|
Tau Piscium
Tau Piscium (τ Piscium) is an orange-hued star in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. With an apparent visual magnitude of +4.52, it is a dim star but visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 19.32 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 169 light years from the Sun. It is most likely (96% chance) a member of the thin disk population. This is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K0.5 IIIb. It is about 2.27 billion years and is a red clump star on the horizontal branch, which indicates it is generating energy through helium fusion at its core. The star has 1.7 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to about 10 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 45 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 4,624 K. Naming In Chinese, (), meaning ''Legs'', refers to an asterism consisting of τ Piscium, η Andromedae, 65 Piscium, ζ Andromedae, ε ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving the positions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium Fusion
The triple-alpha process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions by which three helium-4 nuclei (alpha particles) are transformed into carbon. Triple-alpha process in stars Helium accumulates in the cores of stars as a result of the proton–proton chain reaction and the carbon–nitrogen–oxygen cycle. Nuclear fusion reaction of two helium-4 nuclei produces beryllium-8, which is highly unstable, and decays back into smaller nuclei with a half-life of , unless within that time a third alpha particle fuses with the beryllium-8 nucleus to produce an excited resonance state of carbon-12, called the Hoyle state, which nearly always decays back into three alpha particles, but once in about 2421.3 times releases energy and changes into the stable base form of carbon-12. When a star runs out of hydrogen to fuse in its core, it begins to contract and heat up. If the central temperature rises to 108 K, six times hotter than the Sun's core, alpha particles can fuse fast enough to get ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
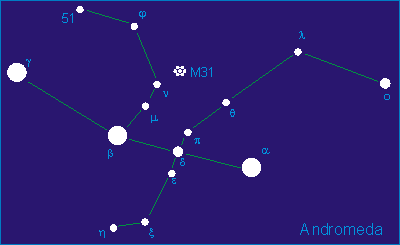
Delta Andromedae
Delta Andromedae, Latinized from δ Andromedae, is a triple star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. The system is visible to the naked eye as a point of light with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 3.28. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of approximately from the Sun. The system is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −10 km/s. In Chinese, (), meaning ''Legs (asterism)'', refers to an asterism consisting of δ Andromedae, η Andromedae, 65 Piscium, ζ Andromedae, ι Piscium, ε Andromedae, π Andromedae, ν Andromedae, μ Andromedae, β Andromedae, σ Piscium, τ Piscium, 91 Piscium, υ Piscium, φ Piscium, χ Piscium and ψ1 Piscium. Consequently, the Chinese name for δ Andromedae itself is (, en, the Fifth Star of Legs.) Apart from its Bayer designation, it was also given the title ''Delta'' by Elijah H. Burritt in his star atlas. This is a long-period spectroscopic binary with an orbital pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Andromedae
Epsilon Andromedae, Latinized from ε Andromedae, is a star in the constellation of Andromeda. It can be seen with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.4. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 21.04 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 155 light years from the Sun. The system is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −84 km/s. Its orbit in the Milky Way is highly eccentric, causing it to move rapidly relative to the Sun and its neighboring stars. Properties This is an evolved G-type giant star with a stellar classification of . The suffix notation indicates there is a strong underabundance of iron in the spectrum, and an overabundance of cyanogen (CN). ε Andromedae is believed to be a red clump star which is fusing helium in its core. It has about the same mass as the Sun, but has expanded to nine times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 51 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Andromedae
Zeta Andromedae (Zeta And, ζ Andromedae, ζ And) is a star system in the constellation Andromeda. It is approximately 189 light-years from Earth. Zeta Andromedae is the star's Bayer designation. It also has the Flamsteed designation 34 Andromedae and multiple other designations in stellar catalogues. Location The star's location is in the northern constellation Andromeda, in which it is the second-most southerly of the stars in this often drawn characteristic shape representing the mythical princess asterism, after η Andromedae. System The system is a spectroscopic binary whose is classified as an orange K-type giant with a mean apparent magnitude of +4.08. Due to brightness changes caused by the ellipsoidal shape of that object, the system is also an RS Canum Venaticorum-type variable star. Its brightness varies from magnitude +3.92 to +4.14 with a period of 17.77 days, and its spectrum shows strong and variable Ca II H and K lines. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
65 Piscium , Gobi 65, or Paneer 65
{{Numberdis ...
65 may refer to: * 65 (number) * ''65'' (film), an upcoming American science fiction thriller film * One of the years 65 BC, AD 65, 1965, 2065 * A type of dish in Indian cuisine, such as Chicken 65 Chicken 65 is a spicy, deep-fried chicken dish originating from Hotel Buhari, Chennai, India, as an entrée, or quick snack. The flavour of the dish can be attributed to red chillies, but the exact set of ingredients for the recipe can vary. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Andromedae
Eta Andromedae (Eta And, η Andromedae, η And) is a spectroscopic binary star in the constellation of Andromeda. It consists of two G-type subgiant or giant stars orbiting each other with a period of 115.7 days and has an overall apparent visual magnitude of approximately 4.403.The spectroscopic binary eta Andromedae: Determination of the orbit by optical interferometry, C. A. Hummel et al., ''Astronomical Journal'' 106, #6 (December 1993), pp. 2486–2492, , . History Eta Andromedae was discovered to be a double-lined spectroscopic binary in a series of spectra taken in 1899 and 1900. Its orbit was computed in 1946 from spectroscopic observations. Because spectroscopy only reveals the radial velocity of a star towards or away from the viewer, such a computation does not determine all orbital elements. In observations made from 1990 to 1992, Eta Andromedae was resolved interferometrically by the Mark III Stellar Interferometer at Mount Wilson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legs (Chinese Constellation)
The Legs mansion (奎宿, pinyin: Kuí Xiù) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the western mansions of the White Tiger. Cultural significance In East Asian cultures, the Legs mansion (Kuí Xiù) represents wisdom, scholarship and literature. A notable example is a structure known as "Kuiwen Pavilion" (奎文閣) in the many Confucius temples in China and other East Asian countries. Asterisms See also *Kui Xing Kui Xing (), originally called 奎星 (also ''kuí xīng''), also known as 大魁夫子 "Great Master Kui" or 大魁星君 "Great Kui the Star Lord", is a character in Chinese folk religion, Chinese religion, the Shen (Chinese religion), Deity of ... {{Chinese constellation Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature when the body's emissivity curve (as a function of wavelength) is not known. When the star's or planet's net emissivity in the relevant wavelength band is less than unity (less than that of a black body), the actual temperature of the body will be higher than the effective temperature. The net emissivity may be low due to surface or atmospheric properties, including greenhouse effect. Star The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per ''surface area'' () as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law . Notice that the total ( bolometric) luminosity of a star is then , where is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. The term itself is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos, photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it being a spherical surface that is perceived to emit light. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered. A photosphere is the deepest region of a luminous object, usually a star, that is transparent to photons of certain wavelengths. Temperature The surface of a star is defined to have a temperature given by the effective temperature in the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Stars, except neutron stars, have no solid or liquid surface. Therefore, the photosphere is typically used to describe the Sun's or another star's visual surface. Composition of the Sun The Sun is composed primari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun's Luminosity
The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal solar luminosity is defined by the International Astronomical Union to be . This does not include the solar neutrino luminosity, which would add , or , i.e. a total of (the mean energy of the solar photons is 26 MeV and that of the solar neutrinos 0.59 MeV, i.e. 2.27%; the Sun emits photons and as many neutrinos each second, of which per m2 reach the Earth each second). The Sun is a weakly variable star, and its actual luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle (sunspot cycle) that causes a quasi-periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Other variations over the last 200–300 years are thought to be much smaller than this. Determination Solar luminosity is related to solar irradiance (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |