|
Tal-y-bont, Conwy
Tal-y-Bont is a small village in Conwy County Borough, Wales and lies in the Conwy Valley, west of the River Conwy, on the B5106 road, from the town of Conwy to the north, and six miles from Llanrwst to the south, and in the community of Caerhun. It lies adjacent to the village of Dolgarrog to the south, and below the small settlement of Llanbedr-y-Cennin to the west. The population is around 400. The 'Bont' (the mutated form of ''pont'', Welsh for "bridge") in the name probably refers to the bridge over the Afon Dulyn, a tributary of the nearby River Conwy, which runs through the village. The village is served by buses and the nearby Dolgarrog railway station. Castell, the oldest section of Tal-y-Bont, has a bar/restaurant and a 5-acre garden centre. The village also has a shop and post office and a café, formerly Y Bedol Pub. Access to Snowdonia and the Carneddau Tal-y-Bont is the starting point for the road to Llyn Eigiau and the southern Carneddau mountains. Access ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caerhun
Caerhun () is a scattered rural Community (Wales), community, and former Community (Wales), civil parish, on the west bank of the River Conwy. It lies to the south of Henryd and the north of Dolgarrog, in Conwy County Borough, Wales, and includes several small villages and hamlets including Llanbedr-y-Cennin, Llanbedr-y-cennin, Rowen, Conwy, Rowen, Tal-y-bont, Conwy, Tal-y-bont and Ty'n-y-groes. It was formerly in the historic county of Caernarvonshire. At the 2001 census, it had a population of 1,200, increasing to 1,292 at the 2011 census. It includes a large part of the Carneddau range including the lakes of Llyn Eigiau, Llyn Dulyn and Llyn Melynllyn. Features Surrounding the 14th-century parish church of St Mary's Church, Caerhun, St. Mary are the banks of the castra, Roman fort of Canovium. The excavations of the Roman site were directed by P.K. Baillie Reynolds, of Aberystwyth University, over a period of four summers in the 1920s,. Page found on Kanovium Project websit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
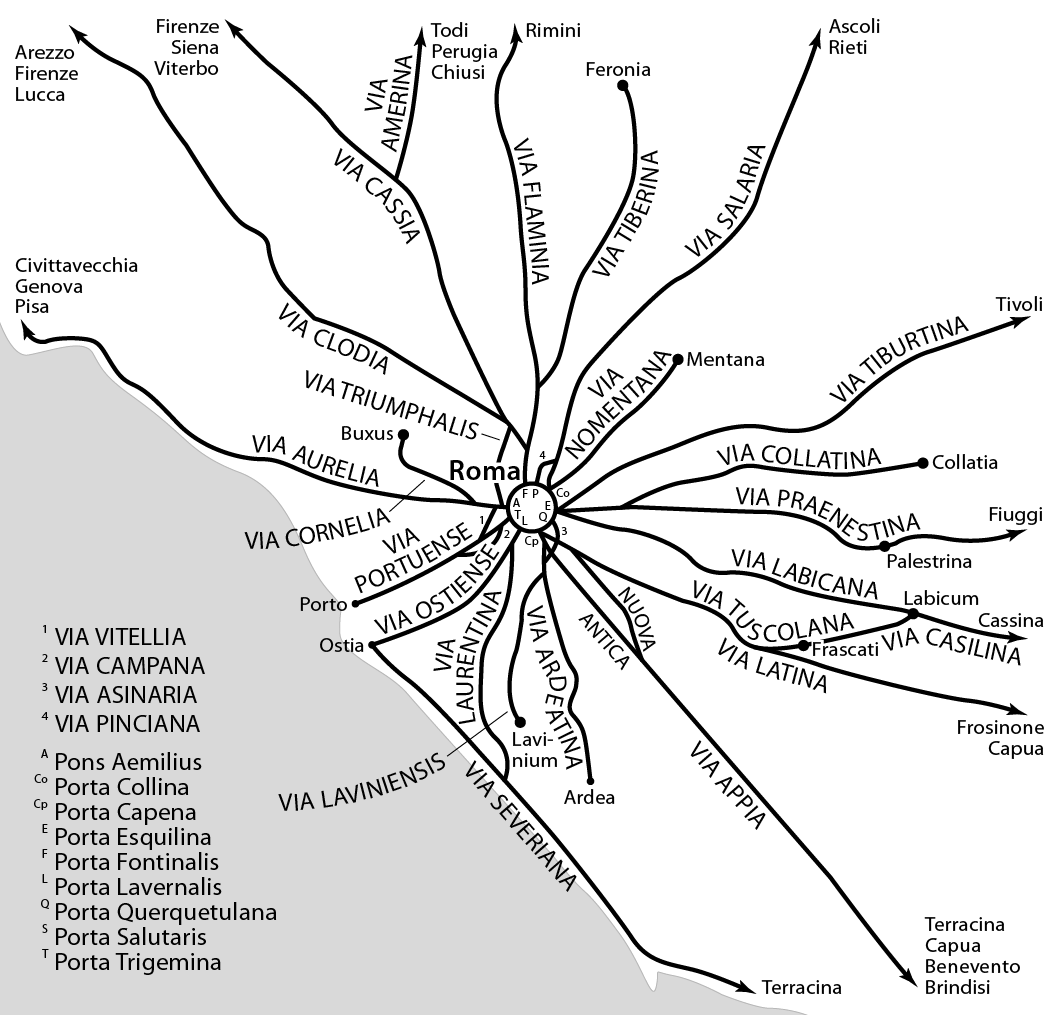
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canovium
Canovium was a fort in the Roman province of Britannia. Its site is located at Caerhun in the Conwy valley, in the county borough of Conwy, in North Wales. Etymology The fort appears in the Antonine Itinerary as ''Conovio'' and in the Ravenna Cosmography as ''Canubio''. The first element possibly represents a borrowing into Latin of a pre-existing Brythonic name for the wetland area (from a word meaning reeds, ''cawn'' in Modern Welsh). Although the second element may derive froNovius(meaning new), it has also been proposed that the –ovium termination may simply mean ''water'' or ''river''. Both of these etymologies would seem to reflect the purpose of building a new fort at this location, to control the lowest fording point across the river Conwy. Early history Canovium was a square fort built in timber at an important river crossing (at Tal-y-Cafn) by the Roman army around AD 75, possibly to house a 500-strong regiment of foot-soldiers. Rebuilding in stone began in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Fort
''Castra'' () is a Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discussion about the typologies of Roman fortifications. In English usage, ''castrum'' commonly translates to "Roman fort", "Roman camp" and "Roman fortress". Scholastic convention tends to translate ''castrum'' as "fort", "camp", "marching camp" or "fortress". Romans used the term ''castrum'' for different sizes of camps – including large legionary fortresses, smaller forts for cohorts or for auxiliary forces, temporary encampments, and "marching" forts. The diminutive form ''castellum'' was used for fortlets, typically occupied by a detachment of a cohort or a ''centuria''. Etymology ''Castrum'' appears in Oscan and Umbrian, two other Italic languages, suggesting an origin at least as old as Proto-Italic language. Julius Pokorny traces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamlet (place)
A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. This is often simply an informal description of a smaller settlement or possibly a subdivision or satellite entity to a larger settlement. Sometimes a hamlet is defined for official or Administrative division, administrative purposes. The word and concept of a hamlet can be traced back to Anglo-Normans, Norman England, where the Old French came to apply to small human settlements. Etymology The word comes from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman ', corresponding to Old French ', the diminutive of Old French ' meaning a little village. This, in turn, is a diminutive of Old French ', possibly borrowed from (West Germanic languages, West Germanic) Franconian languages. It is related to the modern French ', Dutch language, Dutch ', Frisian languages, Frisian ', German ', Old English ', and Modern English ''home''. By country Afghanistan In Afghanistan, the counterpart of the hamlet is the Qila, qala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llandudno
Llandudno (, ) is a seaside resort, town and community (Wales), community in Conwy County Borough, Wales, located on the Creuddyn peninsula, which protrudes into the Irish Sea. In the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 UK census, the community – which includes Gogarth, Penrhyn Bay, Craigside, Glanwydden, Penrhynside, and Bryn Pydew – had a population of 19,700 (rounded to the nearest 100). The town's name means "Church of Saint Tudno". Llandudno is a major seaside resort in Wales, and as early as 1861 was being called 'the Queen of the Welsh Watering Places' (a phrase later also used in connection with Tenby and Aberystwyth; the word 'resort' came a little later). Historic counties of Wales, Historically a part of Caernarfonshire, Llandudno was formerly in the district of Aberconwy within Gwynedd until 1996. History The town of Llandudno developed from Stone Age all the way through to Iron Age settlements over many hundreds of years on the slopes of the limestone headland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillfort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roman Empire, Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of Earthworks (Archaeology), earthworks or stone Rampart (fortification), ramparts, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. If enemies were approaching, the inhabitants would spot them from a distance. Prehistoric Europe saw a growing population. It has been estimated that in about 5000 BC during the Neolithic between 2 million and 5 million lived in Europe; in the Late Iron Age it had an estimated population of around 15 to 30 million. Outside Greece and Italy, which were more densely populated, the vast majority of settlements in the Iron Age were small, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
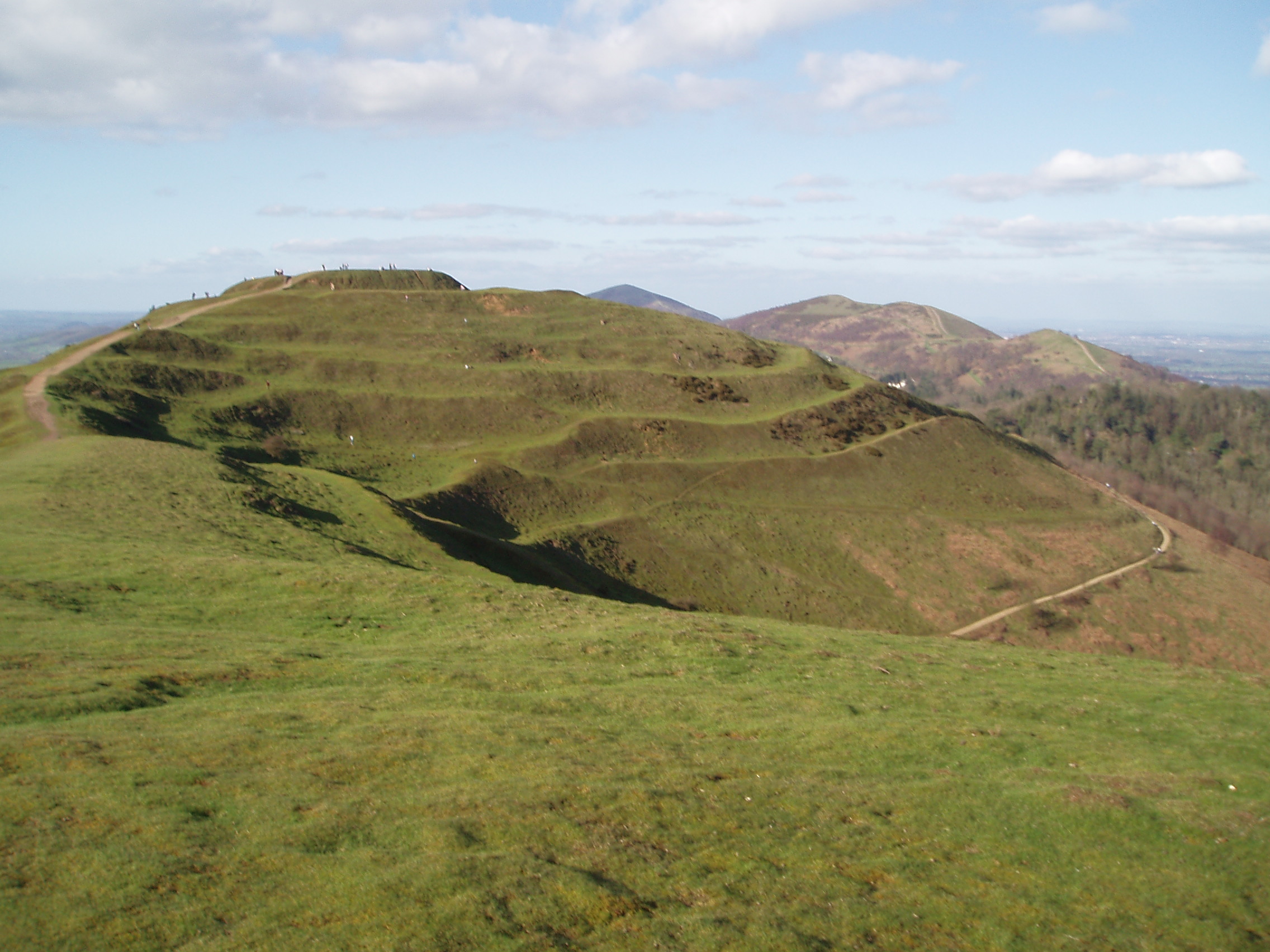
Pen-y-Gaer
Pen y Gaer (or Pen-y-gaer) is the location of a Bronze Age and Iron Age hillfort near the village of Llanbedr-y-Cennin in the Conwy valley, Wales. A natural defensive site, it had a long history of occupation, indicated by the complexity of the defences, which were amended over time. There are two Bronze Age cairns on the north-west slope, and extensive prehistoric and later field systems are nearby. The remains as seen today are mostly of Iron Age origin, but further earthworks, probably of medieval origin, lie on the south-eastern slopes. The remains of the two walls of stone can be seen, as can those of a chevaux-de-frise. The entrance is to the west, and access can be gained from a car park, reached by the road from the village. See also * List of hillforts in Wales External links Royal Commission site, with photosA BBC page {{DEFAULTSORT:Pen Y Gaer Caerhun Archaeological sites in Conwy County Borough Hillforts in Conwy County Borough Mountains and hills of Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnedd Llewelyn
Carnedd Llewelyn, also spelled Carnedd Llywelyn, is a mountain massif in the Carneddau range in Snowdonia, north-west Wales. It is the highest point of the Carneddau at and the second-highest peak by relative height in Wales, 49th in the British Isles and lies on the border between Gwynedd and Conwy. Topography and ascent routes Carnedd Llewelyn lies in the middle of the main north-east to south-west ridge of the Carneddau, between Carnedd Dafydd to the south-west and Foel Grach to the north. A short subsidiary ridge links it to Yr Elen to the north-west. It can be climbed from Gerlan, above Bethesda, taking the path following Afon Llafar then continuing to the summit of Yr Elen before following the short ridge to Carnedd Llewelyn. Another path starts from Helyg on the A5, taking the track to the reservoir then following the slopes above Craig yr Ysfa to the summit. An alternative is to reach it by following the main ridge, either from Pen yr Ole Wen or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foel Fras
Foel-fras (944 m / 3,097 ft) is a mountain in the Carneddau range, about 10 km east of Bethesda in North Wales. It lies on the border between the counties of Gwynedd and Conwy. With a summit elevation of 944 metres (3,074 feet), it is officially the eleventh-highest summit in Wales. Foel-fras is located at the northern end of the main ridge of the Carneddau, between Drum to the north and Foel Grach to the south with the subsidiary summit of Garnedd Uchaf (925 m / 3,034 ft) between it and Foel Grach. Due south and 400 m below lies the reservoir of Llyn Dulyn, while the smaller reservoir of Llyn Anafon lies to the north. Because of its position, it is the first of the Welsh 3000s reached when doing this walk from the northern end. It can be climbed by driving up the small road signposted " Aber Falls" in the village of Abergwyngregyn, passing the car park for the falls and continuing to a small car park at the end of the road. From there it is possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drum (Wales)
Drum () ( Welsh: Y Drum = ''the ridge'') is a summit in the Carneddau mountains in northern Wales, 2 km north-east of Foel-fras. It is 771 m (2,526 ft) high. It is also known as Carnedd Penyborth-Goch. Its eastern slopes are drained by the Afon Tafolog, a tributary of Afon Roe which flows through the village of Rowen before joining the River Conwy The River Conwy (; ) is a river in north Wales. From its source to its discharge in Conwy Bay it is long and drains an area of 678 square km. "Conwy" was formerly anglicised as "Conway." The name 'Conwy' derives from the old Welsh words ''c ....Nuttall, John & Anne (1999). The Mountains of England & Wales - Volume 1: Wales (2nd edition ed.). Milnthorpe, Cumbria: Cicerone. . See also * Blue Joker, an experimental airborne early-warning radar, tested from a site high on the mountain in 1956 References Mountains and hills of Snowdonia Hewitts of Wales Nuttalls Mountains and hills of Conwy County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |