|
Taru Adjective
This article deals with Japanese equivalents of English adjectives. Types of adjective In Japanese, nouns and verbs can modify nouns, with nouns taking the 〜の particles when functioning attributively (in the genitive case), and verbs in the attributive form ( 連体形 ). These are considered separate classes of words, however. Most of the words that can be considered to be adjectives in Japanese fall into one of two categories – variants of verbs, and nouns: *adjectival verb (Japanese: 形容詞, ', literally 形容 "description" or "appearance" + 詞 "word"), or ''i''-adjectives :These can be considered specialized verbs, in that they inflect for various aspects such as past tense or negation, and they can be used predicatively to end a sentence, without the need for any other "to be" verb. For example, ' (暑い) "hot": ::暑い日 () ("a hot day") ::今日は暑い。(.) ("Today is hot.") * adjectival noun ( 形容動詞, ', literally 形容 "description" or "app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Language
is spoken natively by about 128 million people, primarily by Japanese people and primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language. Japanese belongs to the Japonic or Japanese- Ryukyuan language family. There have been many attempts to group the Japonic languages with other families such as the Ainu, Austroasiatic, Koreanic, and the now-discredited Altaic, but none of these proposals has gained widespread acceptance. Little is known of the language's prehistory, or when it first appeared in Japan. Chinese documents from the 3rd century AD recorded a few Japanese words, but substantial Old Japanese texts did not appear until the 8th century. From the Heian period (794–1185), there was a massive influx of Sino-Japanese vocabulary into the language, affecting the phonology of Early Middle Japanese. Late Middle Japanese (1185–1600) saw extensive grammatical changes and the first appearance of European loanwords. The basis of the standard dialect moved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Clause
A relative clause is a clause that modifies a noun or noun phraseRodney D. Huddleston, Geoffrey K. Pullum, ''A Student's Introduction to English Grammar'', CUP 2005, p. 183ff. and uses some grammatical device to indicate that one of the arguments in the relative clause refers to the noun or noun phrase. For example, in the sentence ''I met a man who wasn't too sure of himself'', the Dependent clause, subordinate clause ''who wasn't too sure of himself'' is a relative clause since it modifies the noun ''man'' and uses the pronoun ''who'' to indicate that the same "man" is referred to in the subordinate clause (in this case as its subject (grammar), subject). In many European languages, relative clauses are introduced by a special class of pronouns called ''relative pronouns'', such as ''who'' in the example just given. In other languages, relative clauses may be marked in different ways: they may be introduced by a special class of conjunctions called ''relativizers'', the main verb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
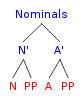
Nominal (linguistics)
In linguistics, the term ''nominal'' refers to a category used to group together nouns and adjectives based on shared properties. The motivation for nominal grouping is that in many languages nouns and adjectives share a number of morphological and syntactic properties. The systems used in such languages to show agreement can be classified broadly as gender systems, noun class systems or case marking, classifier systems, and mixed systems. Typically an affix related to the noun appears attached to the other parts of speech within a sentence to create agreement. Such morphological agreement usually occurs in parts within the noun phrase, such as determiners and adjectives. Languages with overt nominal agreement vary in how and to what extent agreement is required. History The history of research on ''nominals'' dates back to European studies on Latin and Bantu in which agreement between ''nouns'' and ''adjectives'' according to the class of the ''noun'' can be seen overtly. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Middle Japanese
was a stage of the Japanese language following Early Middle Japanese and preceding Early Modern Japanese. It was a period of transition in which the language shed many of its archaic features and became closer to its modern form. The period spanned roughly 500 years from the 12th century to the 16th century and is customarily divided into Early and Late periods. Politically, the first half of Late Middle Japanese was the end of the Heian period, known as ''Insei'' and the Kamakura period. The second half of Late Middle Japanese was the Muromachi period. Background The late 12th century was a time of transition from the aristocratic society of nobles in the Heian period to the feudal society of the warrior class. Accompanying that change, the political center moved with the establishment of various shogunates in the east. Various new Buddhist movements began and literacy increased because of their spread. In the mid-16th century, Portuguese Christian missionaries arrived in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Japanese
is the oldest attested stage of the Japanese language, recorded in documents from the Nara period (8th century). It became Early Middle Japanese in the succeeding Heian period, but the precise delimitation of the stages is controversial. Old Japanese was an early member of the Japonic language family. No genetic links to other language families have been proven. Old Japanese was written using man'yōgana, using Chinese characters as syllabograms or (occasionally) logograms. It featured a few phonemic differences from later forms, such as a simpler syllable structure and distinctions between several pairs of syllables that have been pronounced identically since Early Middle Japanese. The phonetic realization of these distinctions is uncertain. Internal reconstruction points to a pre-Old Japanese phase with fewer consonants and vowels. As is typical of Japonic languages, Old Japanese was primarily an agglutinative language with a subject–object–verb word order, adjectives and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Verb
In linguistics, a compound verb or complex predicate is a multi-word compound that functions as a single verb. One component of the compound is a ''light verb'' or ''vector'', which carries any inflections, indicating tense, mood, or aspect, but provides only fine shades of meaning. The other, "primary", component is a verb or noun which carries most of the semantics of the compound, and determines its arguments. It is usually in either base or n Verb + Verb compounds''conjunctive participial'' form. A compound verb is also called a "complex predicate" because the semantics, as formally modeled by a predicate, is determined by the primary verb, though both verbs appear in the surface form. Whether Noun+Verb (N+V) compounds are considered to be "compound verbs" is a matter of naming convention. Generally, the term ''complex predicate'' usually includes N+V compounds, whereas the term ''compound verb'' is usually reserved for V+V compounds. However, several authors specially I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Modifier
A compound modifier (also called a compound adjective, phrasal adjective, or adjectival phrase) is a compound of two or more attributive words: that is, two or more words that collectively modify a noun. Compound modifiers are grammatically equivalent to single-word modifiers, and can be used in combination with other modifiers. (In the preceding sentence, "single-word" is itself a compound modifier.) The constituents of compound modifiers need not be adjectives; combinations of nouns, determiners, and other parts of speech are also common. For example, ''man-eating (shark)'' and ''one-way (street)''. The punctuation of compound modifiers in English depends on their grammatical role. Attributive compounds—modifiers within the noun phrase—are typically hyphenated, whereas the same compounds used as predicates will typically not be (if they are temporary compounds), unless they are permanent compounds attested as dictionary headwords. Compound adjectives Words that function as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-finite Verb
A nonfinite verb is a derivative form of a verb unlike finite verbs. Accordingly, nonfinite verb forms are inflected for neither number nor person, and they cannot perform action as the root of an independent clause. In English, nonfinite verbs include infinitives, participles and gerunds. Nonfinite verb forms in some other languages include converbs, gerundives and supines. Formally, nonfinite verb forms lack the three grammatical features ( mood, tense and voice) that are "associated, independently or relatively, with ... the act of predication." Generally, they also lack a subject dependent. One or more nonfinite verbs may be associated with a finite verb in a finite clause: the elements of a verb catena, or verb chain. Because English lacks most inflectional morphology, the finite and the nonfinite forms of a verb may appear the same in a given context. Examples The following sentences each contain one finite verb (underlined) and multiple nonfinite verbs (in bold): ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
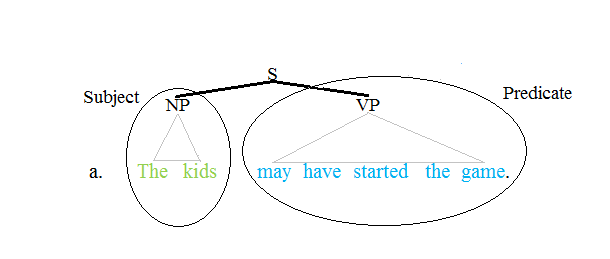
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in one of two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject, and the other views it as just the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake''. By the second definition, the predicate of the same sentence is just the content verb ''likes'', whereby ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the arguments of this predicate. Differences between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of predicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Grammar
Japanese is an agglutinative, synthetic, mora-timed language with simple phonotactics, a pure vowel system, phonemic vowel and consonant length, and a lexically significant pitch-accent. Word order is normally subject–object–verb with particles marking the grammatical function of words, and sentence structure is topic–comment. Its phrases are exclusively head-final and compound sentences are exclusively left-branching. Sentence-final particles are used to add emotional or emphatic impact, or make questions. Nouns have no grammatical number or gender, and there are no articles. Verbs are conjugated, primarily for tense and voice, but not person. Japanese adjectives are also conjugated. Japanese has a complex system of honorifics with verb forms and vocabulary to indicate the relative status of the speaker, the listener, and persons mentioned. In language typology, it has many features different from most European languages. Distinctive aspects of modern Japanese senten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |