|
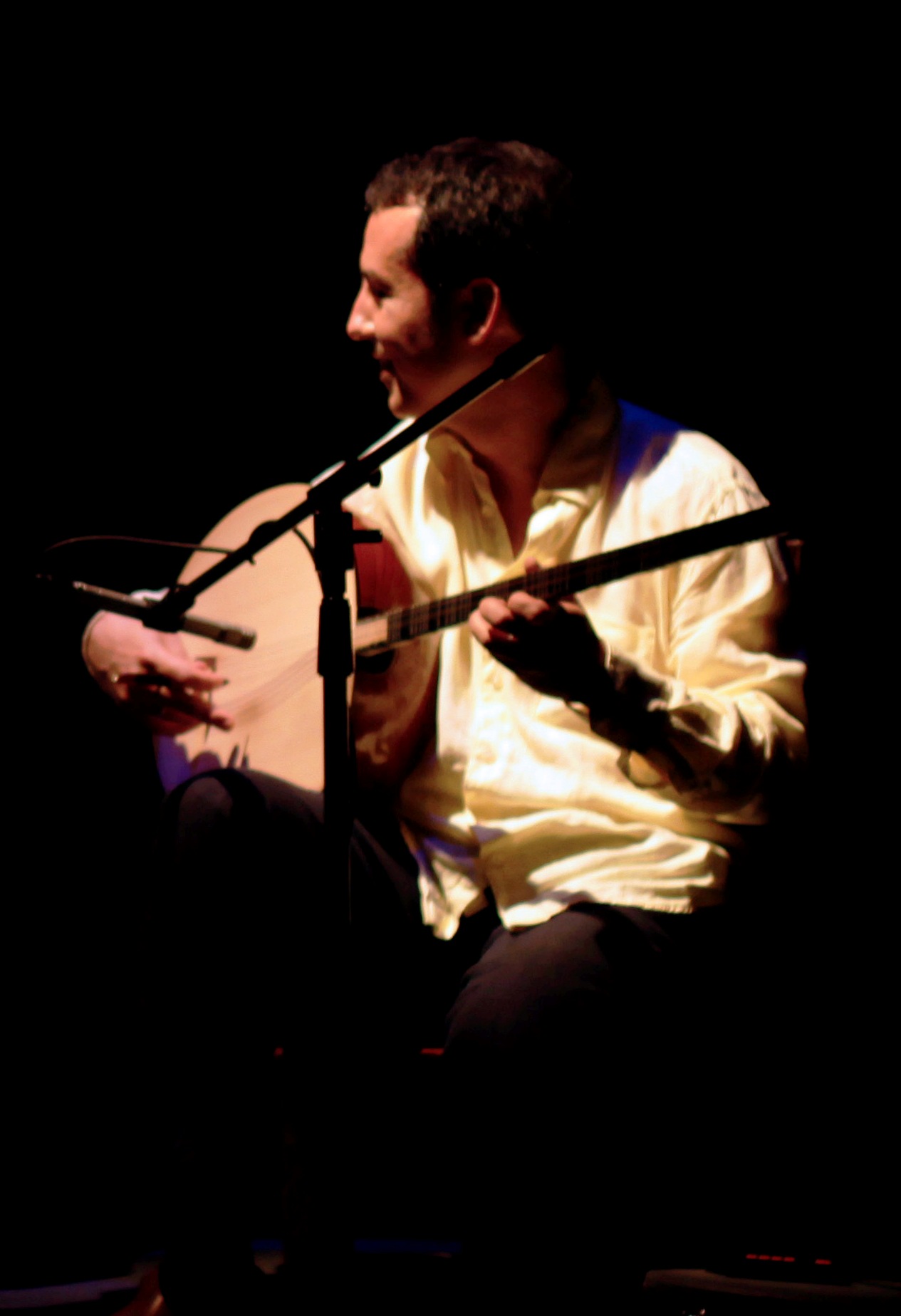
Tambouras
The tambouras ( el, ταμπουράς ) is a Greek traditional string instrument of Byzantine origin. It has existed since at least the 10th century, when it was known in Assyria and Egypt. At that time, it might have between two and six strings, but Arabs adopted it, and called it a Tanbur. The characteristic long neck bears two strings, tuned five notes apart. It also similar to the Turkish ''tambur'' and each of them have same origin. Tanbur, a Persian word, according to some scholars taken from Sumerian ‘Pan Tur, meaning “Little bow”. History Origins It is considered that the ''tambouras ancestor is the ancient Greek ''pandouris'', also known as '' pandoura'', ''pandouros'' or ''pandourida'' (πανδουρίς, πανδούρα, πάνδουρος), from which the word is derived. The ''tambouras'' is mentioned in the Byzantine epic of Digenis Akritas, when the hero plays his θαμπούριν, ''thambourin'' (medieval form of ''tambouras''): Name The name re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouzouki
The bouzouki (, also ; el, μπουζούκι ; alt. pl. ''bouzoukia'', from Greek ), also spelled buzuki or buzuci, is a musical instrument popular in Greece. It is a member of the long-necked lute family, with a round body with a flat top and a long neck with a fretted fingerboard. It has steel strings and is played with a plectrum producing a sharp metallic sound, reminiscent of a mandolin but pitched lower. There are two main types of bouzouki: the ''trichordo'' (''three-course'') has three pairs of strings (known as courses) and the ''tetrachordo'' (''four-course'') has four pairs of strings. The instrument was brought to Greece in the early 1900s by Greek refugees from Anatolia, and quickly became the central instrument to the rebetiko genre and its music branches. It is now an important element of modern Laïko pop Greek music. Etymology The name ''bouzouki'' comes from the Turkish word , meaning "broken" or "modified", and comes from a particular re-entrant tuning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanbur
The term ''Tanbur'' ( fa, تنبور, ) can refer to various long-necked string instruments originating in Mesopotamia, Southern or Central Asia. According to the '' New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', "terminology presents a complicated situation. Nowadays the term tanbur (or tambur) is applied to a variety of distinct and related long-necked lutes used in art and folk traditions. Similar or identical instruments are also known by other terms." These instruments are used in the traditional music of Iran, India, Kurdistan, Armenia, Afghanistan, Azerbaijan (especially Avar community), Pakistan, Turkey, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan. Origins Tanburs have been present in Mesopotamia since the Akkadian era, or the third millennium BC. Three figurines have been found in Susa that belong to 1500 BC, and in hands of one of them is a tanbur-like instrument. Also an image on the rocks near Mosul that belong to about 1000 B shows tanbur players. Playing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamburica
Tamburica ( or ) or tamboura ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", tamburica, тамбурица, little tamboura; hu, tambura; el, Ταμπουράς, Tampourás; sometimes written tamburrizza or tamburitza), refers to a family of long-necked lutes popular in Southern Europe and Central Europe, especially Serbia (in Vojvodina, Mačva and Posavo-Tamnava), Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia (of which it is the national string instrument), Slovenia, and Hungary ( predominantly amongst its ethnic South Slavic minority groups). It is also known in Burgenland, Austria. All took their name and some characteristics from the Persian tanbur but also resemble the mandolin and guitar in the sense that its strings are plucked and often paired. The frets may be moveable to allow the playing of various modes. The variety of tamburica shapes known today were developed in Serbia and Croatia by a number of indigenous contributors near the end of the 19th century. History There is little reliable data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Tambur
The ''tambur'' (spelled in keeping with TDK conventions) is a fretted string instrument of Turkey and the former lands of the Ottoman Empire. Like the ney, the armudi (lit. pear-shaped) kemençe and the kudüm, it constitutes one of the four instruments of the basic quartet of Turkish classical music. Of the two variants, one is played with a plectrum (''mızraplı tambur'') and the other with a bow ('' yaylı tambur''). The player is called a ''tamburî''.Tambur Republic of Turkey - Ministry of Culture and Tourism History and development There are several hypotheses as to the origin of the instrument. One suggests that it descended from the kopuz, a string instrument still in use among the Turkic peoples of Central Asia and the Caspian region. T ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandoura
The pandura ( grc, πανδοῦρα, ''pandoura'') or pandore, an ancient string instrument, belonged in the broad class of the lute and guitar instruments. Akkadians played similar instruments from the 3rd millennium BC. Ancient Greek artwork depicts such lutes from the 3rd or 4th century BC onward. Ancient Greece The ancient Greek ''pandoura'' was a medium or long-necked lute with a small resonating chamber, used by the ancient Greeks. It commonly had three strings: such an instrument was also known as the ''trichordon'' (three-stringed) (τρίχορδον, McKinnon 1984:10). Its descendants still survive as the Kartvelian panduri, the Greek tambouras and bouzouki, the North African kuitra, the Eastern Mediterranean saz and the Balkan tamburica and remained popular also in the near east and eastern Europe, too, usually acquiring a third string in the course of time, since the fourth century BC. Renato Meucci (1996) suggests that the some Italian Renaissance descendants o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šargija
thumb The ''šargija'' ( sh, šargija, шаргија; sq, sharki or sharkia), anglicized as ''shargia'', is a plucked, fretted long necked lute used in the folk music of various Balkan countries, including Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Croatia, Albania, North Macedonia and Kosovo. The instrument is part of a larger family of instruments which includes the Balkan ''tambura'' and the ''bağlama'' (or ''tambura saz''), ''tamburica'', and the '' tambouras''. History The instrument was studied by musicologists in the 20th century. Their studies have been characterized as speculative and nationalistic. More recently, an American researcher, Richard March, concluded that the tambura arrived in the Balkans with Turkish people in the 1500s. It was adopted by people living in the Balkans, including "urban Muslim Slavs" and "Bosnia Christians." It also arrived in Croatia with laborers. Today the ''šargija'' is played by Albanians, Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats. The ''sharki'' is used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambur
The ''tambur'' (spelled in keeping with TDK conventions) is a fretted string instrument of Turkey and the former lands of the Ottoman Empire. Like the ney, the armudi (lit. pear-shaped) kemençe and the kudüm, it constitutes one of the four instruments of the basic quartet of Turkish classical music. Of the two variants, one is played with a plectrum (''mızraplı tambur'') and the other with a bow ('' yaylı tambur''). The player is called a ''tamburî''.Tambur Republic of Turkey - Ministry of Culture and Tourism History and development There are several hypotheses as to the origin of the instrument. One suggests that it descended from the kopuz, a string instrument still in use among the Turkic peoples of Central Asia and the Caspian region. T ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandura
The pandura ( grc, πανδοῦρα, ''pandoura'') or pandore, an ancient string instrument, belonged in the broad class of the lute and guitar instruments. Akkadians played similar instruments from the 3rd millennium BC. Ancient Greek artwork depicts such lutes from the 3rd or 4th century BC onward. Ancient Greece The ancient Greek ''pandoura'' was a medium or long-necked lute with a small resonating chamber, used by the ancient Greeks. It commonly had three strings: such an instrument was also known as the ''trichordon'' (three-stringed) (τρίχορδον, McKinnon 1984:10). Its descendants still survive as the Kartvelian panduri, the Greek tambouras and bouzouki, the North African kuitra, the Eastern Mediterranean saz and the Balkan tamburica and remained popular also in the near east and eastern Europe, too, usually acquiring a third string in the course of time, since the fourth century BC. Renato Meucci (1996) suggests that the some Italian Renaissance descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, , or , ''Kiní Neoellinikí Glóssa''), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the languages sometimes referred to as Standard Modern Greek. The end of the Medieval Greek period and the beginning of Modern Greek is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic features of the modern language arose centuries earlier, beginning around the fourth century AD. During most of the Modern Greek period, the language existed in a situation of diglossia, with regional spoken dialects existing side by side with learned, more archaic written forms, as with the vernacular and learned varieties ('' Dimotiki'' and '' Katharevousa'') that co-existed in Greece throughout much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Varieties Varieties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanpura
The tanpura (), also referred to as tambura and tanpuri, is a long-necked plucked string instrument, originating in India, found in various forms in Indian music. It does not play melody, but rather supports and sustains the melody of another instrument or singer by providing a continuous harmonic bourdon or drone. A tanpura is not played in rhythm with the soloist or percussionist: as the precise timing of plucking a cycle of four strings in a continuous loop is a determinant factor in the resultant sound, it is played unchangingly during the complete performance. The repeated cycle of plucking all strings creates the sonic canvas on which the melody of the raga is drawn. The combined sound of all strings–each string a fundamental tone with its own spectrum of overtones–supports and blends with the external tones sung or played by the soloist. Hindustani musicians favour the term ''tanpura'' whereas Carnatic musicians say ''tambura''; ''tanpuri'' is a smaller va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |