|
Tanystropheids
Tanystropheidae is an extinct family of mostly marine archosauromorph reptiles that lived throughout the Triassic Period. They are characterized by their long, stiff necks formed from elongated cervical vertebrae with very long cervical ribs. Some tanystropheids such as '' Tanystropheus'' had necks that were several meters long, longer than the rest of their bodies. Tanystropheids are known from Europe, Asia (Russia, China, and Saudi Arabia), North America and probably South America (Brazil). The presence of tanystropheids in Europe and China indicate that they lived along much of the coastline of the Tethys Ocean. However, species in western North America are found in terrestrial deposits, suggesting that as a group, tanystropheids were ecologically diverse. Relationships among tanystropheid species have been difficult to resolve because most specimens were flattened during fossilization and are preserved two-dimensionally. Three-dimensional fossils are known from Europe and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanystropheus Longobardicus
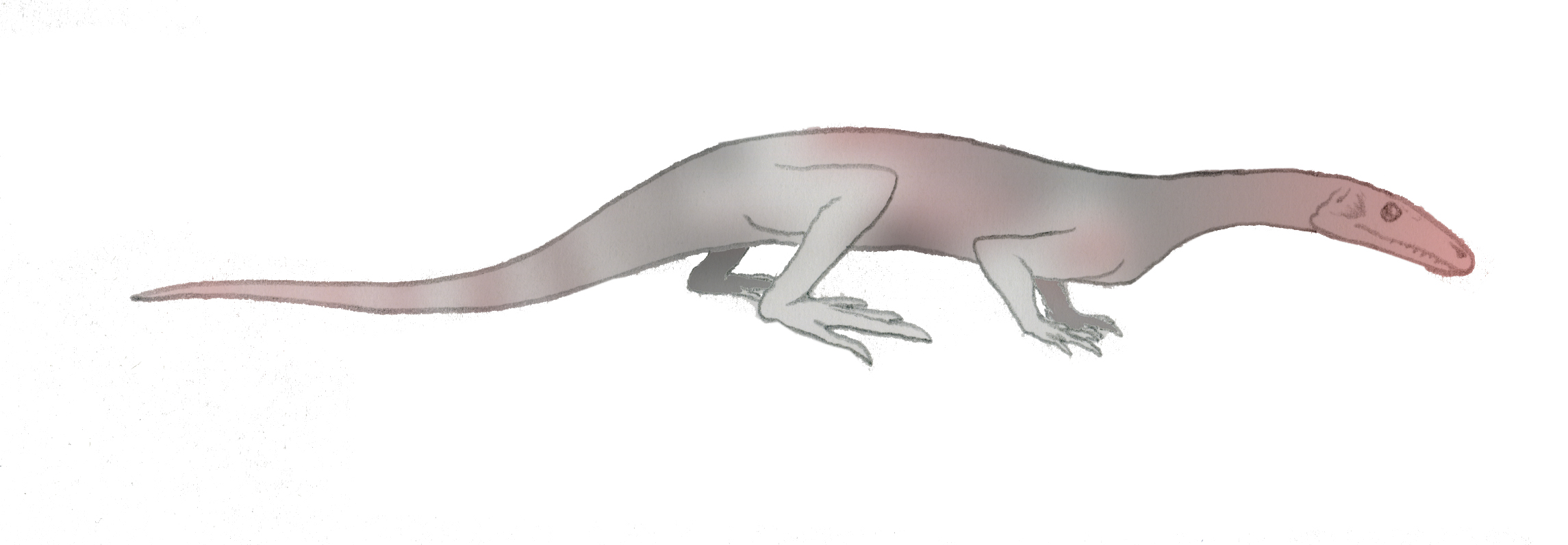
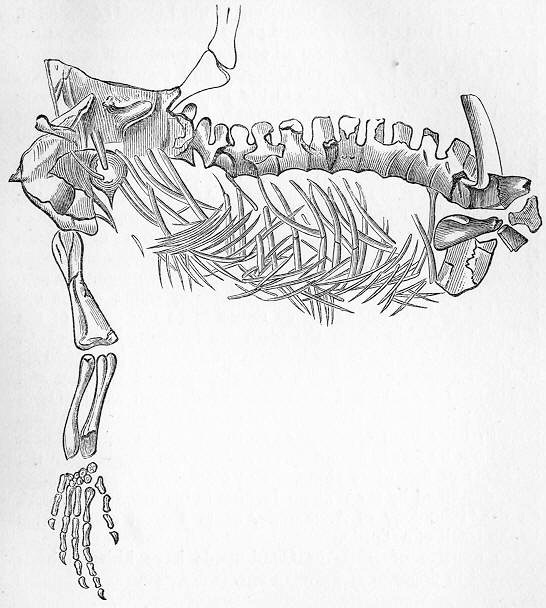
''Tanystropheus'' (Greek ~ 'long' + 'hinged') is an extinct archosauromorph reptile from the Middle and Late Triassic epochs. It is recognisable by its extremely elongated neck, which measured long—longer than its body and tail combined. The neck was composed of 12–13 extremely elongated vertebrae. With its very long but relatively stiff neck, ''Tanystropheus'' has been often proposed and reconstructed as an aquatic or semi-aquatic reptile, a theory supported by the fact that the creature is most commonly found in semi-aquatic fossil sites wherein known terrestrial reptile remains are scarce. Fossils have been found in Europe. Complete skeletons of small individuals are common in the Besano Formation at Monte San Giorgio in Italy and Switzerland; other fossils have been found in the Middle East and China, dating from the Middle Triassic to the early part of the Late Triassic (Anisian, Ladinian, and Carnian stages).Dal Sasso, C. and Brillante, G. (2005). ''Dinosaurs of Italy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
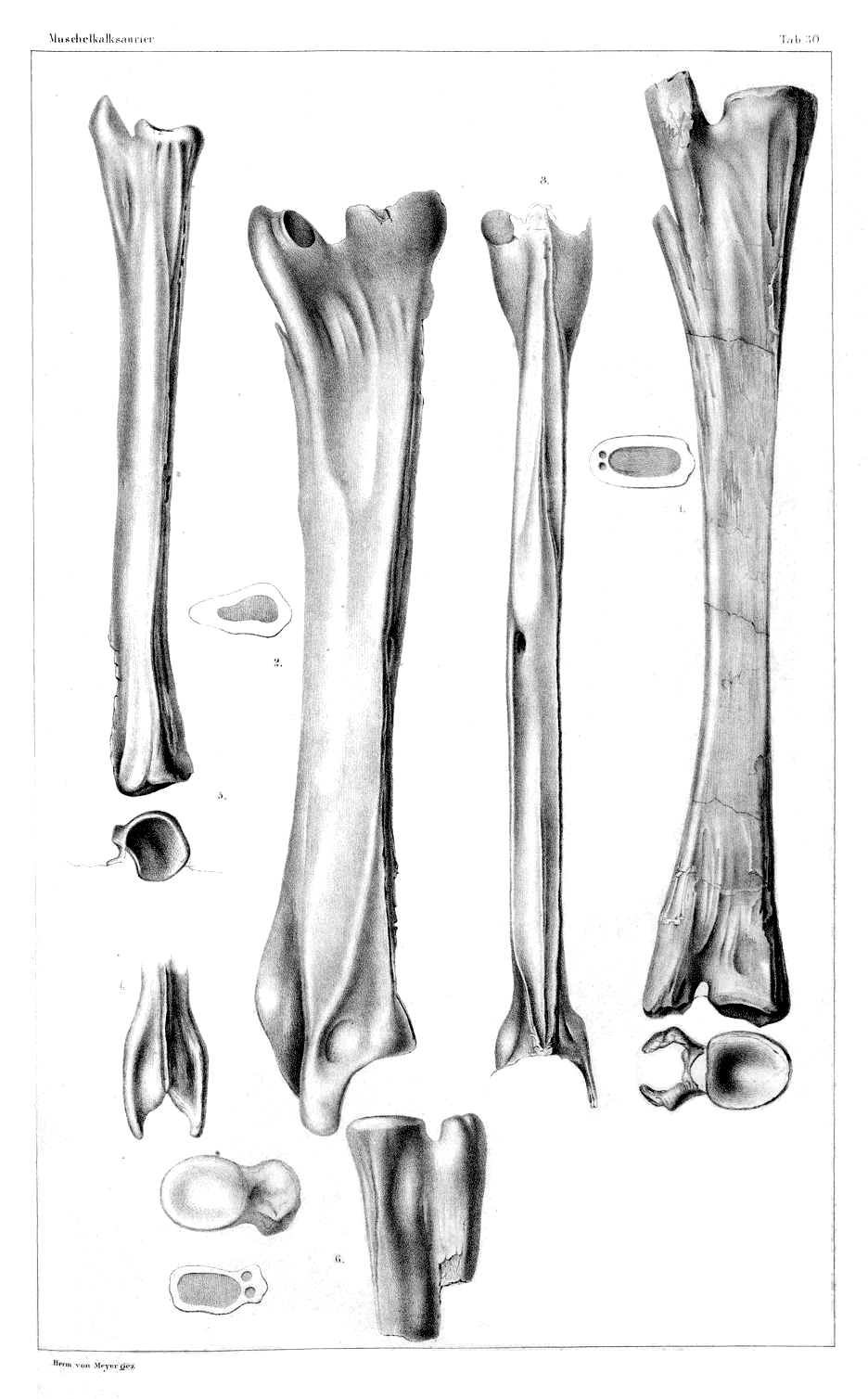
Protanystropheus
''Protanystropheus'' is an extinct genus of archosauromorph from the Middle Triassic (Anisian stage) of Poland, Germany, Austria and the Netherlands. It was named by Sennikov in 2011 and the type species is ''Protanystropheus antiquus'', first described in 1908 by German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene under the name ''Tanystropheus antiquus'' (some authors still prefer to include this species within ''Tanystropheus''). Sennikov (2011) referred to ''Protanystropheus'' several vertebrae, including those belonging to "''Thecodontosaurus ''Thecodontosaurus'' ("socket-tooth lizard") is a genus of herbivorous basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the late Triassic period (Rhaetian age). Its remains are known mostly from Triassic "fissure fillings" in South England. ''The ...''" ''primus'', but such a referral has later been questioned, because these specimens may represent other basal archosauromorphs. References Tanystropheids Prehistoric reptile genera Anisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuyuansaurus
''Fuyuansaurus'' is an extinct genus of "protorosaur" reptiles (probably part of Tanystropheidae) known from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian stage) Falang Formation of southern China. ''Fuyuansaurus'' was first named by Nicholas C. Fraser, Olivier Rieppel and Li Chun in 2013 and the type species is ''Fuyuansaurus acutirostris''. This genus is known from a single partial skeleton, IVPP V17983. This skeleton includes part of the skull, most of the neck, and portions of the trunk, shoulder girdle, and hip. ''Fuyuansaurus'' can be distinguished from other "protorosaurs" by its elongated and slender snout. Like ''Tanystropheus'', it possessed an elongated neck, but it differs from most tanystropheids in the structure of its hip. Nevertheless, Ezcurra and Butler classified it as a tanystropheid in 2018, as did Spiekman et al. in 2021. Description The skull was crushed and incomplete, with the tip of the snout broken off and the middle part of the skull obscured by the part of the ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanystropheus
''Tanystropheus'' (Greek ~ 'long' + 'hinged') is an extinct archosauromorph reptile from the Middle Triassic, Middle and Late Triassic epochs. It is recognisable by its extremely elongated neck, which measured long—longer than its body and tail combined. The neck was composed of 12–13 extremely elongated vertebrae. With its very long but relatively stiff neck, ''Tanystropheus'' has been often proposed and reconstructed as an aquatic or semi-aquatic reptile, a theory supported by the fact that the creature is most commonly found in semi-aquatic fossil sites wherein known terrestrial reptile remains are scarce. Fossils have been found in Europe. Complete skeletons of small individuals are common in the Besano Formation at Monte San Giorgio in Italy and Switzerland; other fossils have been found in the Middle East and China, dating from the Middle Triassic to the early part of the Late Triassic (Anisian, Ladinian, and Carnian stages).Dal Sasso, C. and Brillante, G. (2005). ''Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinocephalosauridae
Dinocephalosauridae is an extinct clade of marine and terrestrial archosauromorph reptiles that lived throughout the Triassic period. Like tanystropheids, they are characterized by their long necks, lengthened by either addition of cervical vertebrae or elongation of the individual bones. Dinocephalosaurids are known from Europe (Poland, Germany, Austria, Netherlands) and China. Some members (i.e. '' Dinocephalosaurus'') are solely marine animals, most likely living near the coastlines of the Tethys Ocean, while other members (i.e. ''Pectodens'' were purely terrestrial, suggesting wide ecological diversity in just the few known species in this family. Classification In 2021, a phylogenetic study was conducted by S. Spiekman, N. Fraser, and T. Schayer in an attempt to clarify the systematics of " protorosaur" groups. A total of 16 individual trees were found using different character scoring methods and unstable OTU Otu or OTU may refer to: * Otu: ** Otu, Iran, a village in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozimek Volans
''Ozimek'' (named after the Ozimek, town of the same name) is a genus of sharovipterygidae, sharovipterygid archosauromorpha, archosauromorph reptile, known from Late Triassic deposits in Poland and closely related to the Kyrgyzstani ''Sharovipteryx''. It contains one species, ''O. volans'', named in 2016 by Jerzy Dzik and Tomasz Sulej. Like ''Sharovipteryx'', ''Ozimek'' had long, slender limbs with the hindlimbs longer than the forelimbs; the hindlimbs likely supported gliding membranes as fossilized in ''Sharovipteryx''. Another unusual characteristic was the shoulder girdle, where the massive coracoids formed a shield-like structure covering the bottom of the shoulder region that would have limited mobility. In other respects, such as its long neck, it was a typical member of the non-natural grouping Protorosauria. Phylogenetic analysis has indicated that it, possibly along with ''Sharovipteryx'', may have been an unusual member of the protorosaur group Tanystropheidae, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharovipterygidae
Sharovipterygidae is a family of strange gliding archosauromorphs from the mid-Triassic of Eurasia, notable for their short forelimbs and long, wing-like hindlimbs, which supported membranes for gliding. They are represented by ''Sharovipteryx ''Sharovipteryx'' ("Sharov's wing", known until 1981 as ''Podopteryx'', "foot wing"), is a genus of early gliding reptiles containing the single species ''Sharovipteryx mirabilis''. It is known from a single fossil and is the only glider with a m ...'' and '' Ozimek volans''. A 2019 phylogenetic analysis suggested that ''Ozimek'', and by extension ''Sharovipteryx'', may belong to the Tanystropheidae. References Middle Triassic reptiles of Asia Prehistoric archosauromorphs Gliding animals Late Triassic reptiles of Asia Late Triassic reptiles of Europe Prehistoric reptile families {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czatkowiella
''Czatkowiella'' is an extinct genus of long-necked archosauromorph known from Early Triassic (Olenekian age) rocks of Czatkowice 1, Poland. It was first named by Magdalena Borsuk−Białynicka and Susan E. Evans in 2009 and the type species is ''Czatkowiella harae''. Phylogeny Cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... after Borsuk−Białynicka & Evans (2009). Cladogram after Spiekman ''et al.'' 2021: References Prehistoric archosauromorphs Prehistoric reptile genera Olenekian genera Early Triassic reptiles of Europe Fossils of Poland Fossil taxa described in 2009 {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolacerta
''Prolacerta'' is a genus of archosauromorph from the lower Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. The only known species is ''Prolacerta broomi''. The generic name ''Prolacerta'' is derived from Latin meaning “before lizard” and its species name ''broomi'' is in commemoration of the famous paleontologist Robert Broom, who discovered and studied many of the fossils found in rocks of the Karoo Supergroup. When first discovered, ''Prolacerta'' was considered to be ancestral to modern lizards, scientifically known as lacertilians. However, a study by Gow (1975) instead found that it shared more similarities with the lineage that would lead to archosaurs such as crocodilians and dinosaurs (including birds). ''Prolacerta'' is considered by modern paleontologists to be among the closest relatives of the Archosauriformes. History of discovery ''Prolacerta'' was first described by Francis Rex Parrington in 1935 from a single skull recovered near the small town, Middelburg, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protorosaurus
''Protorosaurus'' ("first lizard") is a genus of lizard-like early reptiles. Members of the genus lived during the late Permian period in what is now Germany and Great Britain. Once believed to have been an ancestor to lizards, ''Protorosaurus'' is now known to be one of the oldest and most primitive members of Archosauromorpha, the group that would eventually lead to archosaurs such as crocodilians and dinosaurs. Description ''Protorosaurus'' grew up to in length, and was a slender, lizard-like animal, vaguely resembling a monitor lizard, with long legs and a long neck. Discovery ''Protorosaurus'' was one of the first fossil reptiles to be described, being initially described in Latin in 1710 by from a specimen found in Thuringia in Germany, who considered the animal to be a crocodile, and most similar to the Nile crocodile (''C. niloticus''). Over a century later, in publications in 1830 and 1832 Hermann von Meyer recognised ''Protorosaurus'' as distinct extinct reptile a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesairosaurus
''Jesairosaurus'' is an extinct genus of early archosauromorph reptile known from the Illizi Province of Algeria. It is known from a single species, ''Jesairosaurus lehmani''. Although a potential relative of the long-necked tanystropheids, this lightly-built reptile could instead be characterized by its relatively short neck as well as various skull features. Etymology and discovery Zarzaïtine fossil material has been known since 1957. Much of the material has been recovered by French expeditions in the late 1950s and 1960s, and deposited at the Laboratoire de Paleontologie (Paleontology department) at the Museum national d'Histoire naturalle in Paris. Algerian fossils were prepared at this institution over subsequent years. Several putative procolophonid skeletons reported in 1971 were later determined to belong to " prolacertiforms" in 1990. The term "prolacertiform" is now considered to refer to an unnatural polyphyletic grouping of early archosauromorphs, distant relatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |