|
Taşköprü Family
The Taşköprü family is a Turkish family that rose to prominence in the Ottoman Empire for the important scholars, judges and artists it produced. Many important historians and teachers were born in this family. They were a center of ''ulama'', training other prominent scholars. Among the best known members of the family is Taşköprülüzade İsameddin Ahmed bin Mustafa, better known as Taşköprüzade, famous for his great biographic encyclopedia. Taşköprüzade's father, Muslih al-Din Mustafa, was a noted scholar, the teacher of the Ottoman Sultan Selim I. Muslih al-Din Mustafa was the director of a medrese in Taşköprü, from which fact his son's name was derived. Ahmet (Taşköprüzade) was trained by his father, and later completed his edcutation in Istanbul. While several members of them family became judges, they are said to have preferred to act as '' müderris''. They also made significant contributions in the fields of poetry, literature and calligraphy. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed The Conqueror
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Sultan Mehmed, links=no), was an Ottoman sultan who ruled from August 1444 to September 1446, and then later from February 1451 to May 1481. In Mehmed II's first reign, he defeated the crusade led by John Hunyadi after the Hungarian incursions into his country broke the conditions of the truce Peace of Szeged. When Mehmed II ascended the throne again in 1451, he strengthened the Ottoman navy and made preparations to attack Constantinople. At the age of 21, he conquered Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and brought an end to the Byzantine Empire. After the conquest Mehmed claimed the title Caesar of the Roman Empire ( ota, قیصر روم, Qayser-i Rûm, links=no), based on the fact that Constantinople had been the seat and capital of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayezid II
Bayezid II ( ota, بايزيد ثانى, Bāyezīd-i s̱ānī, 3 December 1447 – 26 May 1512, Turkish: ''II. Bayezid'') was the eldest son and successor of Mehmed II, ruling as Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1481 to 1512. During his reign, Bayezid II consolidated the Ottoman Empire and thwarted a Safavid rebellion soon before abdicating his throne to his son, Selim I. He evacuated Sephardi Jews from Spain after the proclamation of the Alhambra Decree, and resettled them throughout Ottoman lands, especially in Salonica. Early life Bayezid II was the son of Mehmed II (1432–1481) and Gülbahar Hatun, she is generally accepted as the real mother of Bayezid II. There are sources that claim that Bayezid was the son of Sittişah Hatun. This would make Ayşe Gülbahar Hatun a first cousin of Bayezid II. However, the marriage of Sittisah Hatun took place two years after Bayezid was born and the whole arrangement was not to Mehmed's liking. Born in Demotika, Bayezid II was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Üç Şerefeli Mosque
The Üç Şerefeli Mosque ( tr, Üç Şerefeli Camii) is a 15th-century Ottoman mosque in Edirne, Turkey. History The Üç Şerefeli Mosque was commissioned by Ottoman sultan Murad II (1421–1444,1446– 1451), and built between 1438 and 1447. It is located in the historical center of the city, close to the Selimiye Mosque and Old Mosque. The name refers to unusual minaret with three balconies ( tr, üç şerefeli). The architect of the mosque is not known. It is built of Burgaz limestone with a main dome that is 24 m in diameter. When first built the dome was the largest in any Ottoman building. The mosque was severely damaged by fire in 1732 and by an earthquake in 1748 but was repaired on the order of Mahmut I. The two blue and turquoise underglaze-painted tile panels in the tympana of the windows were probably produced by the same group of tilemakers who had decorated the Yeşil Mosque (1419–21) in Bursa where the tiles are signed as "the work of the masters of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimetoka
Didymoteicho ( el, Διδυμότειχο, Didymóteicho ) is a city located on the eastern edge of the Evros regional unit of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, in northeastern Greece. It is the seat of the municipality of the same name. The town (pop. 9,263 in 2011) sits on a plain and located south east of Svilengrad, south of Edirne, Turkey and Orestiada, west of Uzunköprü, Turkey, about 20 km north of Soufli and about 90 km north of Alexandroupoli. The municipality of Didymóteicho has a land area of 565.4 km² and a population of 19,493 inhabitants. Name "Didymoteicho" is the modern Greek form of , ''Didymóteichon'', from , ''dídymos'', "twin" and , ''teîchos'', "wall". The name first appears in 591/592, and most resulted from the refortification of the city under Justinian I (see below). The corrupted short form ''Dimotica'' or ''Demotica'' or variants thereof are attested in Western languages since the late 12th century (early forms ''Timoticon'', ''Dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skopje
Skopje ( , , ; mk, Скопје ; sq, Shkup) is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre. The territory of Skopje has been inhabited since at least 4000 BC; remains of Neolithic settlements have been found within the old Kale Fortress that overlooks the modern city centre. Originally a Paeonian city, Scupi became the capital of Dardania in the second century BC. On the eve of the 1st century AD, the settlement was seized by the Romans and became a military camp. When the Roman Empire was divided into eastern and western halves in 395 AD, Scupi came under Byzantine rule from Constantinople. During much of the early medieval period, the town was contested between the Byzantines and the Bulgarian Empire, whose capital it was between 972 and 992. From 1282, the town was part of the Serbian Empire, and acted as its capital city from 1346 to 1371. In 1392, Skopje was conquered by the Ottoman Turks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black". , motto = , image_map = , mapsize = , map_caption = , image_map1 = , mapsize1 = , map_caption1 = , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Asia#Syria Aleppo , pushpin_label_position = left , pushpin_relief = yes , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Aleppo in Syria , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_type2 = District , subdivision_type3 = Subdistrict , subdivision_name1 = Aleppo Governorate , subdivision_name2 = Mount Simeon (Jabal Semaan) , subdivision_name3 = Mount Simeon ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jannat Al-Mu'alla
Jannat al-Mu'alla ( ar, جَنَّة ٱلْمُعَلَّاة, Jannah al-Muʿallāh, lit=The Most Exalted Paradise), also known as the "Cemetery of Ma'la" ( ar, مَقْبَرَة ٱلْمَعْلَاة, link=no ') and ''Al-Ḥajūn'' ( ar, ٱلْحَجُوْن, link=no), is a cemetery to the north of ''Al-Masjid Al-Haram'', and near the Mosque of the Jinn in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. It is the place where the Islamic prophet Muhammad's wife, grandfather, and other ancestors are buried. History Many of Muhammad's relatives were buried in this cemetery before his Hijrah in 622. Many domes and structures have been built or rebuilt over known graves over the years. Tombs in this cemetery were demolished in 1925, the same year that the Jannat al-Baqi' cemetery in Medina was demolished by Saudi King, Ibn Saud. This happened despite protests by the international Islamic community. Some Shiites continue to mourn the day the House of Saud demolished shrines in Al-Baqi, which has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above sea level. Its last recorded population was 1,578,722 in 2015. Its estimated metro population in 2020 is 2.042million, making it the List of cities in Saudi Arabia by population, third-most populated city in Saudi Arabia after Riyadh and Jeddah. Pilgrims more than triple this number every year during the Pilgrimage#Islam, pilgrimage, observed in the twelfth Islamic calendar, Hijri month of . Mecca is generally considered "the fountainhead and cradle of Islam". Mecca is revered in Islam as the birthplace of the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. The Hira cave atop the ("Mountain of Light"), just outside the city, is where Muslims believe the Quran was first revealed to Muhammad. Vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
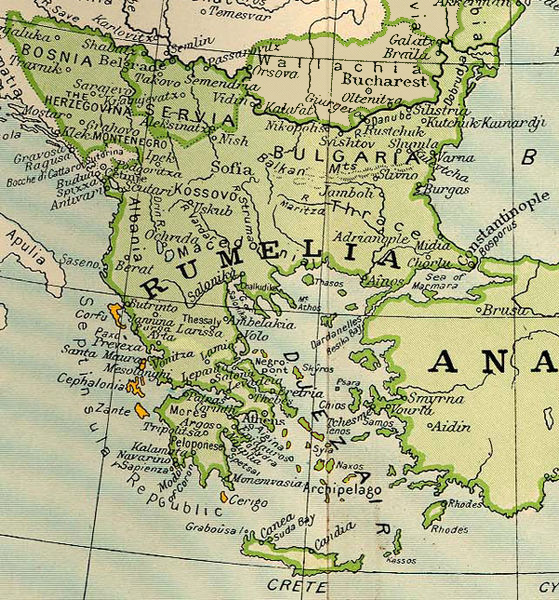
Rumelia
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Names of the Greeks#Romans (Ῥωμαῖοι), Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine Rite, Byzantine rite, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and Vassal state, vassals in Europe that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Ottoman Empire, Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish language, Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish language, Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheikh Hamdullah
Sheikh Hamdullah (1436–1520) ( tr, Şeyh Hamdullah), born in Amasya, Ottoman Empire, was a master of Islamic calligraphy. Life and work Sheikh Hamdullah was born in Amasya, a north-central town in Anatolia. His father, Mustafa Dede, was a Sheik of the Suhrawardi order, and had migrated from Bukhara (in present-day Uzbekistan) to Anatolia. In Amasya, he studied the six scripts under the tutelage of Hayreddin Mar'asi. He learned the traditional method of the old masters, but struggled to reproduce it. While studying, he met Bâyezïd, the son of Sultan Mehmed, the Conqueror who was a fellow student, and the pair became friends. When Bâyezïd assumed the throne in 1481, following his father's death, he invited his friend, Sheikh Hamdullah, to the capital, Istanbul. Hamdullah went on to become a master calligrapher at the Imperial Palace. In 1485, Bâyezïd II acquired seven works by the great calligrapher, Yaqut al-Musta'simi. Bâyezïd then encouraged his court calligrapher, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |