|
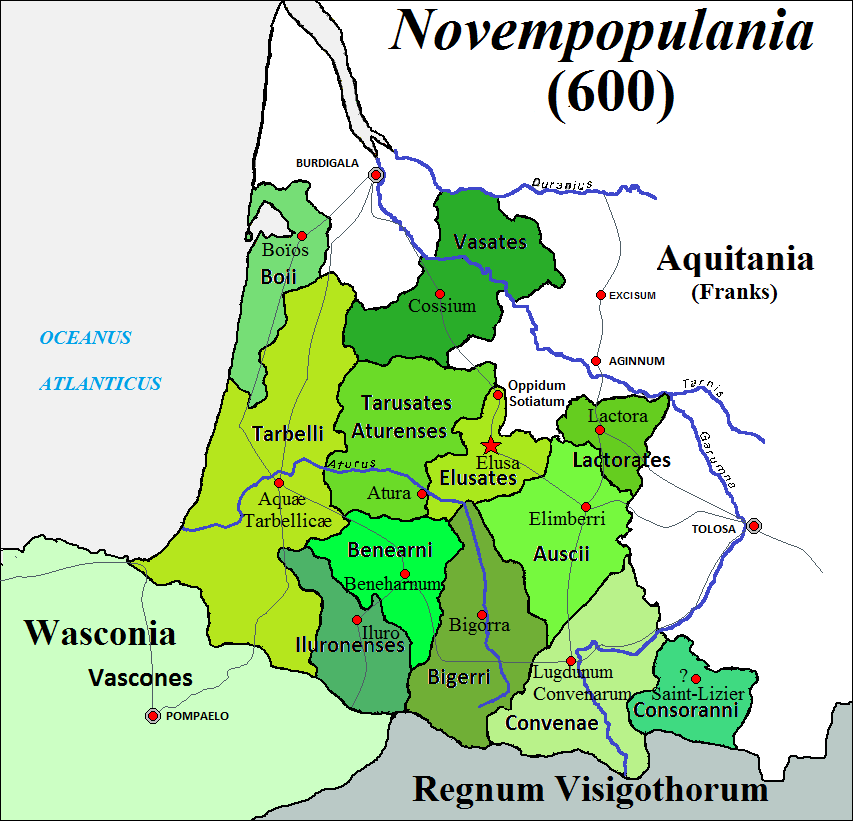
Tarbelli
The Tarbelli were an Aquitani tribe dwelling in the present-day regions of Labourd and Chalosse, in the west of Aquitania, during the Iron Age. Alongside the Auscii, they were one of the most powerful peoples of Aquitania. They were subjugated in 56 BC by the Roman forces of Caesar's legatus P. Licinius Crassus. Name They are mentioned as ''Tarbelli'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), as ''Tárbelloi'' (Τάρβελλοι) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), as ''Tarbelli Quattuorsignani'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), and as ''Tarbellus'' on an inscription., s.v. ''Tarbelli (Quattuorsignani)''. Joaquín Gorrochategui proposed to see the name as the suffix ''tar''- attached to the adjective ''bel'' ('black'), which is common in Aquitanian onomastics. Geography The Tarbelli lived in the regions of Labourd and Chalosse, on both sides of the Adour river. Their territory was located east of the Atlantic Ocean, north of the Vardulli, south of the Cocosates, west of the Tarusates, Atures and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquitani
The Aquitani were a tribe that lived in the region between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic ocean, and the Garonne, in present-day southwestern France in the 1st century BCE. The Romans dubbed this region ''Gallia Aquitania''. Classical authors such as Julius Caesar and Strabo clearly distinguish the Aquitani from the other peoples of Gaul, and note their similarity to others in the Iberian Peninsula. During the process of Romanization, the Aquitani gradually adopted Latin (Vulgar Latin) and the Roman civilization. Their old language, the Aquitanian language, was a precursor of the Basque language Trask, L. ''The History of Basque'' Routledge: 1997 and the substrate for the Gascon language (one of the Romance languages) spoken in Gascony. History At the time of the Roman conquest, Julius Caesar, who defeated them in his campaign in Gaul, describes them as making up a distinct part of Gaul: Despite apparent cultural and linguistic connections to (Vascones), the area of Aquit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallia Aquitania
Gallia Aquitania ( , ), also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France, where it gives its name to the modern region of Aquitaine. It was bordered by the provinces of Gallia Lugdunensis, Gallia Narbonensis, and Hispania Tarraconensis.John Frederick Drinkwater (1998). "Gaul (Transalpine)". ''The Oxford Companion to Classical Civilization.'' Ed. Simon Hornblower and Antony Spawforth. Oxford University PressOxford Reference Online Tribes of Aquitania Fourteen Celtic tribes and over twenty Aquitanian tribes occupied the area from the northern slopes of the Pyrenees in the south to the ''Liger'' (Loire) river in the north. The major tribes are listed at the end of this section.''Strabo: The Geography''The Aquitani There were more than twenty tribes of Aquitani, but they were small and lacking in repute; the majority of the tribes lived along the ocean, while the others reached up into the interior and to the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocosates
The Cocosates or Cocosates Sexsignani were an Aquitani tribe dwelling in present-day Landes during the Iron Age. Name They are mentioned as ''Cocosates'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), and as ''Cocosates Sexsignani'' by Pliny (1st c. AD). The etymology of the name remains obscure. It can be derived from the Gaulish stem ''cocos''- ('scarlet red') attached to the suffix -''ates'' ('belonging to'). Red is a colour commonly used in personal names (''Cocus'', ''Cocca'', ''Cocidius'', etc.) and associated with warfare., s.v. ''Cocosates (Sexsignani)''. Geography The Cocosates lived in present-day Landes. Their territory was located east of the Atlantic Ocean, west of the Oscidates and Sotiates, north of the Tarbelli and Tarusates, and south of the Boii., Map 25: Hispania Tarraconensis. Their chief town was known as Caequosa (modern Sescouze, near Castets). Political organization The Cocosates were a confederation of six tribes. They were probably clients of the neighbouring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labourd
Labourd ( eu, Lapurdi; la, Lapurdum; Gascon: ''Labord'') is a former French province and part of the present-day Pyrénées Atlantiques ''département''. It is one of the traditional Basque provinces, and identified as one of the territorial component parts of the Basque Country by many, especially by the Basque nationalists. Labourd extends from the Pyrenees to the river Adour, along the Bay of Biscay. To the south is Gipuzkoa and Navarre in Spain, to the east is Basse-Navarre, to the north are the Landes. It has an area of almost and a population of over 200,000 (115,154 in 1901; 209,913 in 1990), the most populous of the three French Basque provinces. Over 25% of the inhabitants speak Basque (17% in the Bayonne-Anglet-Biarritz zone, 43% in the rest). Labourd has also long had a Gascon-speaking tradition, noticeably next to the banks of the river Adour but also more diffusely throughout the whole viscounty (about 20% in Bayonne-Anglet-Biarritz). The main town of Labourd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auscii
The Auscii or Ausci were an Aquitani tribe dwelling around present-day Auch during the Iron Age. Alongside the Tarbelli, they were one of the most powerful peoples of Aquitania. Name They are mentioned as ''Ausci'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), Pliny (1st c. AD) and Pomponius Mela (mid-1st c. AD), and as ''Au̓skíois'' (Αὐσκίοις) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD)., s.v. ''Auscii''. The ethnonym ''Auscii'' may be related to the prefix ''eusk''-, meaning 'Basque' in the Basque language ('' euskara''). The city of Auch, attested as ''civitas Auscius'' in the early 4th century AD, is named after the tribe. Geography Their territory was located north of the Onobrisates, west of the Cambolectri and Volcae Tectosages, south of the Lactorates, west of the Atures. The chief town of the Auscii was known as Elimberrum (modern Auch), whose name can be compared to the Basque ''ili-berri'' ('new town'). Culture It is believed that the Auscii spoke a form or dialect of the Aqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dax, Landes
Dax (; oc, Dacs; eu, Akize) is a commune in Nouvelle-Aquitaine, southwestern France, sub-prefecture of the Landes department. It is known as a spa destination, specialising in mud treatment for rheumatism and similar ailments. Dax is also known for its tauromachy culture, especially during the August ferias, one of the most crowded festival events in France with 800,000 people attending over five days. It is also a market town, former bishopric and busy local centre, especially for the Chalosse area. Geography Dax lies on the river Adour, 30 km from the Atlantic Ocean and 42 km northwest of Bayonne. Dax station has rail connections to Paris, Hendaye, Tarbes, Bordeaux, Bayonne and Pau. History It was first established by the Romans, and its reputation is supposed to date from a visit by Julia, the daughter of the first Emperor Octavian Augustus. Its Roman name was ''Civitas Aquensium''. In the Middle Ages, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquitanian Language
The Aquitanian language was the language of the ancient Aquitani, spoken on both sides of the western Pyrenees in ancient Aquitaine (approximately between the Pyrenees and the Garonne, in the region later known as Gascony) and in the areas south of the Pyrenees in the valleys of the Basque Country before the Roman conquest. It probably survived in Aquitania north of the Pyrenees until the Early Middle Ages. Archaeological, toponymical, and historical evidence shows that it was a language or group of languages that represent a precursor of the Basque language. The most important pieces of evidence are a series of votive and funerary texts in Latin, dated to the first three centuries AD, which contain about 400 personal names and 70 names of gods. History Aquitanian and its modern relative, Basque, are commonly thought to be Pre-Indo-European languages, remnants of the languages spoken in Western Europe before the arrival of Indo-European speakers. Some claims have been made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |