|
Tbx4
T-box refers to a group of transcription factors involved in embryonic limb and heart development. Every T-box protein has a relatively large DNA-binding domain, generally comprising about a third of the entire protein that is both necessary and sufficient for sequence-specific DNA binding. All members of the T-box gene family bind to the "T-box", a DNA consensus sequence of TCACACCT. Members T-boxes are especially important to the development of embryos, found in zebrafish oocyte by Bruce et al 2003 and ''Xenopus laevis'' oocyte by Xanthos et al 2001. They are also expressed in later stages, including adult mouse and rabbit studied by Szabo et al 2000. Mutations in the first one found caused short tails in mice, and thus the protein encoded was named brachyury, Greek for "short-tail". In mice this gene is named ''Tbxt'', and in humans it is named ''TBXT''. Brachyury has been found in all bilaterian animals that have been screened, and is also present in the cnidaria. The mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
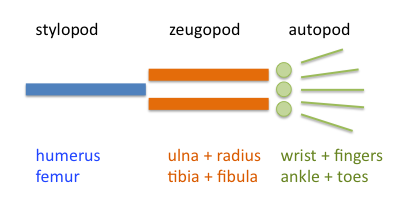
Limb Bud
The limb bud is a structure formed early in vertebrate limb development. As a result of interactions between the ectoderm and underlying mesoderm, formation occurs roughly around the fourth week of development. In the development of the human embryo the upper limb bud appears in the third week and the lower limb bud appears four days later. The limb bud consists of undifferentiated mesoderm cells that are sheathed in ectoderm. As a result of cell signaling interactions between the ectoderm and underlying mesoderm cells, formation of the developing limb bud occurs as mesenchymal cells from the lateral plate mesoderm and somites begin to proliferate to the point where they create a bulge under the ectodermal cells above. The mesoderm cells in the limb bud that come from the lateral plate mesoderm will eventually differentiate into the developing limb’s connective tissues, such as cartilage, bone, and tendon. Moreover, the mesoderm cells that come from the somites will eventually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limb Development
Limb development in vertebrates is an area of active research in both developmental and evolutionary biology, with much of the latter work focused on the transition from fin to limb. Limb formation begins in the morphogenetic limb field, as mesenchymal cells from the lateral plate mesoderm proliferate to the point that they cause the ectoderm above to bulge out, forming a limb bud. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) induces the formation of an organizer at the end of the limb bud, called the apical ectodermal ridge (AER), which guides further development and controls cell death. Programmed cell death is necessary to eliminate webbing between digits. The limb field is a region specified by expression of certain Hox genes, a subset of homeotic genes, and T-box transcription factors – Tbx5 for forelimb or wing development, and Tbx4 for leg or hindlimb development. Establishment of the forelimb field (but not hindlimb field) requires retinoic acid signaling in the developing trunk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TBX5 (gene)
T-box transcription factor TBX5, (T-box protein 5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TBX5'' gene. This gene is a member of a phylogenetically conserved family of genes that share a common DNA-binding domain, the T-box. T-box genes encode transcription factors involved in the regulation of developmental processes. This gene is closely linked to related family member T-box 3 (ulnar mammary syndrome) on human chromosome 12. ''TBX5'' is located on the long arm of chromosome 12. ''TBX5'' produces a protein called T-box protein 5 that acts as a transcription factor. ''TBX5'' is involved with forelimb and heart development. This gene impacts the early development of the forelimb by triggering fibroblast growth factor, FGF10. Function ''TBX5'' is involved with the development of the four heart chambers, the electrical conducting system, and the septum separating the right and left sides of the heart. ''TBX5'' is a transcription factor that codes for the protein called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TBX5
T-box transcription factor TBX5, (T-box protein 5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TBX5'' gene. This gene is a member of a phylogenetically conserved family of genes that share a common DNA-binding domain, the T-box. T-box genes encode transcription factors involved in the regulation of developmental processes. This gene is closely linked to related family member T-box 3 (ulnar mammary syndrome) on human chromosome 12. ''TBX5'' is located on the long arm of chromosome 12. ''TBX5'' produces a protein called T-box protein 5 that acts as a transcription factor. ''TBX5'' is involved with forelimb and heart development. This gene impacts the early development of the forelimb by triggering fibroblast growth factor, FGF10. Function ''TBX5'' is involved with the development of the four heart chambers, the electrical conducting system, and the septum separating the right and left sides of the heart. ''TBX5'' is a transcription factor that codes for the protein called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TBX4
T-box refers to a group of transcription factors involved in embryonic limb and heart development. Every T-box protein has a relatively large DNA-binding domain, generally comprising about a third of the entire protein that is both necessary and sufficient for sequence-specific DNA binding. All members of the T-box gene family bind to the "T-box", a DNA consensus sequence of TCACACCT. Members T-boxes are especially important to the development of embryos, found in zebrafish oocyte by Bruce et al 2003 and ''Xenopus laevis'' oocyte by Xanthos et al 2001. They are also expressed in later stages, including adult mouse and rabbit studied by Szabo et al 2000. Mutations in the first one found caused short tails in mice, and thus the protein encoded was named brachyury, Greek for "short-tail". In mice this gene is named ''Tbxt'', and in humans it is named ''TBXT''. Brachyury has been found in all bilaterian animals that have been screened, and is also present in the cnidaria. The mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Ectodermal Ridge
The apical ectodermal ridge (AER) is a structure that forms from the ectodermal cells at the distal end of each limb bud and acts as a major signaling center to ensure proper development of a limb. After the limb bud induces AER formation, the AER and limb mesenchyme—including the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA)—continue to communicate with each other to direct further limb development. The position of the limb bud, and hence the AER, is specified by the expression boundaries of Hox genes in the embryonic trunk. At these positions, the induction of cell outgrowth is thought to be mediated by a positive feedback loop of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) between the intermediate mesoderm, the lateral plate mesoderm and the surface ectoderm. FGF8 in the intermediate mesoderm signals to the lateral mesoderm, restricting the expression of FGF10 through intermediate Wnt signals. Then, FGF10 in the lateral plate mesoderm signals to the surface ectoderm to create the AER, which ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TBX3
T-box transcription factor TBX3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TBX3'' gene. T-box 3 (TBX3) is a member of the T-box gene family of transcription factors which all share a highly conserved DNA binding domain known as the T-box. The T-box gene family consists of 17 members in mouse and humans that are grouped into five subfamilies, namely Brachyury (T), T-brain (Tbr1), TBX1, TBX2, and TBX6. Tbx3 is a member of the Tbx2 subfamily which includes TBX2, Tbx2, Tbx4 and TBX5 (gene), Tbx5. The human TBX3 gene maps to chromosome 12 at position 12q23-24.1 and consists of 7 exons which encodes a 723 amino acid protein (ENSEMBL assembly release GRCh38.p12). Transcript splicing Alternative splicing, Alternative processing and splicing results in at least 4 distinct TBX3 Protein isoform, isoforms with TBX3 and TBX3+2a being the predominant isoforms. TBX3+2a results from alternative splicing of the second intron which leads to the addition of the +2a exon and consequently this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holt–Oram Syndrome
Holt–Oram syndrome (also called atrio-digital syndrome, atriodigital dysplasia, cardiac-limb syndrome, heart-hand syndrome type 1, HOS, ventriculo-radial syndrome) is an autosomal dominant disorder that affects bones in the arms and hands (the upper limbs) and often causes heart problems. The syndrome may include an absent radial bone in the forearm, an atrial septal defect in the heart, or heart block. It affects approximately 1 in 100,000 people. Presentation All people with Holt-Oram syndrome have, at least one, abnormal wrist bone, which can often only be detected by X-ray. Other bone abnormalities are associated with the syndrome. These vary widely in severity, and include a missing thumb, a thumb that looks like a finger, upper arm bones of unequal length or underdeveloped, partial or complete absence of bones in the forearm, and abnormalities in the collar bone or shoulder blade. Bone abnormalities may affect only one side of the body or both sides; if both sides ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpal Bones
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the wrist is to facilitate effective positioning of the hand and powerful use of the extensors and flexors of the forearm, and the mobility of individual carpal bones increase the freedom of movements at the wrist.Kingston 2000, pp 126-127 In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of bones in the wrist between the radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those of the metacarpus do. The corresponding part of the foot is the tarsus. The carpal bones allow the wrist to move and rotate vertically. Structure Bones The eight carpal bones may be conceptually organized as either two transverse rows, or three longitudinal columns. When c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zone Of Polarizing Activity
The zone of polarizing activity (ZPA) is an area of mesenchyme that contains signals which instruct the developing limb bud to form along the anterior/posterior axis. Limb bud is undifferentiated mesenchyme enclosed by an ectoderm covering. Eventually, the limb bud develops into bones, tendons, muscles and joints. Limb bud development relies not only on the ZPA, but also many different genes, signals, and a unique region of ectoderm called the apical ectodermal ridge (AER). Research by Saunders and Gasseling in 1948 identified the AER and its subsequent involvement in proximal distal outgrowth. Twenty years later, the same group did transplantation studies in chick limb bud and identified the ZPA. It wasn't until 1993 that Todt and Fallon showed that the AER and ZPA are dependent on each other. Patterning Patterning along the limb bud requires signals from many sources. Specifically, proteins called transcription factors (TF) help control the rate at which a gene is transcrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Septal Defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one common ventricle. The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes. The membranous portion, which is close to the atrioventricular node, is most commonly affected in adults and older children in the United States. It is also the type that will most commonly require surgical intervention, comprising over 80% of cases. Membranous ventricular septal defects are more common than muscular ventricular septal defects, and are the most common congenital cardiac anomaly. Signs and symptoms Ventricular septal defect is usually symptomless at birth. It usually manifests a few weeks after birth. VSD is an acyanotic congenital heart defect, aka a lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast Growth Factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by macrophages; they are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in their function lead to a range of developmental defects. These growth factors typically act as systemic or locally circulating molecules of extracellular origin that activate cell surface receptors. A defining property of FGFs is that they bind to heparin and to heparan sulfate. Thus, some are sequestered in the extracellular matrix of tissues that contains heparan sulfate proteoglycans and are released locally upon injury or tissue remodeling. Families In humans, 23 members of the FGF family have been identified, all of which are ''structurally'' related signaling molecules: * Members FGF1 through FGF10 all bind fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). FGF1 is also known as ''acidic fibroblast growth factor'', and FGF2 is also known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |