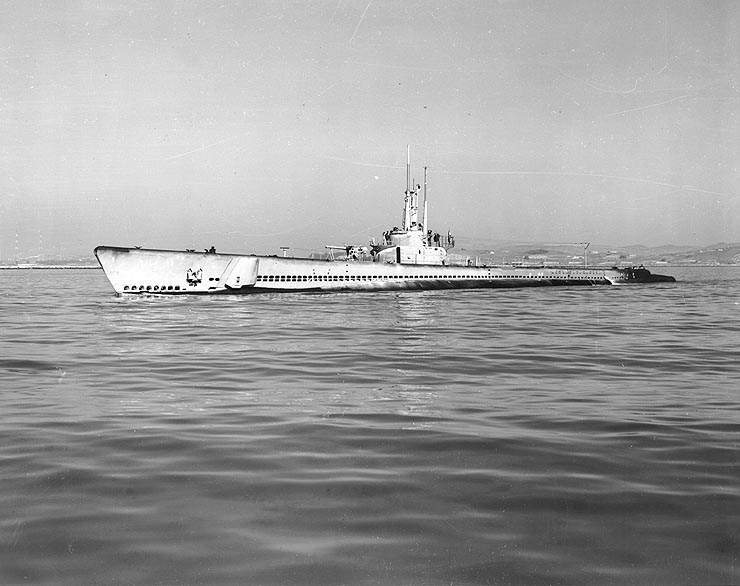
Tench-class Submarine
''Tench''-class submarines were a type of submarine built for the United States Navy (USN) between 1944 and 1951. They were an improvement over the and es, only about 35 to 40 tons larger, but more strongly built and with a slightly improved internal layout. One of the ballast tanks was converted to carry fuel, increasing range from to . This improvement was also made on some boats of the previous two classes.Friedman through 1945, pp. 209, 351 Further improvements were made beginning with SS-435, which are sometimes referred to as the ''Corsair'' class. Initial plans called for 80 to be built, but 51 were cancelled in 1944 and 1945 when it became apparent that they would not be needed to defeat Japan. The remaining 29 were commissioned between October 1944 (''Tench'') and February 1951 (''Grenadier''). The last submarine of the ''Tench'' class, as well as the last submarine which served during World War II, remaining in service with the U.S. Navy was USS ''Tigrone'' (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The May Incident
Andrew Jackson May (June 24, 1875 – September 6, 1959) was a Kentucky attorney, an influential New Deal-era politician, and chairman of the House Military Affairs Committee during World War II, infamous for his rash disclosure of classified naval information that may have resulted in the loss of 10 American submarines and 800 sailors, and his subsequent unrelated conviction for bribery. May was a Democratic member of United States House of Representatives from Kentucky during the 72nd to 79th sessions of Congress.Biographical Directory of the United States Congress: Andrew Jackson May URL accessed 2008-02-14. Education and early career May was born on Beaver Creek, near[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type XXI Submarine
Type XXI submarines were a class of German diesel–electric ''Elektroboot'' (German: "electric boat") submarines designed during the Second World War. One hundred and eighteen were completed, with four being combat-ready. During the war only two were put into active service and went on patrols, but these were not used in combat. They were the first submarines designed to operate primarily submerged, rather than spending most of their time as surface ships that could submerge for brief periods as a means of escaping detection. They incorporated many batteries to increase the time they could spend submerged, to as much as several days, and they only needed to surface to periscope depth for recharging via a snorkel. The design included many general improvements as well: much greater underwater speed by an improved hull design, greatly improved diving times, power-assisted torpedo reloading and greatly improved crew accommodations. However, the design was also flawed in many ways, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballast Tank
A ballast tank is a compartment within a boat, ship or other floating structure that holds water, which is used as ballast to provide hydrostatic stability for a vessel, to reduce or control buoyancy, as in a submarine, to correct trim or list, to provide a more even load distribution along the hull to reduce structural hogging or sagging stresses, or to increase draft, as in a semi-submersible vessel or platform, or a SWATH, to improve seakeeping. Using water in a tank provides easier weight adjustment than the stone or iron ballast used in older vessels, and makes it easy for the crew to reduce a vessel's draft when it enters shallower water, by temporarily pumping out ballast. Airships use ballast tanks mainly to control buoyancy and correct trim. History The basic concept behind the ballast tank can be seen in many forms of aquatic life, such as the blowfish or argonaut octopus. The concept has been invented and reinvented many times by humans to serve a variety of purpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Hull
A submarine hull has two major components, the ''light hull'' and the ''pressure hull''. The light hull (''casing'' in British usage) of a submarine is the outer non-watertight hull which provides a hydrodynamically efficient shape. The pressure hull is the inner hull of a submarine that maintains structural integrity with the difference between outside and inside pressure at depth. Shapes Modern submarines are usually cigar-shaped. This design, already visible on very early submarines, is called a "teardrop hull". It is structurally efficient for withstanding external pressure, and significantly reduces the hydrodynamic drag on the sub when submerged, but decreases the sea-keeping capabilities and increases drag while surfaced. History The concept of an outer hydrodynamically streamlined light hull separated from the inner pressure hull was first introduced in the early pioneering submarine Ictineo I designed by the Spanish inventor Narcís Monturiol in 1859. However, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type VII Submarine
Type VII U-boats were the most common type of German World War II U-boat. 703 boats were built by the end of the war. The lone surviving example, , is on display at the Laboe Naval Memorial located in Laboe, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Conception and production The Type VII was based on earlier German submarine designs going back to the World War I Type UB III and especially the cancelled Type UG. The type UG was designed through the Dutch dummy company ''NV Ingenieurskantoor voor Scheepsbouw Den Haag'' (I.v.S) to circumvent the limitations of the Treaty of Versailles, and was built by foreign shipyards. The Finnish ''Vetehinen'' class and Spanish Type E-1 also provided some of the basis for the Type VII design. These designs led to the Type VII along with Type I, the latter being built in AG Weser shipyard in Bremen, Germany. The production of Type I was stopped after only two boats; the reasons for this are not certain. The design of the Type I was further used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleet Submarine
A fleet submarine is a submarine with the speed, range, and endurance to operate as part of a navy's battle fleet. Examples of fleet submarines are the British First World War era K class and the American World War II era ''Gato'' class. The term has survived in Britain to refer to modern nuclear-powered attack submarines. In the United States Navy, the term came to be used primarily for the long-range submarines that served in World War II. Examples United States The term was used by the United States Navy to distinguish submarines suitable for long range patrols in the Pacific Ocean from earlier classes such as the United States S-class submarines. The initial goal, pursued with frequent interruptions since the ''AA-1''-class (aka ''T''-class) launched 1918–19, was to produce a submarine with a surfaced speed of 21 knots to operate with the Standard-type battleships of the surface fleet. Most of the nine "V-boats" launched 1924-33 (''V-1'' through ''V-6'') were either a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balao-class Submarine
The ''Balao'' class was a successful design of United States Navy submarine used during World War II, and with 120 boats completed, the largest class of submarines in the United States Navy. An improvement on the earlier , the boats had slight internal differences. The most significant improvement was the use of thicker, higher yield strength steel in the pressure hull skins and frames, which increased their test depth to . ''Tang'' actually achieved a depth of during a test dive, and exceeded that test depth when taking on water in the forward torpedo room while evading a destroyer. Design The ''Balao''s were similar to the ''Gato''s, except they were modified to increase test depth from to . In late 1941, two of the Navy's leading submarine designers, Captain Andrew McKee and Commander Armand Morgan, met to explore increasing diving depth in a redesigned ''Gato''. A switch to a new High-Tensile Steel (HTS) alloy, combined with an increase in hull thickness from to , wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |