|
Takefu Sōdō
is a city located in Fukui Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 83,078 in 20.341 households and the population density of 360 persons per km². The total area of the city was . The modern city of Echizen was established on October 1, 2005, from the merger of the city of Takefu and the town of Imadate (from Imadate District); although the Echizen Basin has been an important regional center for over 1,500 years. The city is home to the largest number of cultural assets in Fukui Prefecture and has many former castle sites and prehistoric archeological sites. Geography Echizen is located in central Fukui Prefecture, bordered by mountains on three sides. Neighbouring municipalities *Fukui Prefecture ** Fukui ** Sabae ** Ikeda ** Minamiechizen ** Echizen (town) Climate Echizen has a Humid climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') influenced by its proximity to the Sea of Japan, and is characterized by warm, wet summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities Of Japan
A is a local administrative unit in Japan. Cities are ranked on the same level as and , with the difference that they are not a component of . Like other contemporary administrative units, they are defined by the Local Autonomy Law of 1947. City status Article 8 of the Local Autonomy Law sets the following conditions for a municipality to be designated as a city: *Population must generally be 50,000 or greater (原則として人口5万人以上) *At least 60% of households must be established in a central urban area (中心市街地の戸数が全戸数の6割以上) *At least 60% of households must be employed in commerce, industry or other urban occupations (商工業等の都市的業態に従事する世帯人口が全人口の6割以上) *Any other conditions set by prefectural ordinance must be satisfied (他に当該都道府県の条例で定める要件を満たしていること) The designation is approved by the prefectural governor and the Minister for Internal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikeda, Fukui
is a town located in Fukui Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 2,628 in 943 households and the population density of 14 persons per km². The total area of the town was . Geography Ikeda is located in the Imadate District, of central Fukui Prefecture, bordered by Gifu Prefecture to the south, Shiga Prefecture to the south and surrounded by mountains on all sides. Mount Kanmuri is the highest elevation at 1256 meters. The Asuwa River flows through the town. Ikeda consists mostly of narrow agricultural plains and small villages between steep, 1000–1500 m mountains in a main north-south valley and several branch valleys. The setting of the town, the old shrine in the town center, and a beautiful waterfall on the lower road to Ono are all local landmarks and are praised for their beauty, and occasionally attract tour buses from as far away as Osaka. Ikeda endures heavy snowfall in the winter, and access to neighboring towns, over mountain passes except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Hino River
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshisada Nitta
was a samurai lord of the Nanboku-chō period Japan. He was the head of the Nitta clan in the early fourteenth century, and supported the Southern Court of Emperor Go-Daigo in the Nanboku-chō period. He famously marched on Kamakura, besieging and capturing it from the Hōjō clan in 1333. Later he fought the Takauji brothers on the Emperor's behalf in a see-saw campaign which saw the capital change hands several times. After a peaceful compromise was agreed, Yoshisada was entrusted with two royal princes. At the siege of Kanegasaki (1337), both princes were killed, along with Yoshisada's son, although Yoshisada was able to escape. He committed seppuku when his horse was killed at the siege of Kuromaru. Early life Yoshisada was born in 1301, the eldest son of Nitta Tomouji. He succeeded his father and became the lord of Nitta Manor in Kōzuke Province in 1317. At this time, he also became the head of the Nitta clan. Yoshisada courted a daughter of a court noble, Kōtō-Nai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Court (Japan)
The , also known as the Ashikaga Pretenders or Northern Pretenders, were a set of six pretenders to the throne of Japan during the Nanboku-chō period from 1336 through 1392. The present Imperial House of Japan is descended from the Northern Court emperors. The Northern dynasty is also referred to as the "senior line" or the ; Jimyō-in was a temple and retirement residence of this line's emperors Go-Fukakusa and Fushimi. Nanboku-chō overview The origins of the Northern Court go back to Emperor Go-Saga, who reigned from 1242 through 1246. Go-Saga was succeeded in turn by two of his sons, Emperor Go-Fukakusa and Emperor Kameyama. On his death bed in 1272, Go-Saga insisted that his sons adopt a plan in which future emperors from the two fraternal lines would ascend the throne in alternating succession. This plan proved to be unworkable, resulting in rival factions and rival claimants to the throne. In 1333, when the Southern Emperor Go-Daigo staged the Kenmu Restoration and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiba Takatsune
was the Constable (''shugo'') of Echizen Province during the 14th century Nanboku-chō Wars in Japan. He acted to block the northward progress of Nitta Yoshisada, who supported the Emperor's Southern Court against the ''shōgun''s Northern Court. Shiba, in his role as Constable, served the ''shōgun'' and thus the Northern Court. In 1336, an ally of Nitta named Uryū Tamotsu attacked Shiba's castle, which fell soon afterwards. Two years later, Shiba was ordered by the shogun Ashikaga Takauji to attack Uryū's fortress at Somayama. The attack failed, and Shiba was forced to fight Nitta's forces again in the defense of the Kuromaru (Black Fortress). With the aid of forces sent by Takauji and warrior monks from Heisenji, the fortress was held, and Nitta Yoshisada mortally wounded in the battle. Despite this great victory, Shiba was defeated once again in 1340, when the newly throned Emperor Go-Murakami sent an army to attack the Kuromaru. Shiba was forced to surrender. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanboku-chō Period
The Nanboku-chō period (南北朝時代, ''Nanboku-chō jidai'', "North and South court period", also known as the Northern and Southern Courts period), spanning from 1336 to 1392, was a period that occurred during the formative years of the Muromachi (Ashikaga) shogunate of Japanese history.During the early period, there existed a Northern Imperial Court, established by Ashikaga Takauji in Kyoto, and a Southern Imperial Court, established by Emperor Go-Daigo in Yoshino. Ideologically, the two courts fought for 50 years, with the South giving up to the North in 1392. However, in reality the Northern court was under the power of the Ashikaga shogunate and had little real independence. The destruction of the Kamakura shogunate of 1333 and the failure of the Kenmu Restoration in 1336 opened up a legitimacy crisis for the new shogunate. Institutional changes in the estate system ('' shōen'') that formed the bedrock of the income of nobles and warriors altered the status of the var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nara Period
The of the history of Japan covers the years from CE 710 to 794. Empress Genmei established the capital of Heijō-kyō (present-day Nara). Except for a five-year period (740–745), when the capital was briefly moved again, it remained the capital of Japanese civilization until Emperor Kanmu established a new capital, Nagaoka-kyō, in 784, before moving to Heian-kyō, modern Kyoto, a decade later in 794. Japanese society during this period was predominantly agricultural and centered on village life. Most of the villagers followed Shintō, a religion based on the worship of natural and ancestral spirits named ''kami.'' The capital at Nara was modeled after Chang'an, the capital city of the Tang dynasty. In many other ways, the Japanese upper classes patterned themselves after the Chinese, including adopting the Chinese writing system, Chinese fashion, and a Chinese version of Buddhism. Literature Concentrated efforts by the imperial court to record its history produced the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provincial Temple
were Buddhist temples established in each of the provinces of Japan by Emperor Shōmu during the Nara period (710 – 794). History Shōmu (701 – 756?) decreed both a ''kokubun-ji'' for monks and a for nuns to be established in each province. Tōdai-ji, the provincial temple of Yamato Province, served as the head of all ''kokubun-ji'', and Hokke-ji held that duty for the ''kokubunni-ji''. Modern place names Modern place names based on this etymology include: *Kokubunji, Kagawa *Kokubunji, Tokyo * Kokubunji, Tochigi See also * 735–737 Japanese smallpox epidemic * Fuchū * Glossary of Japanese Buddhism * Ichinomiya is a Japanese historical term referring to the Shinto shrines with the highest rank in a province. Shrines of lower rank were designated , , , and so forth. ''Encyclopedia of Shinto'' ''Ichi no miya'' retrieved 2013-5-14. The term gave rise t ... References Buddhist temples in Japan Buddhist archaeological sites in Japan Former provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokufu
are the capitals of the historical Provinces of Japan. History As part of the Taika Reform (645) which aimed at a centralization of the administration following the Chinese model (''ritsuryō''), the kokufu and with it the office of the kokushi, replacing the older ''Kuni no miyatsuko'', developed in the 660s. The ''Wamyō Ruijushō'' (Collection of Japanese Names) from 935 contains the earliest listing of the capitals of the provinces and their location. The location of the original capitals of the 8th and 9th century are not passed down. When during the Muromachi Period, starting in the 14th century, the functions of the kokushi were increasingly transferred to military governors (''shugo''), the provincial governments (''kokuga'') lost their importance. Organisation In the center of the kokufu lay the provincial government (''kokuga'') with its offices (administration, farming, finance, police and military) and the official building of the kokushi, known as . In the peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echizen Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the northern portion of Fukui Prefecture in the Hokuriku region of Japan. Echizen bordered on Kaga, Wakasa, Hida, and Ōmi Provinces. It was part of Hokurikudō Circuit. Its abbreviated form name was . History Ancient and classical Echizen was an ancient province of Japan and is listed as one of the original provinces in the '' Nihon Shoki''. The region as a whole was sometimes referred to as . In 507, during a succession crisis, the king of Koshi was chosen to become the 26th emperor of Japan, Emperor Keitai. In 701 AD, per the reforms of the Taihō Code, Koshi was divided into three separate provinces: Echizen, Etchū, and Echigo. The original Echizen included all of what is now Ishikawa Prefecture. In 718 A.D., four districts of northern Echizen ( Hakui District, Noto District (also called Kashima District), Fugeshi District and Suzu District), were separated to form Noto Province. During the Nara period, the poet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
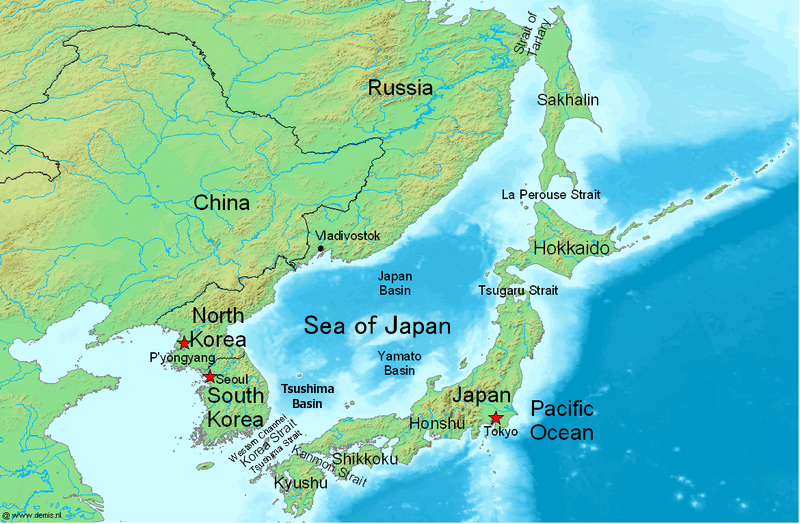
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |