|
Tasmanian Central Highlands Forests
The Tasmanian Central Highland forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in Australia. It covers Tasmania's Central Highlands region. Geography The Tasmanian Central Highland forests covers the Central Highlands, also known as the Central Plateau, of Tasmania. It is bounded on the west, northwest, and southwest by the humid Tasmanian temperate rain forests ecoregion, and on the northeast, east, and southeast by the drier Tasmanian temperate forests. Portions of the plateau were glaciated during the ice ages. Glaciers carved many depressions in the landscape, including Lake St. Clair and many smaller lakes and tarns. Climate The ecoregion has a temperate climate. It is Tasmania's coldest region, and temperatures often fall to or below freezing during the three to four winter months, often overnight. Snowfall is most common in the spring. Average annual precipitation is highest in the west, averaging up to 2,000 mm, and is lowest in the east in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake St Clair (Tasmania)
Lake St Clair or ''leeawulenna'' is a natural freshwater lake located in the Central Highlands area of Tasmania, Australia. The lake forms the southern end of the Cradle Mountain-Lake St Clair National Park. It has an area of approximately , and a maximum depth of , making it Australia's deepest lake. The lake is fed by Narcissus River, Cuvier River, and Hamilton Creek and marks the start of the River Derwent. The locality of Lake St Clair is in the local government areas of Central Highlands (24%), Meander Valley (12%), and West Coast (64%). The southern end of the lake is about north-west of the town of Hamilton. Geology Lake St Clair was formed through glacial erosion, along with the surrounding river valleys. History Lake St Clair is located on the edge of the Big River Tasmanian Aboriginal nation, and there is evidence that they hunted on the surrounding button grass plains. Numerous small quarries and campgrounds are located nearby, with the closest dated site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
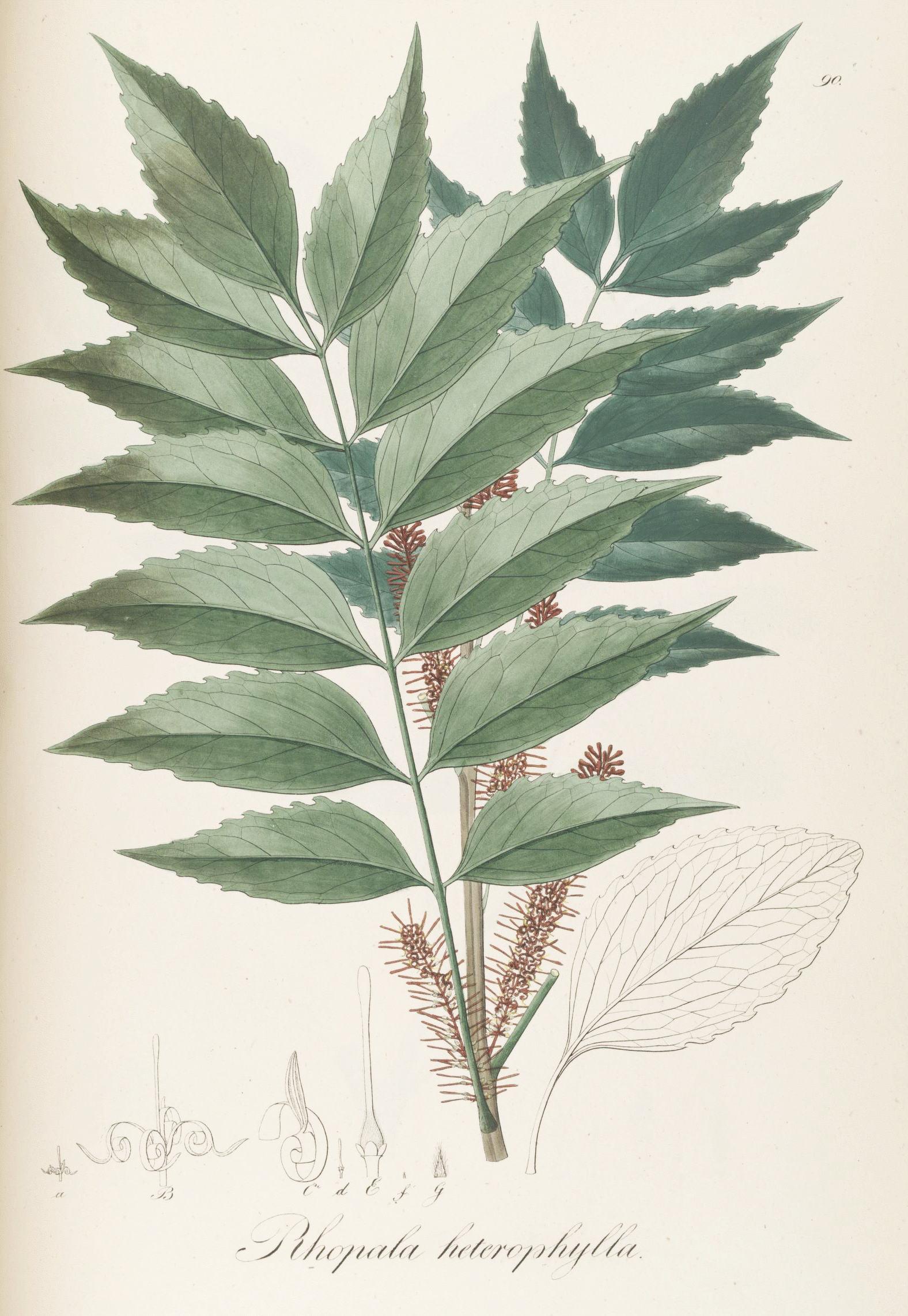
Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genera with about 1,660 known species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae, they make up the order Proteales. Well-known genera include ''Protea'', ''Banksia'', ''Embothrium'', ''Grevillea'', ''Hakea'' and ''Macadamia''. Species such as the New South Wales waratah (''Telopea speciosissima''), king protea (''Protea cynaroides''), and various species of ''Banksia'', ''soman'', and ''Leucadendron'' are popular cut flowers. The nuts of ''Macadamia integrifolia'' are widely grown commercially and consumed, as are those of Gevuina avellana on a smaller scale. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentrations of diversity. Etymology The name Proteaceae was adapted by Robert Brown from the name Proteae coined in 1789 for the family by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, based on the genus ''Protea'', which in 1767 Carl Linnaeus derived from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Wattlebird
The yellow wattlebird (''Anthochaera paradoxa'') is a species of bird in the honeyeater family Meliphagidae. Other names include the long wattlebird or Tasmanian wattlebird. Taxonomy French zoologist François Marie Daudin described the yellow wattlebird in 1800 as ''Corvus paradoxus''. The generic name ''Anthochaera'' derives from the Ancient Greek ''anthos'' 'flower, bloom' and ''khairō'' 'enjoy'. The specific epithet ''paradoxa'' derives from the Ancient Greek ''paradoxos'' meaning 'strange, extraordinary'. Description The yellow wattlebird is the largest of the honeyeaters, and is endemic to Tasmania. They are usually long. Body mass in males averages and in females averages , with the largest males weighing up to . They are named for the wattles hanging from the cheeks.Morcombe, Michael (2012) Field guide to Australian birds. Pascal Press, Glebe, NSW. Revised edition. Yellow wattlebirds are slim birds with a short, strong bill. They have a white face and black-streake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasmanian Thornbill
Tasmanian thornbill (''Acanthiza ewingii'') is a small bushland member of the Acanthizidae (Australian warbler) family, endemic to Tasmania and the Bass Strait Islands. It is a common bird in these regions and is often found occupying the colder, wetter portions of them. The brown thornbill (''Acanthiza pusilla'') will typically occupy the correspondingly drier portions of habitat."The Endemic Birds of Tasmania." Thomas, D.G. 1972. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 8 December 2006. Accessed: 18 July 2007. URL/ref> Description The Tasmanian thornbill is olive-brown above, darkening toward the back and tail, and can exhibit a patch of reddish-brown colouration on the forehead. The wings are dark grey with olive-brown edge lining. Grey on light grey scalloping is present from the chin to breast, with similar scalloping occurring on the sides of the head. The bill, feet, and legs are all dark grey and the eyes are distinctly large and dark, with red irises. It's long, thin, thorn- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasmanian Native Hen
The Tasmanian nativehen (''Tribonyx mortierii'') (palawa kani: piyura) (alternate spellings: Tasmanian native-hen or Tasmanian native hen) is a flightless rail and one of twelve species of birds endemic to the Australian island of Tasmania. Although many flightless birds have a history of extinction at the hands of humans, the species has actually benefited from the introduction of European-style agricultural practices in Tasmania. Its success may also be attributed to the recent extinction of its main predator, the thylacine. Nomenclature The species was originally described in 1840 as ''Tribonyx mortierii'' — the ''mortierii'' being in honour of Barthélemy Charles Joseph Dumortier. Local names include narkie, waterhen and turbo chook. The Palawa kani name for the nativehen is ''piyura'' and is derived from the extinct Paredarerme and Little Swanport languages. Description The Tasmanian nativehen is a stocky flightless bird between in length. The upperparts are olive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wedge-tailed Eagle
The wedge-tailed eagle (''Aquila audax'') is the largest bird of prey in the continent of Australia. It is also found in southern New Guinea to the north and is distributed as far south as the state of Tasmania. Adults of this species have long, broad wings, fully feathered legs, an unmistakable wedge-shaped tail, an elongated maxilla, a strong beak and powerful feet. The wedge-tailed eagle is one of 12 species of large, predominantly dark-coloured booted eagles in the genus '' Aquila'' found worldwide. Genetic research has clearly indicated that the wedge-tailed eagle is fairly closely-related to other, generally large members of the ''Aquila'' genus.Lerner, H., Christidis, L., Gamauf, A., Griffiths, C., Haring, E., Huddleston, C.J., Kabra, S., Kocum, A., Krosby, M., Kvaloy, K., Mindell, D., Rasmussen, P., Rov, N., Wadleigh, R., Wink, M. & Gjershaug, J.O. (2017). ''Phylogeny and new taxonomy of the Booted Eagles (Accipitriformes: Aquilinae)''. Zootaxa, 4216(4), 301–320. A lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
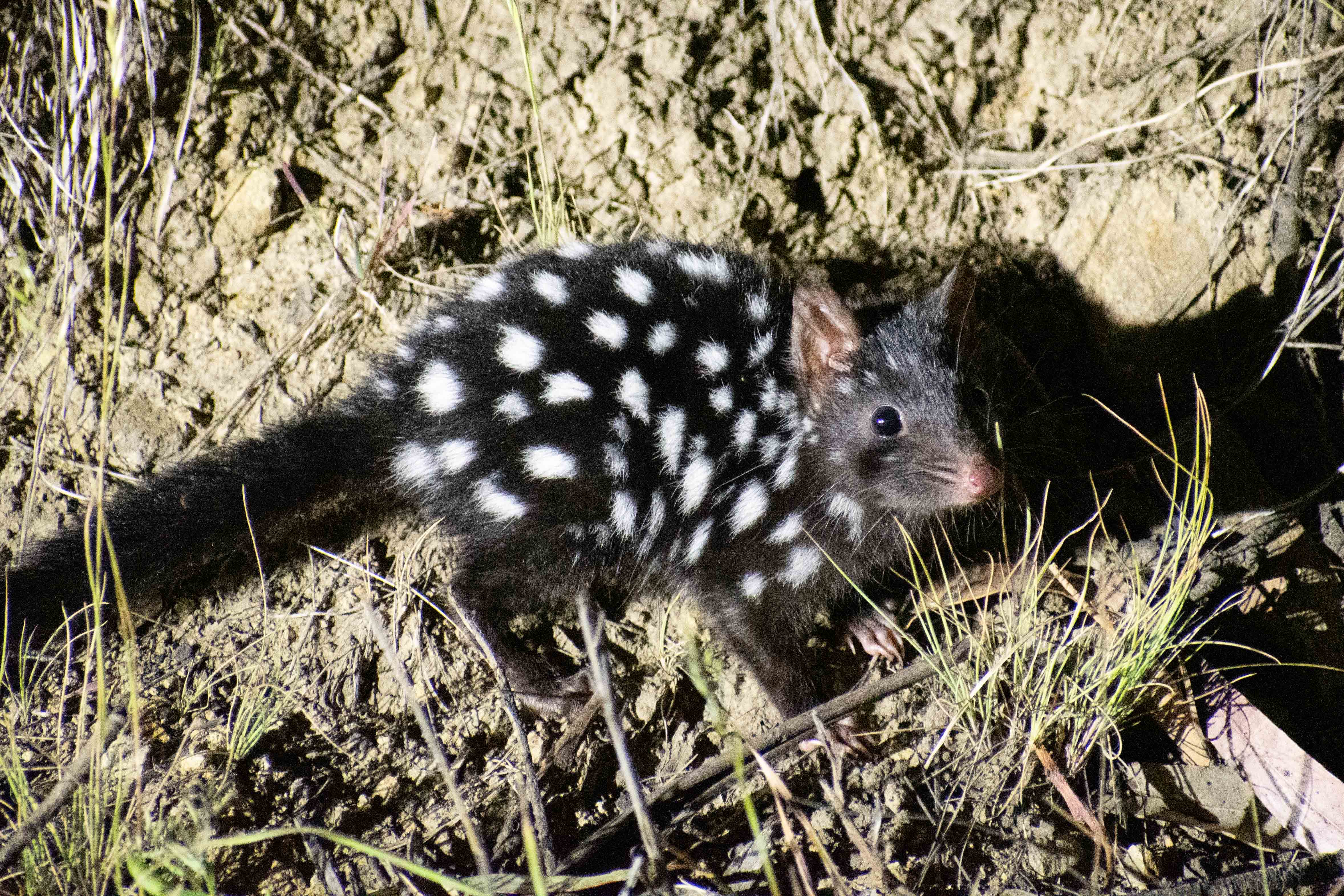
Eastern Quoll
The eastern quoll (''Dasyurus viverrinus'', formerly known as the eastern native cat) is a medium-sized carnivorous marsupial (dasyurid), and one of six extant species of quolls. Endemic to Australia, they occur on the island state of Tasmania, but were considered extinct on the mainland after 1963. The species has been reintroduced to fox-proof fenced sanctuaries Victoria in 2003 and to the Australian Capital Territory in 2016. Taxonomy The eastern quoll is a member of the family Dasyuridae, which includes most carnivorous marsupials. Its species name, ''viverrinus'', indicates it is "ferret-like". There are no recognised subspecies. Description Eastern quolls are about the size of a small domestic cat, with adult males measuring in total length, including the tail, and having an average weight of . Females are significantly smaller, measuring , including a tail, and weighing around . They have a tapering snout, short legs, and erect ears. They can be distinguished fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Barred Bandicoot
The eastern barred bandicoot (''Perameles gunnii'') is a nocturnal, rabbit-sized marsupial endemic to southeastern Australia, being native to the island of Tasmania and mainland Victoria. It is one of three surviving bandicoot species in the genus ''Perameles''. It is distinguishable from its partially-sympatric congener – the long-nosed bandicoot – via three or four dark horizontal bars found on its rump. In Tasmania, it is relatively abundant. The mainland population in Victoria is struggling and is subject to ongoing conservation endeavors. Description The eastern barred bandicoot weighs less than and has a short tail and three to four whitish bars across the rump. The Eastern barred bandicoot has two separated populations, one on the mainland of Australia and one on the island of Tasmania. The Tasmanian form is somewhat larger than the mainland form as the average adult mass is 750 g in Victoria and 1,000 g in Tasmania. It lives for just two to three years and is not g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
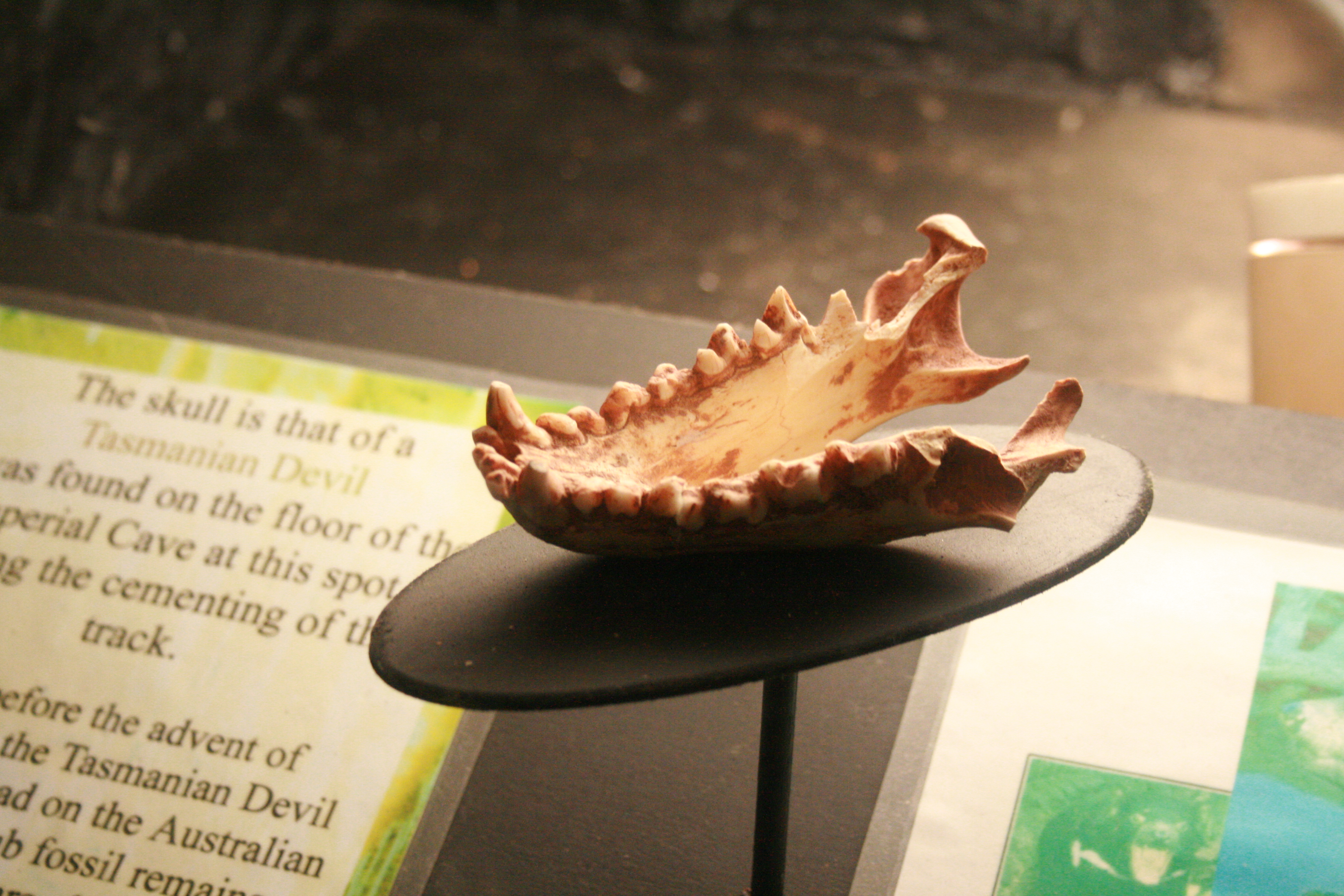
Tasmanian Devil
The Tasmanian devil (''Sarcophilus harrisii'') (palawa kani: purinina) is a carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae. Until recently, it was only found on the island state of Tasmania, but it has been reintroduced to New South Wales in mainland Australia, with a small breeding population. The size of a small dog, the Tasmanian devil became the largest carnivorous marsupial in the world following the extinction of the thylacine in 1936. It is related to quolls, and distantly related to the thylacine. It is characterised by its stocky and muscular build, black fur, pungent odour, extremely loud and disturbing screech, keen sense of smell, and ferocity when feeding. The Tasmanian devil's large head and neck allow it to generate among the strongest bites per unit body mass of any extant predatory land mammal. It hunts prey and scavenges on carrion. Although devils are usually solitary, they sometimes eat and defecate together in a communal location. Unlike most other da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
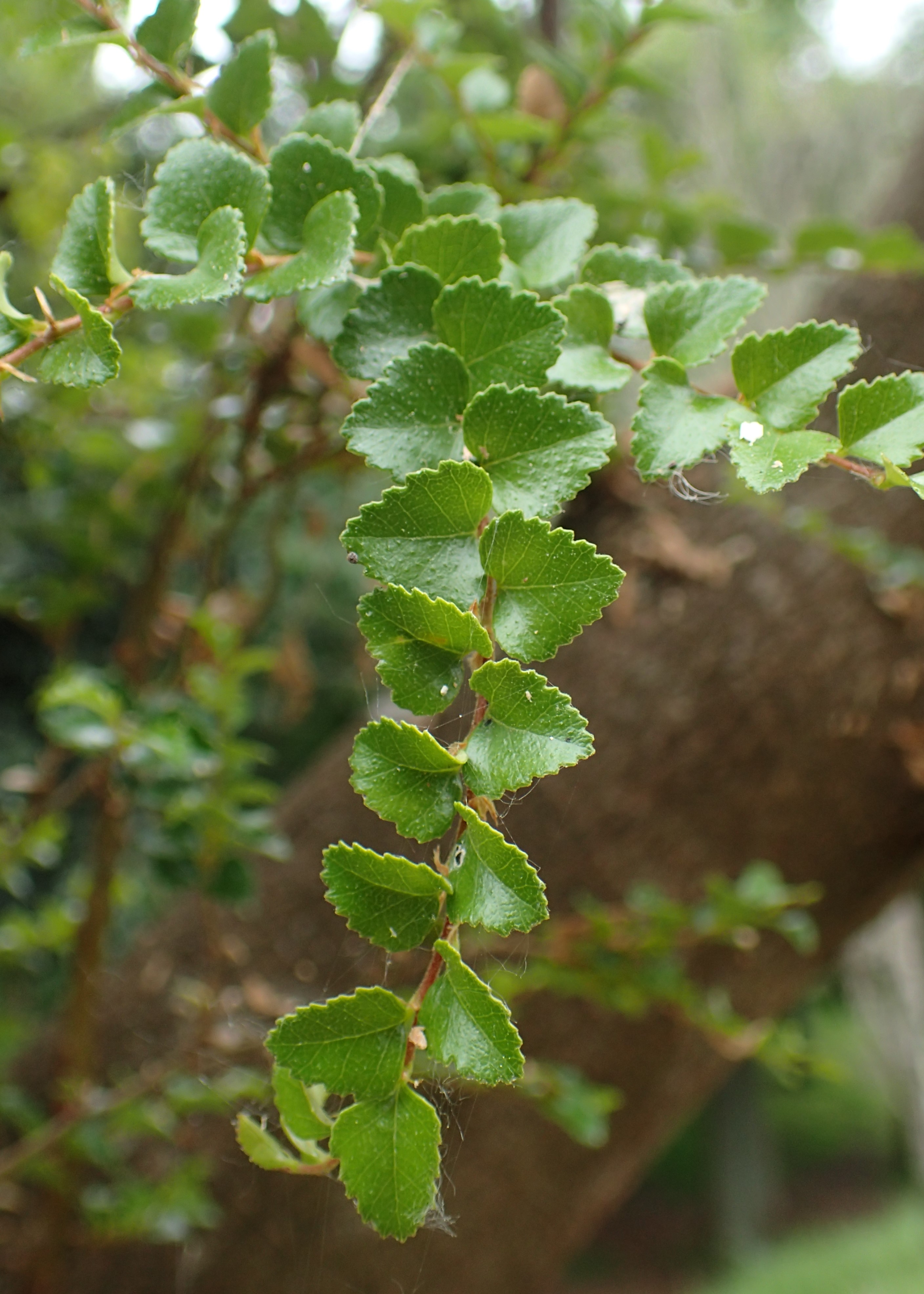
Nothofagus Gunnii
''Nothofagus gunnii'', the tanglefoot or deciduous beech, is a deciduous shrub or small tree endemic to the highlands of Tasmania, Australia. It was described in 1847 by R.C GunnReid, James B.; Hill, Robert S.; Brown, Michael J.; & Hovenden, Mark J. (2005) ''Vegetation of Tasmania''. Monotone art printers. ''N. gunnii'' is a small woody tree with a shrubby appearance known to grow up to . It lives only on mountains due to temperature limitations within the Tasmanian maritime climate and mainly grows at altitudes greater than above sea level. It grows in alpine and sub-alpine regions in the central portions of the island. Though capable of reaching the size of a small tree, it is most common as a thick shrub or woody ground cover, hence its common name of "tanglefoot". Taxonomy Joseph Dalton Hooker described the tanglefoot beech. Common names include tanglefoot or deciduous beech, or fagus,. The species is only distantly related to genus ''Fagus'', the beeches of the Northern Hem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothofagus Cunninghamii
''Nothofagus cunninghamii,'' commonly known as myrtle beech or Tasmanian myrtle, is the dominant species of cool temperate rainforests in Tasmania and Southern Victoria. It has low fire resistance and grows best in partial shade conditions. It has rough bark covered in mosses and epiphytic growth. Its leaves are triangular-shaped, small, and dark green with differentiated margins. It has white unisexual flowers. Description & Habit ''N. cunninghamii'' range from trees of up to 50 meters in protected rainforest valleys to low-growing alpine shrubs less than 1 m tall in exposed conditions. Maximum height is about 55 m. The leaves are simple and alternate, growing 0.5–1.5 cm long, and in Victoria up to 2 cm (0.8 in) long. The leaves are dark green, with new growth brilliant red, pink or orange in spring. They are triangular with irregular minute teeth with craspedodromous veins with all secondary veins terminate at leaf margins and spread from a central primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poa Gunnii
''Poa gunnii'' is a Aboriginal Tasmanians, Tasmanian endemic tussock grass considered one of the most abundant and common in alpine and subalpine environments from about 800 m to above 1400 m. However it can be found to near sea level in the south of the island state where a cooler climate is prevalent. The genus ''Poa'' belongs to the family Poaceae. Tasmania has 16 native and 6 introduced species of ''Poa''. Description ''Poa gunnii'' is a very variable species. The most common subalpine and alpine form is stunted but grows up to 20 cm high while forms of ''P. gunnii'' at lower altitudes towards sea level are usually taller to 70 cm high and with longer leaves. Leaf sheaths, green or purplish; leaves less than 1mm in diameter, hard, usually round in cross-section. Blades up to 30 cm long, inrolled or folded. Ligules up to 2mm long, firm with tiny hairs on their margins and backs. Flowering spikelets are broadly ovate to lanceolate, 2–6 flowered, green ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




