|
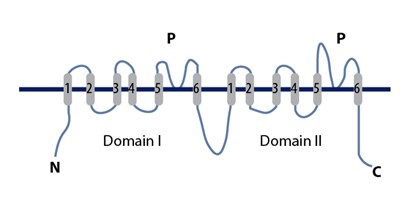
Tandem Pore Domain Potassium Channel
The two-pore-domain or tandem pore domain potassium channels are a family of 15 members that form what is known as leak channels which possess Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz (open) rectification. These channels are regulated by several mechanisms including signaling lipids, oxygen tension, pH, mechanical stretch, and G-proteins . Their name is derived from the fact that the α subunits consist of four transmembrane segments, and each pair of transmembrane segments contains a pore loop between the two transmembrane segments. Thus, each subunit has two pore loops. As such, they structurally correspond to two inward-rectifier α subunits and thus form dimers in the membrane (whereas inward-rectifier α subunits form tetramers). Each single channel does ''not'' have two pores; the name of the channel comes from the fact that ''each subunit'' has two P (pore) domains in its primary sequence. To quote Rang and Dale (2015), "The nomenclature is misleading, especially when they are incorrectly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-pore Channel
Two-pore channels (TPCs) are eukaryotic intracellular voltage-gated and ligand gated cation selective ion channels. There are two known paralogs in the human genome, TPC1s and TPC2s. In humans, TPC1s are sodium selective and TPC2s conduct sodium ions, calcium ions and possibly hydrogen ions. Plant TPC1s are non-selective channels. Expression of TPCs are found in both plant vacuoles and animal acidic organelles. These organelles consist of endosomes and lysosomes. TPCs are formed from two transmembrane non-equivalent tandem Shaker-like, pore-forming subunits, dimerized to form quasi- tetramers. Quasi-tetramers appear very similar to tetramers, but are not quite the same. Some key roles of TPCs include calcium dependent responses in muscle contraction(s), hormone secretion, fertilization, and differentiation. Disorders linked to TPCs include membrane trafficking, Parkinson's disease, Ebola, and fatty liver. As implied by their name, TPC channels possess two pores and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK4
Potassium channel subfamily K member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNK4'' gene. KCNK4 protein channels are also called TRAAK channels. Function ''KNCK4'' is a gene segment that encodes for the TRAAK (TWIK-related Arachidonic Acid-Stimulated K+) subfamily of mechanosensitive potassium channels. Potassium channels play a role in many cellular processes including action potential depolarization, muscle contraction, hormone secretion, osmotic regulation, and ion flow. The K2P4.1 protein is a lipid-gated ion channel that belongs to the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore-forming P domains (K2P). K2P4.1 homodimerizes and functions as an outwardly rectifying channel. It is expressed primarily in neural tissues and is stimulated by membrane stretch and polyunsaturated fatty acids. TRAAK channels are found in mammalian neurons and are part of a protein family of weakly inward rectifying potassium channels. This subfamily of potassium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK18
Potassium channel subfamily K member 18 (KCNK18), also known as TWIK-related spinal cord potassium channel (TRESK) or K2P18.1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNK18'' gene. K2P18.1 is a potassium channel containing two pore-forming P domains. A flaw in this gene could help trigger migraine Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few ho ... headaches. If the gene does not work properly, environmental factors can more easily trigger pain centres in the brain and cause a severe headache. * See also * Tandem pore domain potassium channel References Further reading * * * * * * * External links * Ion channels {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK17
Potassium channel subfamily K member 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNK17'' gene. This gene encodes K2P17.1, one of the members of the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore-forming P domains. This open channel, primarily expressed in the pancreas, is activated at alkaline pH. See also * Tandem pore domain potassium channel References Further reading * * * * * * * External links * {{Ion channels, g3 Ion channels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK16
Potassium channel subfamily K member 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNK16'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene, K2P16.1, is a potassium channel containing two pore-forming P domains. See also * Tandem pore domain potassium channel References Further reading * * * * * External links * Ion channels {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK15
Potassium channel subfamily K member 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNK15'' gene. This gene encodes K2P15.1, one of the members of the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore-forming P domains. K2P15.1 has not been shown to be a functional channel; however, it may require other non-pore-forming proteins for activity. See also * Tandem pore domain potassium channel References Further reading * * * * * External links * Ion channels {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK13
Potassium channel, subfamily K, member 13, also known as KCNK13 is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene, K2P13.1 is a potassium channel containing two pore-forming P domains. See also * Tandem pore domain potassium channel References Further reading * * * * * * External links * Ion channels {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK12
Potassium channel, subfamily K, member 12, also known as KCNK12 is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene, K2P12.1, is a potassium channel containing two pore-forming P domains. See also * Tandem pore domain potassium channel References Further reading * * * * * * * External links * Ion channels {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK10
Potassium channel, subfamily K, member 10, also known as KCNK10 is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene, K2P10.1, is a potassium channel containing two pore-forming P domains. See also * Tandem pore domain potassium channel References Further reading * * * * * * External links * Ion channels {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK9
Potassium channel subfamily K member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNK9'' gene. This gene encodes K2P9.1, one of the members of the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore-forming P domains. This open channel is highly expressed in the cerebellum. It is inhibited by extracellular acidification and arachidonic acid, and strongly inhibited by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate is also known as 12-''O''-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). TASK channels are additionally inhibited by hormones and transmitters that signal through GqPCRs. The resulting cellular depolarization is thought to regulate processes such as motor control and aldosterone Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ... secretion. Despi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK7
Potassium channel, subfamily K, member 7, also known as KCNK7 or K2P7.1 is a protein which is encoded in humans by the ''KCNK7'' gene. K2P7.1 is a potassium channel containing two pore-forming P domains. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the superfamily of potassium channel Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of c ... proteins containing two pore-forming P domains. The product of this gene has not been shown to be a functional channel; It may require other non-pore-forming proteins for activity. See also * Tandem pore domain potassium channel References Further reading * * * * External links * * * Ion channels {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |