|
Taksaris Of Sikkim
Taksaris of Sikkim (also known as Taksari Newars) were owners of minting houses, traders, landed class and their families in the former Kingdom of Sikkim. There were six families - mostly Newars - minting coins for the erstwhile Himalayan kingdom. In the period of British influence, Chogyal of Sikkim gave these families large land estates as Thikadars, a system of hereditary leesee landlords with judicial and administrative power over their respective estates.Migration of Nepalis into Sikkim and its Impact on Political and Economic Life (1774-1975) History After contact with the British, the agrarian Sikkimese society witnessed a drastic change in land use and settlement pattern. The British encouraged migration of Nepalese to Sikkim mainly for agriculture and labour. The two Newar trade families of Lachhimidas Pradhan and Chandrabir Maskey from princely estates of Kathmandu were given land as a contract or ‘’thika’’. These new landlords hence came to be known as Newar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
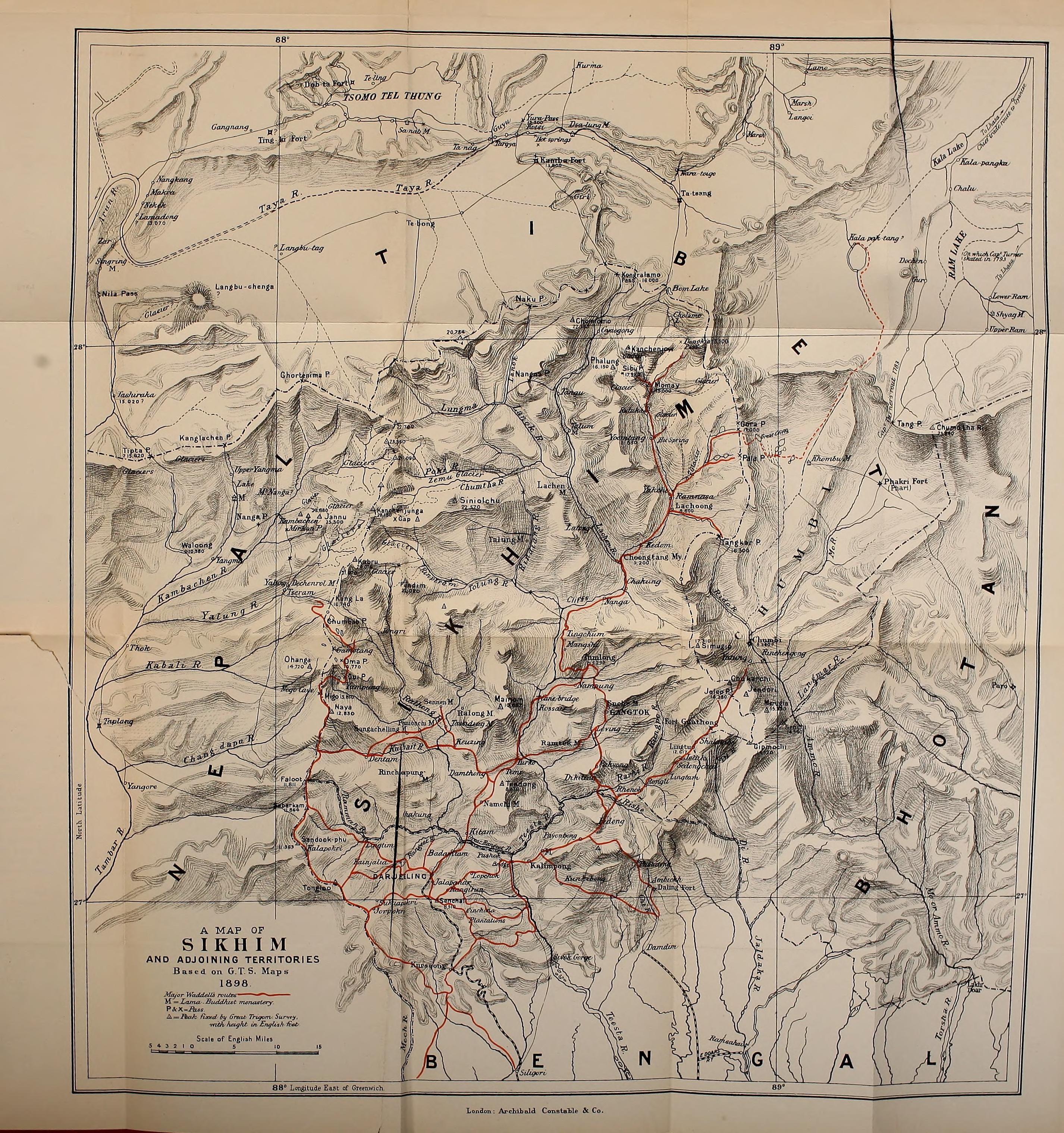
Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siliguri Corridor, which borders Bangladesh. Sikkim is the least populous and second smallest among the Indian states. Situated in the Eastern Himalaya, Sikkim is notable for its biodiversity, including alpine and subtropical climates, as well as being a host to Kangchenjunga, the highest peak in India and third highest on Earth. Sikkim's capital and largest city is Gangtok. Almost 35% of the state is covered by Khangchendzonga National Park – a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Kingdom of Sikkim was founded by the Namgyal dynasty in the 17th century. It was ruled by Buddhist priest-kings known as the Chogyal. It became a princely state of British India in 1890. Following Indian independence, Sikkim continued its protectorate status with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Sikkim
The Kingdom of Sikkim (Classical Tibetan and sip, འབྲས་ལྗོངས།, ''Drenjong''), officially Dremoshong (Classical Tibetan and sip, འབྲས་མོ་གཤོངས།) until the 1800s, was a hereditary monarchy in the Eastern Himalayas which existed from 1642 to 16 May 1975, when it merged with the India, Republic of India. It was ruled by Chogyals of the Namgyal dynasty. History Nepalese-Bhutanese domination In the mid-18th century, Sikkim was invaded by both Nepal (then the Gorkha Kingdom) and Bhutan (then ruled by Gedun Chomphel) and was under both the Gorkha and the Bhutanese rule for more than 40 years. Between 1775 and 1815, almost 180,000 ethnic Nepalis from Eastern and Central Nepal migrated to Sikkim. After the British colonisation of India, however, Sikkim allied itself with British India as they had a common enemy – Nepal. The infuriated Nepalese attacked Sikkim with vengeance, overrunning most of the region including the Terai. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazis And Thikadars Of Sikkim
Kazis and Thikadars of Sikkim also known as Ilakadars were the hereditary feudal lords and the ruling class in former Kingdom of Sikkim. They had administrative and judicial powers within their respective land estates. This system existed since the establishment of the Namgyal dynasty and was further institutionalised under the period of British influence in Sikkim. History Chogyal Phuntsog Namgyal appointed 12 ''Kalons'' or ministers from the Bhutia community and split his kingdom into 12 ''Dzongs'' or administrative units, which each contained a fort. Individual Dzongs were headed by a ''Dzonga'' drawn from amongst the Lepchas. The Limbu chiefs or the Subbas were also given full autonomy of their districts under the King. After contact with the British, the agrarian Sikkimese society witnessed a drastic change in land use and settlement pattern. The British encouraged migration of Nepalese to Sikkim mainly for agriculture and labour. The two Newar trade families of Lachhim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rai Sahib
Rai Sahib / Rao Saheb / Roy Sahib / Rao Sahib abbreviated R.S., was a title of honour issued during the era of British rule in India to individuals who performed faithful service or acts of public welfare to the nation. From 1911 the title was accompanied by a special Title Badge. Translated, ''Rai'' means "King" ''sahib'' means "leader". This was the start level title usually awarded to civilians, which could later be upgraded to Rao Bahadur and then to Dewan Bahadur titles. The title styled ''Rai Sahib'' were awarded to Hindu people of North India, Rao Saheb in Maharashtra and styled ''Rao Sahib'' to Hindu people of South India, however, they were both of same category and spelling was altered to meet with regional differences of pronunciation. The Rai Sahib/Rao Sahib/Roy Sahib and other similar titles issued during British Raj were disestablished in 1947 upon independence of India. Some people awarded the title * Rao Bahadur Satyendra Nath Mukherjee, Awarded Rai Saheb on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newars
Newar (; new, नेवार, endonym: Newa; new, नेवा, Pracalit script:) or Nepami, are the historical inhabitants of the Kathmandu Valley and its surrounding areas in Nepal and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars form a linguistic and cultural community of primarily Indo-Aryan and Tibeto-Burman ethnicities following Hinduism and Buddhism with Nepal Bhasa as their common language. Newars have developed a division of labour and a sophisticated urban civilisation not seen elsewhere in the Himalayan foothills. Newars have continued their age-old traditions and practices and pride themselves as the true custodians of the religion, culture and civilisation of Nepal. Newars are known for their contributions to culture, art and literature, trade, agriculture and cuisine. Today, they consistently rank as the most economically and socially advanced community of Nepal, according to the annual Human Development Index published by UNDP. Nepal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chogyal Of Sikkim
The Chogyal (" Dharma Kings", ) were the monarchs of the former Kingdom of Sikkim, which belonged to the Namgyal dynasty. The Chogyal was the absolute monarch of Sikkim from 1642 to 1975, when the monarchy was abolished and the Sikkimese people voted in a referendum to make Sikkim the 22nd state of India. History From 1642 to 1975, Sikkim was ruled by the Namgyal Monarchy (also called the Chogyal Monarchy), founded by Phuntsog Namgyal, the fifth-generation descendant of Guru Tashi, a prince of the Minyak House who came to Sikkim from the Kham province of Tibet. Chogyal means 'righteous ruler', and was the title conferred upon Sikkim's Buddhist kings during the reign of the Namgyal Monarchy. The reign of the Chogyal was foretold by the patron saint of Sikkim, Guru Rinpoche. The 8th-century saint had predicted the rule of the kings when he arrived in the state. In 1642, Phuntsog Namgyal was crowned as Sikkim's first Chogyal in Yuksom. The crowning of the king was a great e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar
Newar (; new, नेवार, endonym: Newa; new, नेवा, Pracalit script:) or Nepami, are the historical inhabitants of the Kathmandu Valley and its surrounding areas in Nepal and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars form a linguistic and cultural community of primarily Indo-Aryan and Tibeto-Burman ethnicities following Hinduism and Buddhism with Nepal Bhasa as their common language. Newars have developed a division of labour and a sophisticated urban civilisation not seen elsewhere in the Himalayan foothills. Newars have continued their age-old traditions and practices and pride themselves as the true custodians of the religion, culture and civilisation of Nepal. Newars are known for their contributions to culture, art and literature, trade, agriculture and cuisine. Today, they consistently rank as the most economically and socially advanced community of Nepal, according to the annual Human Development Index published by UNDP. Nep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majitar
Majitar is the fastest growing urban village in Pakyong District in the Indian state of Sikkim. The nearest towns are Rangpo ( away) and Singtam (). It is about above sea level giving it a sub-tropical climate. Majitar lies on the National Highway 10 connecting Siliguri and Gangtok. Sikkim Manipal Institute of Technology campus lies in Majitar and Rangpo railway station lies in Khanikhola, Majitar. Demographics Majitar has a large population of Sikkimese Nepalese, Sikkimese Bhutia, Marwari and Bengali people. Although there are students from all over the country, mainly those from Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand and Guwahati live at Sikkim Manipal Institute of Technology. Sikkimese Nepali is the predominant language but because of the presence of student from all over the country, people speak Hindi too. Geography Majitar is located at . It lies on the bank of River Teesta. Transport As Majitar lies on National Highway 10, frequent taxis are available towards many town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rai (title)
''Rai'' ( ur, , ; bn, রায়) is a historical title of royalty and nobility in the Indian subcontinent used by rulers and chieftains of many princely states. It is derived from ''Raja'' (king, prince or chief). The Marathi/Telugu variant Rai was used as a substitute to King. Rai has no trace in sanskrit origin. When Babur conquered Hindustan, he found many principalities which had been subordinated by the Emperor of Hindustan and innumerable others which never have been effectively subdued. When Akbar ascended to the throne, Hindustan had numerous autonomous and semiautonomous rulers. These hereditary rulers were known by various names such as ''Rais'', ''Rajas'', ''Ranas'', and ''Rawals''. During Mughal rule, while conferring a title on a Hindu or Sikh Chief the word Raja or Rai was added to the name of person. The Mughals seems to have inherited the practice of bestowing titles from the Sultans of Delhi. The appellation "Rai" is primarily applied to men, while for wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teesta
Teesta River is a long river that rises in the Pauhunri Mountain of eastern Himalayas, flows through the Indian states of Sikkim and West Bengal through Rangpur, and enters the Bay of Bengal. It drains an area of . In India, it flows through Mangan District, Gangtok District, Pakyong District, Kalimpong district, Darjeeling District, Jalpaiguri District, Cooch Behar districts and the cities of Rangpo, Jalpaiguri and Mekhliganj, Rangpur. It joins the Brahmaputra River at Phulchhari Upazila in Bangladesh. of the river lies in India and in Bangladesh. Teesta is the largest river of Sikkim and second largest river of West Bengal after the Ganges. Course The Teesta River originates from Teesta Khangtse Glacier, west of Pahunri (or Teesta Kangse) glacier above , and flows southward through gorges and rapids in the Sikkim Himalaya. It is fed by streams from Tso Lhamo Lake, Gurudongmar Lake and rivulets arising in the Thangu Valley, Yumthang Valley of Flowers, Dikchu and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangtok
Gangtok is a city, municipality, the capital and the largest populated place of the Indian state of Sikkim. It is also the headquarters of the East Sikkim district, Gangtok District. Gangtok is in the eastern Himalayas, Himalayan range, at an elevation of . The city's population of 100,000 are from different ethnicities of Sikkimese people such as Indian Gorkhas, Bhutia and Lepcha people, Lepchas. Within the higher peaks of the Himalayas and with a year-round mild temperate climate, Gangtok is at the centre of Sikkim's tourism industry. Gangtok rose to prominence as a popular Buddhist pilgrimage sites, Buddhist pilgrimage site after the construction of the Enchey Monastery in 1840. In 1894, the ruling Sikkimese Chogyal, Thutob Namgyal, transferred the capital to Gangtok. In the early 20th century, Gangtok became a major stopover on the trade route between Lhasa in Tibet and cities such as Kolkata (then Calcutta) in British India. After India won its independence from the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangpo
Rangpo is a Municipal town in Pakyong district in the Indian state of Sikkim. The town borders West Bengal's Kalimpong district and is situated along the Teesta river and Rangpo River. It is the first town of Sikkim lying on National Highway 10 that links Siliguri to Gangtok. It is about 300 m above sea level with a sub-tropical climate. It is the 'Gateway to Sikkim' and all vehicles entering Sikkim have to stop at the Rangpo Police check-post. Foreign tourists require documents to enter Sikkim state and have to show them at the police check post. Geography Rangpo is located at . It has an average elevation of 333 metres (1093 feet). The town lies on the belt of two rivers, River Teesta which comes from Dikchu-Singtam-Majitar side, and River Rangpo which comes from Rongli-Rorathang-Kumrek side. Both river meets each other below the town. The conjunction point is named as Indrakil Prayag and is considered as a holy place by Hindus. Since River Teesta is the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |