|
Te Mata Estate
Te Mata Estate is an independent, family-owned Hawke's Bay winery and New Zealand's oldest, in continuous operation since 1895. The winery produces everything on-premises at their Havelock Hills site near Havelock North, south of Napier. Established in the late 19th century by the Chambers family, the winery and original vineyards were the first to be heritage-protected, and is one of New Zealand's most highly regarded wineries. The winery and vineyards are run by the Buck family: John Buck , a former chairman of the Wine Institute of New Zealand and member of the New Zealand Wine Hall of Fame, as well as his three sons Jonathan, Nick and Tobias. Te Mata's flagship ''Coleraine'' wine is regarded by many as New Zealand's finest red wine, and is named after the Buck family's ancestral hometown in Northern Ireland. Te Mata Estate relies on its long-term senior management staff, a permanent vineyard crew and a team of hand-pickers led by senior viticulturist Larry Morgan, and the wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawke's Bay Wine Region
The Hawke's Bay wine region is New Zealand wine, New Zealand's oldest and second-largest wine-production region, on the east coast of the North Island. Production reached 41,000 tonnes in 2018 from of planted vines, representing 10.2% of total national production. Some of the oldest wineries still operating in New Zealand, including Te Mata Estate, Church Road, and Mission Estate, were established in the Hawke's Bay area in the late 19th century. Despite this, it was only established as a geographical indication (GI) in 2018. The GI protects any wine produced within the boundaries of the entire Hawke's Bay Region, but in practice the vineyards are chiefly concentrated in the plains and low hills surrounding the cities of Napier, New Zealand, Napier and Hastings, New Zealand, Hastings. Climate Wines Red wines made from Merlot blends and Syrah are consistently well reviewed. Varietal white wines from Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc, Pinot Gris and Viognier are also produced. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prumnopitys Taxifolia
''Prumnopitys taxifolia'', the mataī ( mi, mataī) or black pine, is an endemic New Zealand coniferous tree that grows on the North Island and South Island. It also occurs on Stewart Island/Rakiura (47 °S) but is uncommon there. It grows up to 40 m high, with a trunk up to 2 m diameter. The leaves are linear to sickle-shaped, 10–15 mm long and 1.5–2 mm broad. The seed cones are highly modified, reduced to a central stem 3–4 cm long bearing 1-6 scales, each scale maturing berry-like, 10–15 mm long, violet-purple with a soft edible pulp covering the single seed. The seeds are dispersed by the New Zealand pigeon (kererū), which eats the 'berries' and passes the seeds in its droppings. Classification The scientific name ''taxifolia'' derives from the resemblance of the leaves to those of the yew (''Taxus''). In the past the species, like the other species of ''Prumnopitys'', was often included in ''Podocarpus''; in this species under the name ''Podo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graves (wine Region)
Graves (, ''gravelly land'') is an important subregion of the Bordeaux wine region. Graves is situated on the left bank of the Garonne River, in the upstream part of the region, southeast of the city Bordeaux and stretches over . Graves is the only Bordeaux subregion which is famed for all three of Bordeaux' three main wine types—reds, dry whites and sweet wines—although red wines dominate the total production. Graves AOC is also the name of one ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) which covers most, but not all of the Graves subregion. The area encompasses villages including Sauternes, Pessac, Talence, Léognan, Martillac, Saint-Morillon, and Portets. The name Graves derives from its intensely gravelly soil.H. Johnson & J. Robinson ''The World Atlas of Wine'' pg 98 Mitchell Beazley Publishing 2005 The soil is the result of glaciers from the Ice Age, which also left white quartz deposits that can still be found in the soil of some of the top winemaking estates.K. MacN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
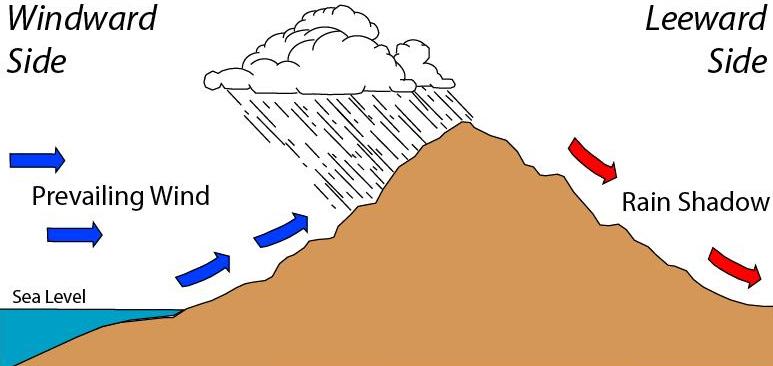
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is driven upslope towards the peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of dry climate region behind the mountain crests. This climate typically takes the form of shrub–steppe, xeric shrublands or even deserts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokotoko
A tokotoko is a traditional Māori carved ceremonial walking stick. On a marae it is a symbol of authority and status for the speaker holding it. Poets from New Zealand who win the award of New Zealand Poet Laureate are presented with a tokotoko, typically by a National Librarian of New Zealand. See also *Ruyi (scepter) * Talking stick *Cane Cane or caning may refer to: *Walking stick or walking cane, a device used primarily to aid walking * Assistive cane, a walking stick used as a mobility aid for better balance *White cane, a mobility or safety device used by many people who are ... References Māori culture {{Māori-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matahiwi Marae
Matahiwi is a farming community upriver from Whanganui, New Zealand, home to the Māori hapū known as Ngā Poutama of the iwi Te Āti Haunui-a-Pāpārangi. The township takes its name from the bush-clad ''puke'' (hill) on the western side of the Whanganui River, right above the local marae, whose name translates as "the face on the ridge" (''mata'', face; ''hiwi'', ridge). History and culture Early settlement The original settlement of Ngā Poutama was across the river at Hikurangi (also known as Poutama). In the 1840s it had a population of about 200. Hikurangi was renamed in 1850 with the biblical name Karatia (Galatia), often spelled Karatea. That settlement is now deserted; the ''urupa'' (burial ground) is still known as Hikurangi. The Kawana flour mill at Matahiwi was named in honour of Governor George Grey, who had donated the millstones as a personal gift to the Ngā Poutama people. It operated for over 50 years from 1854 and was restored in 1980. Matahiwi was a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Library Of New Zealand
The National Library of New Zealand ( mi, Te Puna Mātauranga o Aotearoa) is New Zealand's legal deposit library charged with the obligation to "enrich the cultural and economic life of New Zealand and its interchanges with other nations" (''National Library of New Zealand (Te Puna Mātauranga) Act 2003''). Under the Act, the library's duties include collection, preserving and protecting the collections of the National Library, significant history documents, and collaborating with other libraries in New Zealand and abroad. The library supports schools through its Services to Schools business unit, which has curriculum and advisory branches around New Zealand. The Legal Deposit Office is New Zealand's agency for ISBN and ISSN. The library headquarters is close to the Parliament of New Zealand and the Court of Appeal on the corner of Aitken and Molesworth Streets, Wellington. History Origins The National Library of New Zealand was formed in 1965 when the General Assembly Library ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Poet Laureate
The New Zealand Poet Laureate is a poet appointed by the National Library of New Zealand to represent New Zealand's community of poets, to promote and advocate for poetry, and to produce a number of published works during their two-year tenure as laureate. History of the award The Poet Laureate for New Zealand was not originally appointed by a government agency, but by a commercial company. The award was established by Te Mata Estate, a winery in Hawke's Bay, in 1997, the year of the winery's centenary. Bill Manhire was named the first Te Mata Poet Laureate. In 2007, the National Library of New Zealand took over the appointment of the Poet Laureate, and has appointed the last eight laureates: Michele Leggott, Cilla McQueen, Ian Wedde, Vincent O'Sullivan, C. K. Stead, Selina Tusitala Marsh, David Eggleton, and Chris Tse, 2022-2024. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamay
Gamay is a purple-colored grape variety used to make red wines, most notably grown in Beaujolais and in the Loire Valley around Tours. Its full name is Gamay Noir à Jus Blanc. It is a very old cultivar, mentioned as long ago as the 15th century. It has been often cultivated because it makes for abundant production; however, it can produce wines of distinction when planted on acidic soils, which help to soften the grape's naturally high acidity. History The Gamay grape is thought to have appeared first in the village of the Gamay, south of Beaune, in the 1360s. The grape brought relief to the village growers following the decline of the Black Death. In contrast to the Pinot noir variety, Gamay ripened two weeks earlier and was easier to cultivate. It also produced a strong, fruitier wine in a much larger abundance. In July 1395, the Duke of Burgundy Philippe the Bold outlawed the cultivation of the grape, referring to it as the "disloyal Gaamez" that in spite of its ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hastings, New Zealand
Hastings (; mi, Heretaunga) is an inland city of New Zealand and is one of the two major urban areas in Hawke's Bay, on the east coast of the North Island. The population of Hastings (including Flaxmere) is (as of with a further people in Havelock North and in Clive. Hastings is about 18 kilometres inland of the coastal city of Napier. These two neighbouring cities are often called "The Bay Cities" or "The Twin Cities". The city is the administrative centre of the Hastings District. Since the merger of the surrounding and satellite settlements, Hastings has grown to become one of the largest urban areas in Hawke's Bay. Hastings District is a food production region. The fertile Heretaunga Plains surrounding the city produce stone fruits, pome fruit, kiwifruit and vegetables, and the area is one of New Zealand's major red wine producers. Associated business include food processing, agricultural services, rural finance and freight. Hastings is the major service centre f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
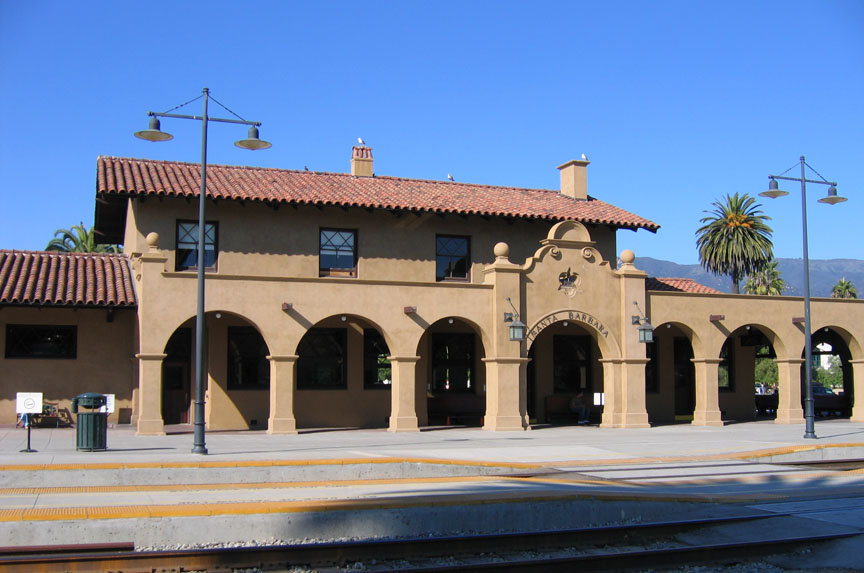
Mission Revival Architecture
The Mission Revival style was part of an architectural movement, beginning in the late 19th century, for the revival and reinterpretation of American colonial styles. Mission Revival drew inspiration from the late 18th and early 19th century Spanish missions in California. It is sometimes termed California Mission Revival, particularly when used elsewhere, such as in New Mexico and Texas which have their own unique regional architectural styles. In Australia, the style is known as Spanish Mission. The Mission Revival movement was most popular between 1890 and 1915, in numerous residential, commercial and institutional structures, particularly schools and railroad depots. Influences All of the 21 Franciscan Alta California missions (established 1769–1823), including their chapels and support structures, shared certain design characteristics. These commonalities arose because the Franciscan missionaries all came from the same places of previous service in Spain and colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920s and 1930s. Through styling and design of the exterior and interior of anything from large structures to small objects, including how people look (clothing, fashion and jewelry), Art Deco has influenced bridges, buildings (from skyscrapers to cinemas), ships, ocean liners, trains, cars, trucks, buses, furniture, and everyday objects like radios and vacuum cleaners. It got its name after the 1925 Exposition internationale des arts décoratifs et industriels modernes (International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts) held in Paris. Art Deco combined modern styles with fine craftsmanship and rich materials. During its heyday, it represented luxury, glamour, exuberance, and faith in socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_interior.jpg)