|
Taxation In Georgia (country)
Taxes in Georgia are collected on both state and local levels. The most important taxes are collected on national level, these taxes include an income tax, corporate taxes and value added tax. On local level property taxes as well as various fees are collected. There are 6 flat tax rates in Georgia - Corporate Profit Tax, Value Added Tax, Excise Tax, Personal Income Tax, Import Tax and Property Tax. Personal Income tax in Georgia are collected at a flat rate of 20% on local-source income. Foreign-source personal income is tax-exempt. However, the definition of "foreign-source" is widely mis-represented, and further reading of the tax code reveals that income from abroad, earned through active work (on a laptop, for example) while physically present in Georgia, would be considered ''Georgian-source'' even if said income was never remitted to Georgia or derives from a foreign source. Personal Income Tax for interest, dividend and royalty is 5%.There are few allowances deductible. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (country)
Georgia (, ; ) is a transcontinental country at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is part of the Caucasus region, bounded by the Black Sea to the west, by Russia to the north and northeast, by Turkey to the southwest, by Armenia to the south, and by Azerbaijan to the southeast. The country covers an area of , and has a population of 3.7 million people. Tbilisi is its capital as well as its largest city, home to roughly a third of the Georgian population. During the classical era, several independent kingdoms became established in what is now Georgia, such as Colchis and Iberia. In the early 4th century, ethnic Georgians officially adopted Christianity, which contributed to the spiritual and political unification of the early Georgian states. In the Middle Ages, the unified Kingdom of Georgia emerged and reached its Golden Age during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar in the 12th and early 13th centuries. Thereafter, the kingdom decl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income Tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Taxation rates may vary by type or characteristics of the taxpayer and the type of income. The tax rate may increase as taxable income increases (referred to as graduated or progressive tax rates). The tax imposed on companies is usually known as corporate tax and is commonly levied at a flat rate. Individual income is often taxed at progressive rates where the tax rate applied to each additional unit of income increases (e.g., the first $10,000 of income taxed at 0%, the next $10,000 taxed at 1%, etc.). Most jurisdictions exempt local charitable organizations from tax. Income from investments may be taxed at different (generally lower) rates than other types of income. Credits of various sorts may be allowed that reduce tax. Some jurisdicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate Taxes
A corporate tax, also called corporation tax or company tax, is a direct tax imposed on the income or capital of corporations or analogous legal entities. Many countries impose such taxes at the national level, and a similar tax may be imposed at state or local levels. The taxes may also be referred to as income tax or capital tax. A country's corporate tax may apply to: * corporations incorporated in the country, * corporations doing business in the country on income from that country, * foreign corporations who have a permanent establishment in the country, or * corporations deemed to be resident for tax purposes in the country. Company income subject to tax is often determined much like taxable income for individual taxpayers. Generally, the tax is imposed on net profits. In some jurisdictions, rules for taxing companies may differ significantly from rules for taxing individuals. Certain corporate acts or types of entities may be exempt from tax. The incidence of corpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
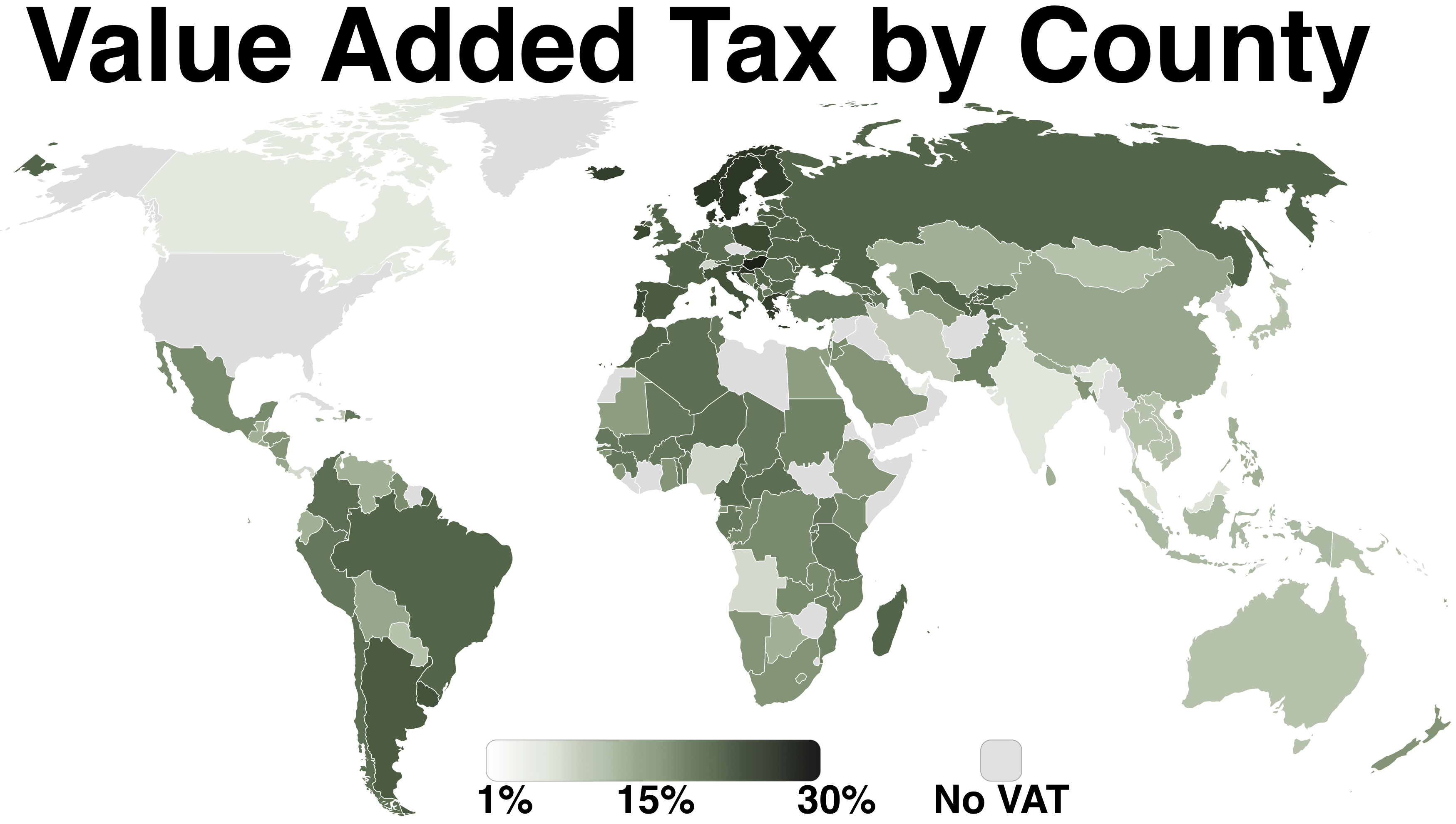
Value Added Tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end consumer. If the ultimate consumer is a business that collects and pays to the government VAT on its products or services, it can reclaim the tax paid. It is similar to, and is often compared with, a sales tax. VAT is an indirect tax because the person who ultimately bears the burden of the tax is not necessarily the same person as the one who pays the tax to the tax authorities. Not all localities require VAT to be charged, and exports are often exempt. VAT is usually implemented as a destination-based tax, where the tax rate is based on the location of the consumer and applied to the sales price. The terms VAT, GST, and the more general consumption tax are sometimes used interchangeably. VAT raises about a fifth of total tax revenues bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Property Taxes
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inheritance or gift and taxes on financial and capital transactions" (see: ), but this article only covers taxes on realty. The tax is levied by the governing authority of the jurisdiction in which the property is located. This can be a national government, a federated state, a county or geographical region or a municipality. Multiple jurisdictions may tax the same property. Often a property tax is levied on real estate. It may be imposed annually or at the time of a real estate transaction, such as in real estate transfer tax. This tax can be contrasted to a rent tax, which is based on rental income or imputed rent, and a land value tax, which is a levy on the value of land, excluding the value of buildings and other improvements. Under a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excise Tax
file:Lincoln Beer Stamp 1871.JPG, upright=1.2, 1871 U.S. Revenue stamp for 1/6 barrel of beer. Brewers would receive the stamp sheets, cut them into individual stamps, cancel them, and paste them over the Bunghole, bung of the beer barrel so when the barrel was tapped it would destroy the stamp. An excise, or excise tax, is any duty (economics), duty on manufactured goods (economics), goods that is levied at the moment of manufacture rather than at sale. Excises are often associated with customs duties, which are levied on pre-existing goods when they cross a designated border in a specific direction; customs are levied on goods that become taxable items at the ''border'', while excise is levied on goods that came into existence ''inland''. An excise is considered an indirect tax, meaning that the producer or seller who pays the levy to the government is expected to try to recover their loss by raising the price paid by the eventual buyer of the goods. Excises are typically imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Import Tax
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and policy that taxes foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. ''Protective tariffs'' are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import quotas and export quotas and other non-tariff barriers to trade. Tariffs can be fixed (a constant sum per unit of imported goods or a percentage of the price) or variable (the amount varies according to the price). Taxing imports means people are less likely to buy them as they become more expensive. The intention is that they buy local products instead, boosting their country's economy. Tariffs therefore provide an incentive to develop production and replace imports with domestic products. Tariffs are meant to reduce pressure from foreign competition and reduce the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Rate
A flat fee, also referred to as a flat rate or a linear rate refers to a pricing structure that charges a single fixed fee for a service, regardless of usage. Less commonly, the term may refer to a rate that does not vary with usage or time of use. Advantages * A business can develop a dependable stance in a market, as consumers have a well-rounded price before the service is undertaken. For instance, a technician may charge $150 for his labor. * Potential costs can be covered. The service may result in inevitable expenses like the parts needed to fix the issue or the items required to complete the order. * No restricted structure is needed, as the pricing system can be adjusted to suit the business using it. Management can thus work out the pricing that best matches the company's objectives, efforts, costs, etc. Disadvantages * The fixed pricing restricts the company's capability to meet the needs of individual consumers, and people search for cheaper alternatives. * Pricing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revenue
In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods and services related to the primary operations of the business. Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some companies receive revenue from interest, royalties, or other fees A fee is the price one pays as remuneration for rights or services. Fees usually allow for overhead (business), overhead, wages, costs, and Profit (accounting), markup. Traditionally, professionals in the United Kingdom (and previously the Repu .... This definition is based on International Accounting Standard, IAS 18. "Revenue" may refer to income in general, or it may refer to the amount, in a monetary unit, earned during a period of time, as in "Last year, Company X had revenue of $42 million". Profit (accounting), Profits or net income generally imply total revenue minus total expenses in a given period. In accountancy, accounting, in the balance statement, revenue is a subsection of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Deduction
Tax deduction is a reduction of income that is able to be taxed and is commonly a result of expenses, particularly those incurred to produce additional income. Tax deductions are a form of tax incentives, along with exemptions and tax credits. The difference between deductions, exemptions, and credits is that deductions and exemptions both reduce taxable income, while credits reduce tax. Above and below the line Above and below the line refers to items above or below adjusted gross income, which is item 37 on the tax year 2017 1040 tax form. Tax deductions above the line lessen adjusted gross income, while deductions below the line can only lessen taxable income if the aggregate of those deductions exceeds the standard deduction, which in tax year 2018 in the U.S., for example, was $12,000 for a single taxpayer and $24,000 for married couple. Limitations Often, deductions are subject to conditions, such as being allowed only for expenses incurred that produce current benefits. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Portfolio Investment
A foreign portfolio investment is a grouping of assets such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. Portfolio investments are held directly by an investor or managed by financial professionals. In economics, foreign portfolio investment is the entry of funds into a country where foreigners deposit money in a country's bank or make purchases in the country's stock and bond markets, sometimes for speculation. Synopsis Most foreign portfolio investments consist of securities and other foreign financial assets that are passively held by the foreign investor. This does not provide the foreign investor with direct ownership of the financial assets and can be relatively liquid depending on the volatility of the market that the investment takes place in. Foreign portfolio investments can be made by individuals, companies, or even governments in international countries. This type of investment is a way for investors to diversify their portfolio with an international advantage. Foreign po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxury Goods
In economics, a luxury good (or upmarket good) is a good for which demand increases more than what is proportional as income rises, so that expenditures on the good become a greater proportion of overall spending. Luxury goods are in contrast to necessity goods, where demand increases proportionally less than income. ''Luxury goods'' is often used synonymously with ''superior goods''. Definition The word "luxury" originated from the Latin word ''luxuria'', which means exuberance, excess, or abundance. A luxury good can be identified by comparing the demand for the good at one point in time against the demand for the good at a different point in time, at a different income level. When personal income increases, demand for luxury goods increases even more than income does. Conversely, when personal income decreases, demand for luxury goods drops even more than income does. For example, if income rises 1%, and the demand for a product rises 2%, then the product is a luxury good. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1950_-_2010.gif)

.png)
