|
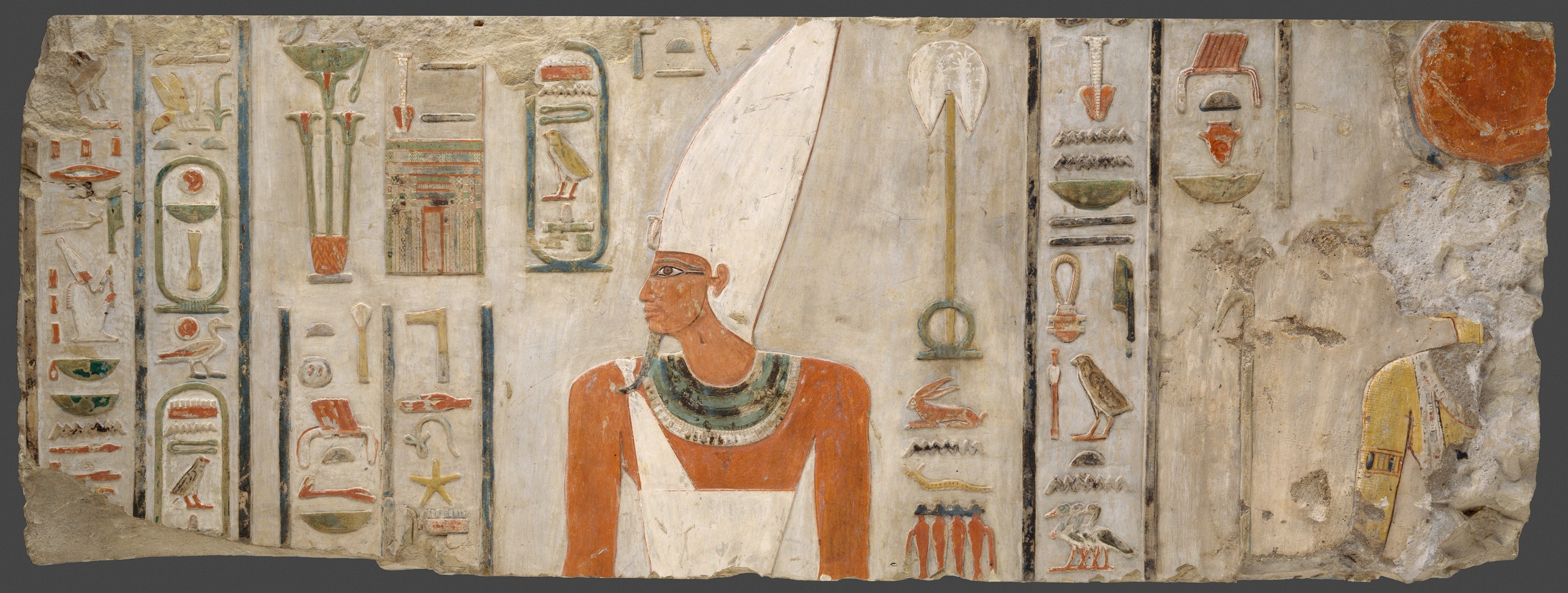
Takelot I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Takelot I was an ancient Libyan ruler who was pharaoh during the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt. Reign Takelot I was the son of Osorkon I and Queen Tashedkhons, who ruled Egypt for thirteen years according to Manetho. Takelot married Queen Kapes, who bore him Osorkon II. Initially, Takelot was believed to be an ephemeral 22nd Dynasty Pharaoh since no monuments at Tanis or Lower Egypt could be conclusively linked to his reign – or even mentioned his existence, except for the famous Stela of Pasenhor, which dates to Year 37 of Shoshenq V. However, since the late 1980s, Egyptologists have assigned several documents mentioning a king Takelot in Lower Egypt to this newly-discovered Takelot (now Takelot I), rather than the previously-known Takelot (now to be called Takelot II). Takelot I's reign was relatively short when compared to the 30+ year reigns of his father Osorkon I and son, Osorkon II. Takelot I, rather than Takelot II, was the king ''Hedjkheperre S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takelot II
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Takelot II Si-Ese was a pharaoh of the Twenty-third Dynasty of Ancient Egypt in Middle and Upper Egypt. He has been identified as the High Priest of Amun Takelot F, son of the High Priest of Amun Nimlot C at Thebes and, thus, the son of Nimlot C and grandson of king Osorkon II according to the latest academic research. Based on two lunar dates belonging to Takelot II, this Upper Egyptian pharaoh is today believed to have ascended to the throne of a divided Egypt in either 845 BC or 834 BC. Most Egyptologists today, including Aidan Dodson, Gerard Broekman, Jürgen von Beckerath, M.A. Leahy and Karl Jansen-Winkeln, also accept David Aston's hypothesis that Shoshenq III was Osorkon II's actual successor at Tanis, rather than Takelot II. As Aidan Dodson and Dyan Hilton write in their comprehensive book on the royal families of Ancient Egypt: Takelot II is likely to have been identical with the High Priest Takelot F, who is stated in heKarnak inscriptions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as (Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → (Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. With the 11th Dynasty ( 21st century BC), Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu. After the rebellion of Thebes against the Hyksos and with the rule of Ahmose I (16th century BC), Amun acquired national importance, expressed in his fusion with the Sun god, Ra, as Amun-Ra (alternatively spelled Amon-Ra or Amun-Re). Amun-Ra retained chief importance in the Egyptian pantheon throughout the New Kingdom (with the exception of the " Atenist heresy" under Akhenaten). Amun-Ra in this period (16th to 11th centuries BC) held the position of transcendental, self-created creator dei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubastis
Bubastis ( Bohairic Coptic: ''Poubasti''; Greek: ''Boubastis'' or ''Boubastos''), also known in Arabic as Tell-Basta or in Egyptian as Per-Bast, was an ancient Egyptian city. Bubastis is often identified with the biblical ''Pi-Beseth'' ( he, פי-בסת ''py-bst'', Ezekiel 30:17). It was the capital of its own nome, located along the River Nile in the Delta region of Lower Egypt, and notable as a center of worship for the feline goddess Bastet, and therefore the principal depository in Egypt of mummies of cats. Its ruins are located in the suburbs of the modern city of Zagazig. Etymology The name of Bubastis in Egyptian is ''Pr-Bȝst.t'', conventionally pronounced ''Per-Bast'' but its Earlier Egyptian pronunciation can be reconstructed as /ˈpaɾu-buˈʀistit/. It is a compound of Egyptian egy, pr, label=none “house" and the name of the goddess Bastet; thus the phrase means "House of Bast". In later forms of Egyptian, sound shifts had altered the pronunciation. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smendes III
Smendes III was a High Priest of Amun at Thebes during the reign of pharaoh Takelot I of the 22nd Dynasty. Biography The name ''Smendes'' is a hellenization of the Egyptian name ''Nesbanebdjed'' (''"He of the ram, lord of Mendes"''), while the ordinal number distinguishes him from the founder of the 21st Dynasty Smendes I, and from the earlier, namesake High Priest of Amun, Smendes II. A scarcely attested High Priest, he is mainly known for some Nile Level Texts at Karnak where he is called ''High Priest of Amun'' and ''son of king Osorkon'': No. 17 (dating to a Year 8 of a deliberately omitted king), No. 18 (Year 13 or 14, king omitted) and No. 19 (Year lost, king omitted).Kitchen, op. cit., § 96; 157. Despite the lack of a conclusive record, it is almost certain that the "king Osorkon" father of Smendes III is Osorkon I: if so, Smendes also was the brother of his two predecessors Iuwelot and Shoshenq C and of the contemporary king Takelot I. Relying on the fact that the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iuwelot
Iuwelot or Iuwlot was a High Priest of Amun at Thebes and military commander during the reign of pharaohs Osorkon I (reigned 922–887 BC) and Takelot I (reigned 885–872 BC) of the 22nd Dynasty. Biography As a son of Osorkon I, Iuwelot was brother of his predecessor Shoshenq C, of his successor Smendes III and of his contemporary king Takelot I. His earliest mention is on the so-called ''Stèle de l'apanage'', from which is known that Iuwelot was a youth in Year 10 of Osorkon I. His name appears later as High Priest of Amun on a Nile Level Text at Karnak (no. 16), dating to a Year 5 of an unknown pharaoh. Scottish Egyptologist Kenneth Kitchen argued that this king could not be Osorkon I, since it would implied that Iuwelot was already ''High Priest'' and ''Army commander of the South'' very early in his life; Kitchen thought it was much more likely that the unnamed pharaoh was Takelot I, and thus that Iuwelot must have been around 40 years old when he was appointed with such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Priests Of Amun
The High Priest of Amun or First Prophet of Amun ('' ḥm nṯr tpj n jmn'') was the highest-ranking priest in the priesthood of the ancient Egyptian god Amun. The first high priests of Amun appear in the New Kingdom of Egypt, at the beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty. History The priesthood of Amun rose in power during the early Eighteenth dynasty through significant tributes to the god Amun by ruler such as Hatshepsut and more importantly Thutmose III. The Amun priesthood in Thebes had four high-ranking priests: * The Chief Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr tpj n jmn''), also referred to as the Chief Priest of Amun. * The Second Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr snnw n jmn''), also referred to as the Second Priest of Amun. * The Third Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr ḫmtnw n jmn khemet-nu''), also referred to as the Third Priest of Amun. * The Fourth Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr jfdw n jmn''), also referred to as the Fourth Priest of Amun. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile Level Texts
The Nile Level Texts (or Nile Quay Texts) are inscribed on the cult terrace (the so-called "quay") at the temple of Karnak, in Thebes, Egypt. This cult terrace itself was constructed during the time of Ramesses II, but the kings of the 22nd to the 26th Dynasties recorded the height of the Nile on its western side. The inscriptions are invaluable records since they are dated to specific years of a certain king's reign. The cult terrace does not bear any inscriptions from the early years of reign of Taharqa, a period that is known from other sources to have been a time of drought. The texts were first examined and recorded by Georges Legrain in 1896, and later recollated by Jürgen von Beckerath in 1953. Many are now damaged or lost through erosion. References * * * *{{cite journal , author=Broekman, Gerardus P. F. , title=The Nile Level Records of the Twenty-second and Twenty-third Dynasties in Karnak: A Reconsideration of Their Chronological Order , journal=Journal of Egyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harsiese A
King Hedjkheperre Setepenamun Harsiese, or Harsiese A, is viewed by the Egyptologist Kenneth Kitchen in his Third Intermediate Period of Egypt to be both a High Priest of Amun and the son of the High Priest of Amun, Shoshenq C. The archaeological evidence does suggest that he was indeed Shoshenq C's son. However, recent published studies by the German Egyptologist Karl Jansen-Winkeln in ''JEA'' 81 (1995) have demonstrated that all the monuments of the first (king) Harsiese show that he was never a High Priest of Amun in his own right. Rather both Harsiese A and his son ..du– whose existence is known from inscriptions on the latter's funerary objects at Coptos – are only attested as Ordinary Priests of Amun. Instead, while Harsiese A was certainly an independent king at Thebes during the first decade of Osorkon II's kingship, he was a different person from a second person who was also called Harsiese: Harsiese B. Harsiese B was the genuine High Priest of Amun, who is attested i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south. In ancient Egypt, Upper Egypt was known as ''tꜣ šmꜣw'', literally "the Land of Reeds" or "the Sedgeland". It is believed to have been united by the rulers of the supposed Thinite Confederacy who absorbed their rival city states during the Naqada III period (c. 3200–3000 BC), and its subsequent unification with Lower Egypt ushered in the Early Dynastic period. Upper and Lower Egypt became intertwined in the symbolism of pharaonic sovereignty such as the Pschent double crown. Upper Egypt remained as a historical region even after the classical period. Geography Upper Egypt is between the Cataracts of the Nile beyond modern-day Aswan, downriver (northward) to the area of El-Ayait, which places modern-day Cairo in Lower Egypt. The northern (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Kingdom Of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt (also known as The Period of Reunification) is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximately 2040 to 1782 BC, stretching from the reunification of Egypt under the reign of Mentuhotep II in the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Twelfth Dynasty. The kings of the Eleventh Dynasty ruled from Thebes and the kings of the Twelfth Dynasty ruled from el-Lisht. The concept of the Middle Kingdom as one of three golden ages was coined in 1845 by German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition evolved significantly throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. Some scholars also include the Thirteenth Dynasty of Egypt wholly into this period, in which case the Middle Kingdom would end around 1650 BC, while others only include it until Merneferre Ay around 1700 BC, last king of this dynasty to be attested in both Upper and Lower Egypt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ushabti
The ushabti (also called shabti or shawabti, with a number of variant spellings) was a funerary figurine used in ancient Egyptian funerary practices. The Egyptological term is derived from , which replaced earlier , perhaps the nisba of "'' Persea'' tree". Ushabtis were placed in tombs among the grave goods and were intended to act as servants or minions for the deceased, should they be called upon to do manual labor in the afterlife. The figurines frequently carried a hoe on their shoulder and a basket on their backs, implying they were intended to farm for the deceased. They were usually written on by the use of hieroglyphs typically found on the legs. They carried inscriptions asserting their readiness to answer the gods' summons to work. The practice of using ushabtis originated in the Old Kingdom of Egypt (c. 2600 to 2100 BCE), with the use of life-sized reserve heads made from limestone, which were buried with the mummy. Most ushabtis were of minor size, and many pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(2865505031).jpg)