|
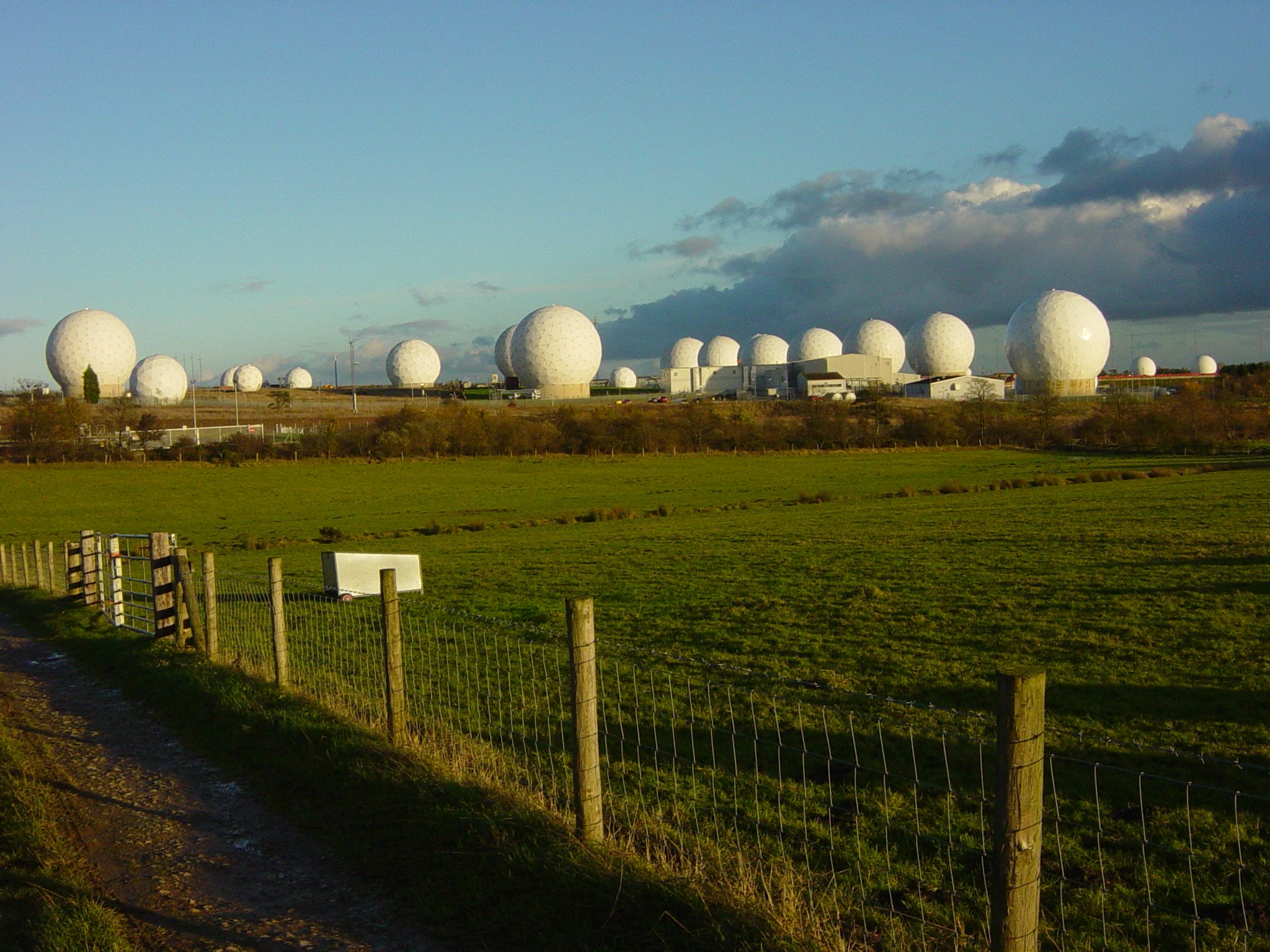
Tamara Passive Sensor
Tamara was the third generation Czechoslovak electronic support measures ( ESM) system that used measurements of time difference of arrival (TDOA) of pulses at three or four sites to accurately detect and track airborne emitters by multilateration. Tamara's designations were KRTP-86 and KRTP-91 and it carried the NATO reporting name of Trash Can. The designation was derived from the Czech phrase "Komplet Radiotechnického Průzkumu" meaning "Radiotechnical Reconnaissance Set". It was claimed to be the only one in the world able to detect military " invisible aircraft". History Development of Tamara by the state-run company Tesla in Pardubice began in 1981 and continued until 1983. Tests of a mobile system began in September 1984 through to 1985. It was finally deployed in 1987 following acceptance tests in October of that year. In 1991 the baseline KRTP-86 Tamara was superseded in production by the improved KRTP-91 Tamara-M. Appearance Unlike its predecessors, Tamara was a mob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי, , common_name = Czechoslovakia , life_span = 1918–19391945–1992 , p1 = Austria-Hungary , image_p1 = , s1 = Czech Republic , flag_s1 = Flag of the Czech Republic.svg , s2 = Slovakia , flag_s2 = Flag of Slovakia.svg , image_flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia.svg , flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia , flag_type = Flag(1920–1992) , flag_border = Flag of Czechoslovakia , image_coat = Middle coat of arms of Czechoslovakia.svg , symbol_type = Middle coat of arms(1918–1938 and 1945–1961) , image_map = Czechoslovakia location map.svg , image_map_caption = Czechoslovakia during the interwar period and the Cold War , national_motto = , anthems = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
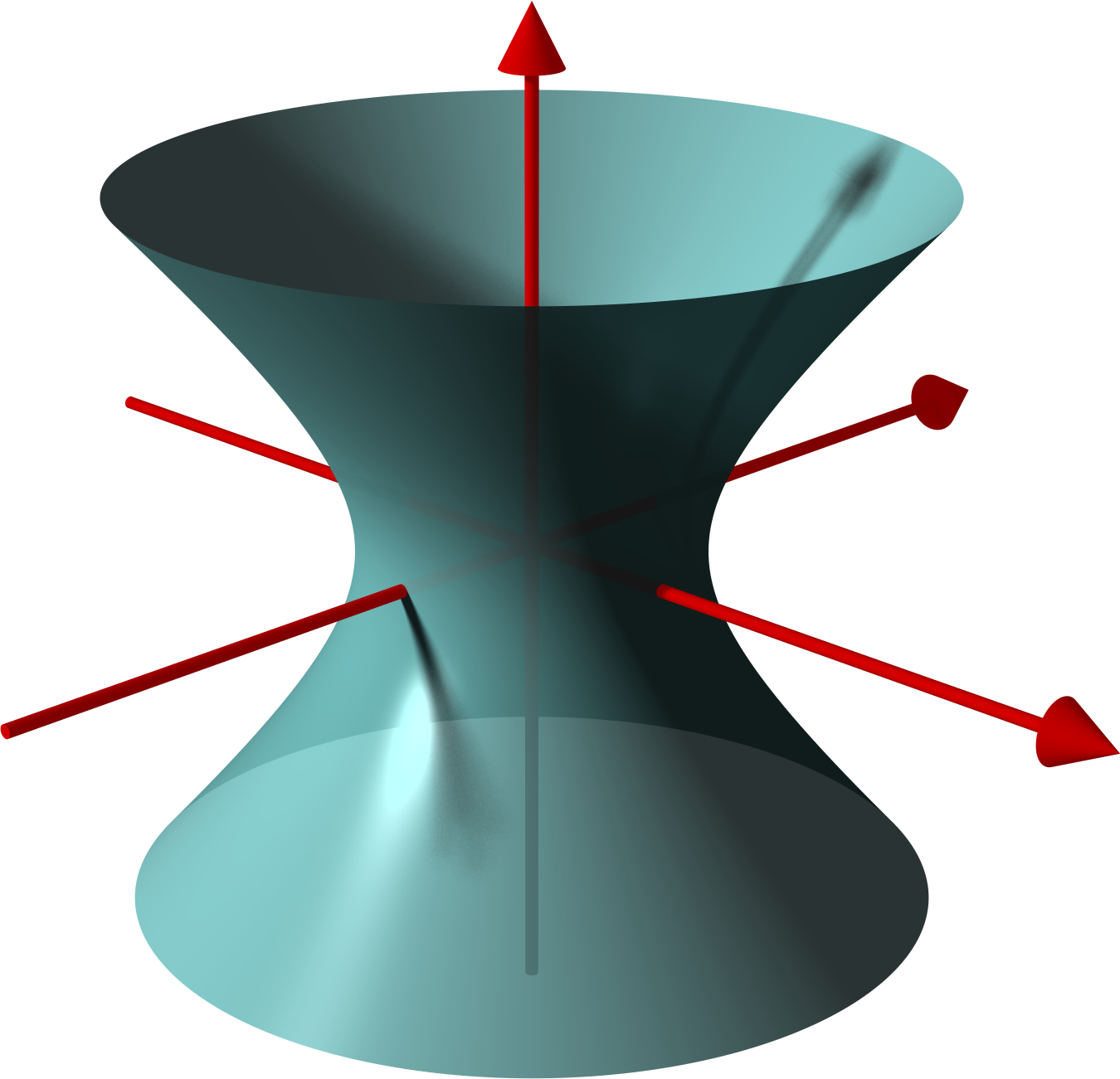
Hyperboloid
In geometry, a hyperboloid of revolution, sometimes called a circular hyperboloid, is the surface generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its principal axes. A hyperboloid is the surface obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. A hyperboloid is a quadric surface, that is, a surface defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, a hyperboloid is characterized by not being a cone or a cylinder, having a center of symmetry, and intersecting many planes into hyperbolas. A hyperboloid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry, and three pairwise perpendicular planes of symmetry. Given a hyperboloid, one can choose a Cartesian coordinate system such that the hyperboloid is defined by one of the following equations: : + - = 1, or : + - = -1. The coordinate axes are axes of symmetry of the hyperboloid and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELINT
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of '' signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication (electronic intelligence—abbreviated to ELINT). Signals intelligence is a subset of intelligence collection management. As classified and sensitive information is usually encrypted, signals intelligence in turn involves the use of cryptanalysis to decipher the messages. Traffic analysis—the study of who is signaling whom and in what quantity—is also used to integrate information again. History Origins Electronic interceptions appeared as early as 1900, during the Boer War of 1899–1902. The British Royal Navy had installed wireless sets produced by Marconi on board their ships in the late 1890s, and the British Army used some limited wireless signalling. The Boers captured some wireless sets and used them to make vital tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VERA Passive Sensor
The VERA passive radar (known as ''Věra'' in Czech) is an electronic support measures (ESM) system that uses measurements of time difference of arrival (TDOA) of pulses at three or four sites to accurately detect and track airborne emitters. It is reportedly able to detect military " invisible aircraft". The manufacturer is , based in Pardubice. Mode of operation The deployed system typically comprises a central site (containing the signal processing equipment and an ESM receiver) and two or three side sites containing only an ESM receiver. The side sites relay the signals received to the central site over a point-to-point microwave link. The central site uses the known propagation delay from the side sites to estimate the TDOA of the pulses at each site. The TDOA of a pulse between one side site and the central site locates the target on a hyperboloid. A second side site provides a second TDOA and hence a second hyperboloid. The intersection of these two hyperboloids plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramona Passive Sensor
Ramona was the second generation Czechoslovak electronic support measures ( ESM) system that uses measurements of time difference of arrival (TDOA) of pulses at three or four sites to accurately detect and track airborne emitters by multilateration. History Ramona's designation was KRTP-81 and it carried the NATO reporting name of Soft Ball. The serial number was derived from the Czech phrase "''Komplet radiotechnického průzkumu''" meaning "Radiotechnical Reconnaissance Set". A later upgraded version was designated KRTP-81M. Ramona was deployed in 1979 and could semi-automatically track 20 targets simultaneously. It superseded Kopáč. Appearance Each receiver comprised a large spherical radome mounted on the top of a 25 m fixed mast. This radome, made of identical segments of polyurethane foam, contained the radio antennas and the microwave components, intermediate frequency preamplifiers and the two-way communications equipment for communicating between central and side si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kopáč Passive Sensor
Kopáč (the word means "''digger''" in Czech) was an early electronic warfare support measures (ESM) system developed in Czechoslovakia in the early 1960s that used measurements of time difference of arrival (TDOA) of pulses at three sites to accurately detect and track airborne emitters. The system used the principle of multilateration and was capable of simultaneously manually tracking up to six targets. It was first deployed in 1963 and was also known by its serial number, PRP-1. The initials PRP come from the Czech "Přesný radiotechnický pátrač", meaning "Accurate Radiotechnical Locator", the name comes from "Korelační pátrač", meaning "Correlation Locator". The concept was derived by Vlastimil Pech and patented in Czechoslovak classified patent 771 on November 13, 1961. Subsequent related patents 830, 852 and 859 were filed by Vladimír Zárybnický in 1962. The system used analogue signal processing and operated in D, G/ H and I/ J bands, as well as specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".Patrick Major, Jonathan Osmond, ''The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany Under Ulbricht 1945–71'', Manchester University Press, 2002, Its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship. The GDR was est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Horizon
Line-of-sight propagation is a characteristic of electromagnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation which means waves travel in a direct path from the source to the receiver. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line. The rays or waves may be diffracted, refracted, reflected, or absorbed by the atmosphere and obstructions with material and generally cannot travel over the horizon or behind obstacles. In contrast to line-of-sight propagation, at low frequency (below approximately 3 MHz) due to diffraction, radio waves can travel as ground waves, which follow the contour of the Earth. This enables AM radio stations to transmit beyond the horizon. Additionally, frequencies in the shortwave bands between approximately 1 and 30 MHz, can be refracted back to Earth by the ionosphere, called skywave or "skip" propagation, thus giving radio transmissions in this range a potentially global reach. However, at frequencies abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identification Friend Or Foe
Identification, friend or foe (IFF) is an identification system designed for command and control. It uses a transponder that listens for an ''interrogation'' signal and then sends a ''response'' that identifies the broadcaster. IFF systems usually use radar frequencies, but other electromagnetic frequencies, radio or infrared, may be used. It enables military and civilian air traffic control interrogation systems to identify aircraft, vehicles or forces as friendly and to determine their bearing and range from the interrogator. IFF is used by both military and civilian aircraft. IFF was first developed during World War II, with the arrival of radar, and several friendly fire incidents. IFF can only positively identify friendly aircraft or other forces. If an IFF interrogation receives no reply or an invalid reply, the object is not positively identified as foe; friendly forces may not properly reply to IFF for various reasons such as equipment malfunction, and parties in the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propagation Delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics. ''Hold time'' is the minimum interval required for the logic level to remain on the input after triggering edge of the clock pulse. Networking In computer networks, propagation delay is the amount of time it takes for the head of the signal to travel from the sender to the receiver. It can be computed as the ratio between the link length and the propagation speed over the specific medium. Propagation delay is equal to ''d / s'' where ''d'' is the distance and ''s'' is the wave propagation speed. In wireless communication, ''s''=''c'', i.e. the speed of light. In copper wire, the speed ''s'' generally ranges from .59c to .77c. This delay is the major obstacle in the development of high-speed computers and is called the interconnect bottleneck in IC systems. Electronics In electronics, digital circuits and digital electronics, the propaga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |