|
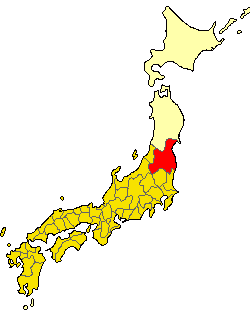
Tako Domain
was a minor feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo-period Japan, located in Shimōsa Province (the northern portion of Chiba Prefecture Japan. It was centered on what is now part of the town of Tako in Katori District. It was ruled for most of its history by the Matsudaira (Hisamatsu) clan. History Tako Domain was originally created for Hoshina Masamitsu in 1590, a retainer of Tokugawa Ieyasu. After the Battle of Sekigahara, he was transferred to Takatō Domain, and Tako Domain passed into the ''tenryō'' territories directly controlled by the Tokugawa shogunate, and administered by ''hatamoto,'' which included members of the Matsudaira (Hisamatsu) clan. In 1713, Matsudaira Katsuyuki, who administered 8000 ''koku'' within Katori District, gained an additional 3000 ''koku'' of revenue in Settsu Province. The combined amount of 12,000 ''koku'' was enough to qualify him as a ''daimyō'' and Tako Domain was revived. He was allowed to build a ''jin'ya'' in what later beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han System
( ja, 藩, "domain") is a Japanese historical term for the estate of a daimyo in the Edo period (1603–1868) and early Meiji period (1868–1912). Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Han"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 283. or (daimyo domain) served as a system of ''de facto'' administrative divisions of Japan alongside the ''de jure'' provinces until they were abolished in the 1870s. History Pre-Edo period The concept of originated as the personal estates of prominent warriors after the rise of the Kamakura Shogunate in 1185, which also saw the rise of feudalism and the samurai noble warrior class in Japan. This situation existed for 400 years during the Kamakura Shogunate (1185–1333), the brief Kenmu Restoration (1333–1336), and the Ashikaga Shogunate (1336–1573). became increasingly important as ''de facto'' administrative divisions as subsequent Shoguns stripped the Imperial provinces () and their officials of their legal powers. Edo period Toyotomi Hideyoshi, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Settsu Province
was a province of Japan, which today comprises the southeastern part of Hyōgo Prefecture and the northern part of Osaka Prefecture. It was also referred to as or . Osaka and Osaka Castle were the main center of the province. Most of Settsu's area comprises the modern day cities of Osaka and Kōbe. History During the Sengoku period, the Miyoshi clan ruled Settsu and its neighbors, Izumi and Kawachi, until they were conquered by Oda Nobunaga. The provinces were ruled subsequently by Toyotomi Hideyoshi. The regents of Hideyoshi's son soon quarreled, and when Ishida Mitsunari lost the Battle of Sekigahara, the area was given to relatives of Tokugawa Ieyasu. It was from then on divided into several domains, including the Asada Domain. Sumiyoshi taisha was designated as the chief Shinto shrine (''ichinomiya'') for the province. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoshina Clan
The is a Japanese clan which claims descent from Emperor Seiwa, and is a branch of the Minamoto clan. They were famous for their role as retainers of the Takeda clan in the 16th century. In the Edo period, the clan produced two ''daimyō'' families: one ruling the Aizu domain, the other one ruling the Iino Domain. The Aizu-Matsudaira were descended from Hoshina Masayuki, a son of Tokugawa Hidetada, adopted by Hoshina Masamitsu. Matsudaira Katamori and Hoshina Masaari, two prominent figures of the Bakumatsu period, were members of the Hoshina clan. Family head # Hoshina Tadanaga # Hoshina Naganao # Hoshina Nagatoki # Hoshina Mitsutoshi # Hoshina Masatomo # Hoshina Masatoshi # Hoshina Masanori # Hoshina Masatoshi # Hoshina Masanao # Hoshina Masamitsu was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Edo period, who served the Tokugawa clan. Masamitsu was the son of Hoshina Masanao, and after having lent his support to Tokugawa Ieyasu at the 1600 Battle of Sekigahara, he was given the Takat� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaku Kuyomon
Kaku may refer to: * Kaku (name) * Kaku (TV channel), a channel of Beijing TV * Kaku, Golestan, a village in Golestan Province, Iran * Kaku, Kurdistan (other), villages in Kurdistan Province, Iran *Kaku, Nepal * Kaku, Rõuge Parish, a village in Rõuge Parish, Võru County, Estonia * Kaku, Võru Parish, a village in Võru Parish, Võru County, Estonia * Käku, a village in Saare County, Estonia * Kaku (footballer), born ''Alejandro Romero Gamarra'', Paraguayan footballer * Michio Kaku populist scientist Fictional characters * Kaku (One Piece), a fictional character from Eiichirō Oda's manga ''One Piece'' * Kaku the Tiger, a student of Charles Darwin Middle School from the cartoon '' My Gym Partner's a Monkey'' * Kaku (king), an ancient king of Sumer * Seiga Kaku, a character from Ten Desires is the thirteenth main game of the ''Touhou Project'' dōjin game, dōjin scrolling shooter series made by Team Shanghai Alice. Gameplay ''Ten Desires'' retains the same core ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimotsuke Province
was a Provinces of Japan, province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today Tochigi Prefecture.Louis-Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''SHimotsuke''" in . Shimotsuke was bordered by Kōzuke Province, Kōzuke, Hitachi Province, Hitachi, Mutsu Province, Mutsu and Shimōsa Province, Shimōsa Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was . Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Shimotsuke was ranked as one of the 13 "great countries" (大国) in terms of importance, and one of the 30 "far countries" (遠国) in terms of distance from the capital. The provincial capital is located in what is now the city of Tochigi, Tochigi, Tochigi. The Ichinomiya of the province is the Futarasan jinja located in what is now the city of Utsunomiya, Tochigi, Utsunomiya. History During the 4th century AD, (Kofun period) the area of modern Gunma and southern Tochigi prefectures were known as . At some unknown point in the 5th century, the area was divided at the Kinugawa River i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffrey Mass
Jeffrey Paul Mass (June 29, 1940 – March 30, 2001) was an American academic, historian, author and Japanologist. He was Yamato Ichihashi Professor of Japanese History at Stanford University.Sanford, John "Jeffrey Mass, a leading authority on Japanese medieval history, dead at 60,"Stanford News Service. April 9, 2001; retrieved 2012-11-9. Early life Mass was born in New York City in 1940. He earned a bachelor's degree in history from Hamilton College in 1961, a master's degree in history from New York University in 1965, and he received his doctorate in history from Yale in 1971.Hamilton College "Hamilton College Honorary Degree Presented in memoriam to Jeffrey P. Mass ’62" retrieved 2012-11-9. Career Mass joined the Stanford University faculty in 1973. He was made a full professor in 1981. After 1987, he spent the late spring and summer of each year teaching at Oxford University. During many years, his research was supported by a Fulbright Research Fellowship, a Mellon Fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadastral
A cadastre or cadaster is a comprehensive recording of the real estate or real property's metes-and-bounds of a country.Jo Henssen, ''Basic Principles of the Main Cadastral Systems in the World,'/ref> Often it is represented graphically in a cadastral map. In most countries, legal systems have developed around the original administrative systems and use the cadastre to define the dimensions and location of land parcels described in legal documentation. A land parcel or cadastral parcel is defined as "a continuous area, or more appropriately volume, that is identified by a unique set of homogeneous property rights". Cadastral surveys document the Boundary (real estate), boundaries of land ownership, by the production of documents, diagrams, sketches, plans (''plats'' in the US), charts, and maps. They were originally used to ensure reliable facts for land valuation and taxation. An example from early England is the Domesday Book in 1086. Napoleon established a comprehensive c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokudaka
refers to a system for determining land value for taxation purposes under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo-period Japan, and expressing this value in terms of ''koku'' of rice. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Koku"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 549. One 'koku' (roughly equivalent to five bushels) was generally viewed as the equivalent of enough rice to feed one person for a year. The actual revenue or income derived holding varied from region to region, and depended on the amount of actual control the fief holder held over the territory in question, but averaged around 40 percent of the theoretical ''kokudaka''. pp. 14–15. The amount taxation was not based on the actual quantity of rice harvested, but was an estimate based on the total economic yield of the land in question, with the value of other crops and produce converted to their equivalent value in terms of rice. The ranking of precedence of the ''daimyō'', or feudal rulers, was determined in part by the ''kokudaka'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han System
( ja, 藩, "domain") is a Japanese historical term for the estate of a daimyo in the Edo period (1603–1868) and early Meiji period (1868–1912). Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Han"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 283. or (daimyo domain) served as a system of ''de facto'' administrative divisions of Japan alongside the ''de jure'' provinces until they were abolished in the 1870s. History Pre-Edo period The concept of originated as the personal estates of prominent warriors after the rise of the Kamakura Shogunate in 1185, which also saw the rise of feudalism and the samurai noble warrior class in Japan. This situation existed for 400 years during the Kamakura Shogunate (1185–1333), the brief Kenmu Restoration (1333–1336), and the Ashikaga Shogunate (1336–1573). became increasingly important as ''de facto'' administrative divisions as subsequent Shoguns stripped the Imperial provinces () and their officials of their legal powers. Edo period Toyotomi Hideyoshi, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ruling emperors before the Meiji Restoration, the events restored practical abilities and consolidated the political system under the Emperor of Japan. The goals of the restored government were expressed by the new emperor in the Charter Oath. The Restoration led to enormous changes in Japan's political and social structure and spanned both the late Edo period (often called the Bakumatsu) and the beginning of the Meiji era, during which time Japan rapidly Industrialisation, industrialized and adopted Western culture, Western ideas and production methods. Foreign influence The Japanese knew they were behind the Western powers when US Commodore (United States), Commodore Matthew C. Perry came to Japan in 1853 in Black Ships, large warshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |