|
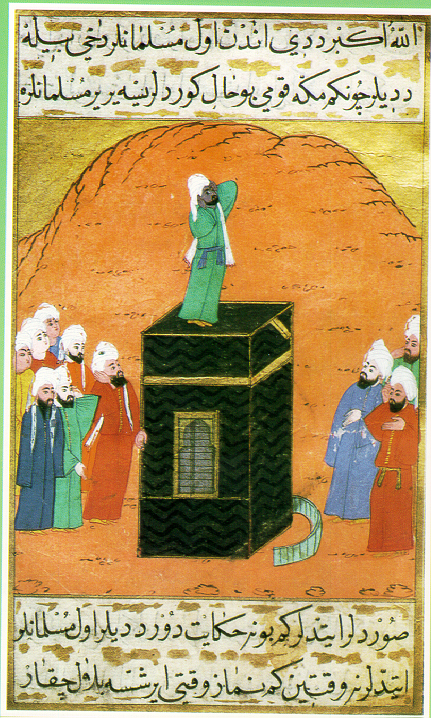
Takbir
The Takbir ( ar, تَكْبِير, , "magnification f God) is the name for the Arabic phrase ' (, ), meaning "God is the greatest". It is a common Arabic expression, used in various contexts by Muslims and Arabs around the world: in formal Salah (prayer), in the Adhan (Islamic call to prayer), in Hajj, as an informal expression of faith, in times of distress or joy, or to express resolute determination or defiance. The phrase is also used by Arab Christians. Exegesis The Arabic word () means ''great'' from the Semitic root '. The Arabic word () is the elative form (''greatest'') of the adjective ''kabīr''. When used in the it is usually translated as ''greatest'', but some authors translate it as ''greater''. The term ' itself is the stem II verbal noun of the triliteral root ', meaning "great", from which ''akbar'' "greater" is derived. The form ' is the nominative of ''Allah'', meaning 'God'.Böwering, Gerhard, ''God and His Attributes'', Encyclopaedia of the Qurʼān, Bril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takbir Of Prayer
The Takbir ( ar, تَكْبِير, , "magnification f God) is the name for the Arabic phrase ' (, ), meaning "God is the greatest". It is a common Arabic expression, used in various contexts by Muslims and Arabs around the world: in formal Salah (prayer), in the Adhan (Islamic call to prayer), in Hajj, as an informal expression of faith, in times of distress or joy, or to express resolute determination or defiance. The phrase is also used by Arab Christians. Exegesis The Arabic word () means ''great'' from the Semitic root '. The Arabic word () is the elative form (''greatest'') of the adjective ''kabīr''. When used in the it is usually translated as ''greatest'', but some authors translate it as ''greater''. The term ' itself is the stem II verbal noun of the triliteral root ', meaning "great", from which ''akbar'' "greater" is derived. The form ' is the nominative of ''Allah'', meaning 'God'.Böwering, Gerhard, ''God and His Attributes'', Encyclopaedia of the Qurʼān, Bril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
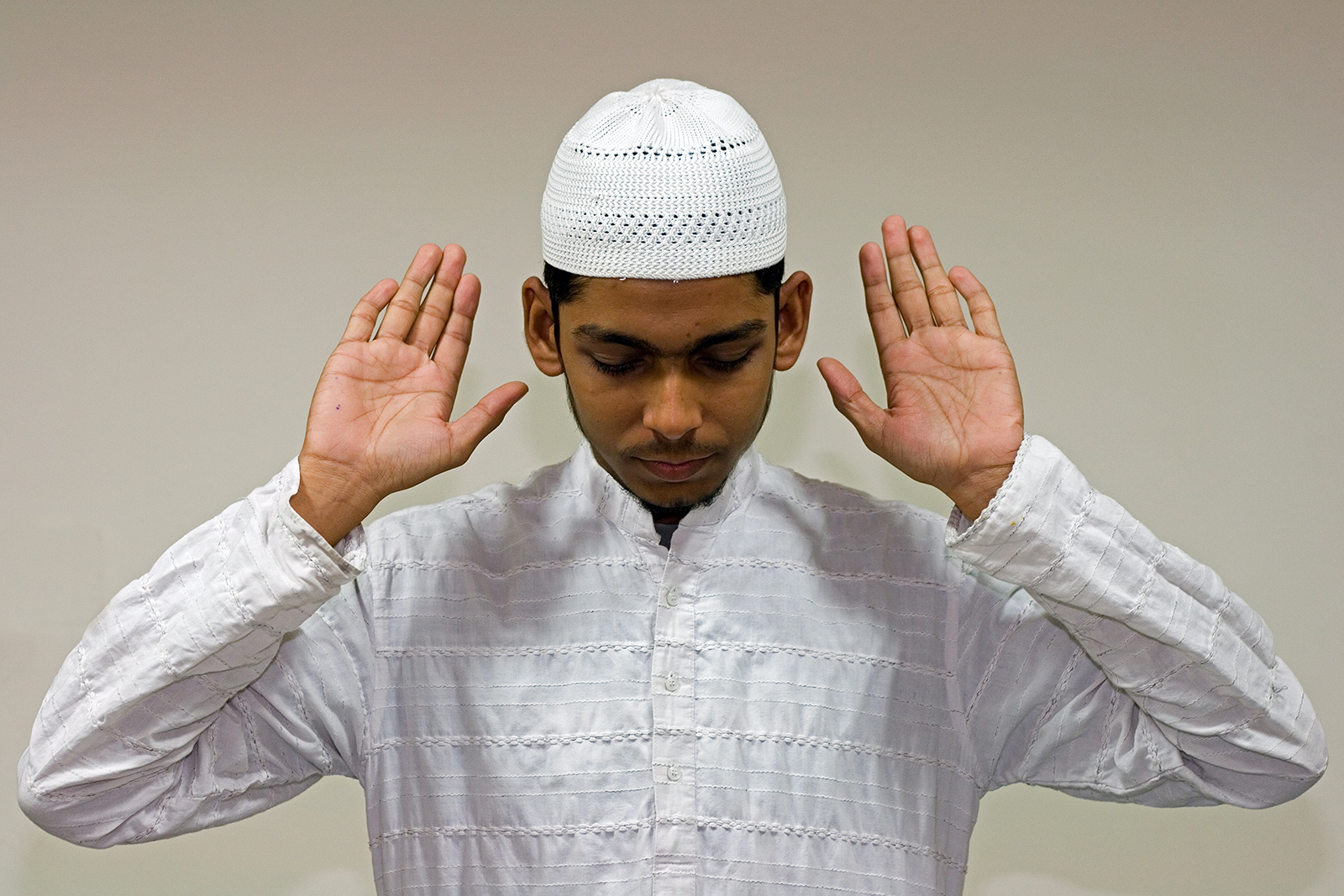
Salah
(, plural , romanized: or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːh, ( or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːtʰin construct state) ), also known as ( fa, نماز) and also spelled , are prayers performed by Muslims. Facing the , the direction of the Kaaba with respect to those praying, Muslims pray first standing and later kneeling or sitting on the ground, reciting prescribed prayers and phrases from the Quran as they bow and prostrate themselves in between. is composed of prescribed repetitive cycles of bows and prostrations, called ( ). The number of s, also known as units of prayer, varies from prayer to prayer. Ritual purity and are prerequisites for performing the prayers. The daily obligatory prayers collectively form the second of the five pillars in Islam, observed three or five times (the latter being the majority) every day at prescribed times. These are usually (observed at dawn), (observed at noon), (observed late in the afternoon), (observed after sunset), and (observed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salah
(, plural , romanized: or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːh, ( or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːtʰin construct state) ), also known as ( fa, نماز) and also spelled , are prayers performed by Muslims. Facing the , the direction of the Kaaba with respect to those praying, Muslims pray first standing and later kneeling or sitting on the ground, reciting prescribed prayers and phrases from the Quran as they bow and prostrate themselves in between. is composed of prescribed repetitive cycles of bows and prostrations, called ( ). The number of s, also known as units of prayer, varies from prayer to prayer. Ritual purity and are prerequisites for performing the prayers. The daily obligatory prayers collectively form the second of the five pillars in Islam, observed three or five times (the latter being the majority) every day at prescribed times. These are usually (observed at dawn), (observed at noon), (observed late in the afternoon), (observed after sunset), and (observed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Language
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal written m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Grammar
Arabic grammar or Arabic language sciences ( ar, النحو العربي ' or ar, عُلُوم اللغَة العَرَبِيَّة ') is the grammar of the Arabic language. Arabic is a Semitic language and its grammar has many similarities with the grammar of other Semitic languages. Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic have largely the same grammar; colloquial spoken varieties of Arabic can vary in different ways. The largest differences between classical and colloquial Arabic are the loss of morphological markings of grammatical case; changes in word order, an overall shift towards a more analytic morphosyntax, the loss of the previous system of grammatical mood, along with the evolution of a new system; the loss of the inflected passive voice, except in a few relict varieties; restriction in the use of the dual number and (for most varieties) the loss of the feminine plural. Many Arabic dialects, Maghrebi Arabic in particular also have significant vowel shifts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iqama
The Iqama or Iqamah ( ar, إِقَامَة, ') is the second call to Islamic Prayer, given immediately before prayer begins. Encyclopaedia of Islam, 2nd Edition Online. Edited by P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel, W.P. Heinrichs The iqama is given a more rapid and less sonorous rendering than the first call, the adhan, because it is intended merely to draw the attention of those already in the mosque, rather than to remind those outside the mosque to come in. The phrases of the iqama and the adhan are the same, though there are variations among sects in the preferred number of repetitions of the phrases. Text The Hanafi and the Shia schools both use the same number of repetitions of the formula for both the Adhan and the Iqama, contrary to all the other Islamic schools. According to the Malikis, everything is said as normal (Allahu Akbar - 2x, Ashadu ala ilaha illa Allah - 1x, Ashadu anna Muhammadur RasoolAllah - 1x, Hayya ala salah - 1x, Hayya alal fala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhan
Adhan ( ar, أَذَان ; also variously transliterated as athan, adhane (in French), azan/azaan (in South Asia), adzan (in Southeast Asia), and ezan (in Turkish), among other languages) is the Islamic call to public prayer (salah) in a mosque recited by a muezzin at prescribed times of the day. Adhan is recited very loudly from the mosque five times a day on most days and all day long during the religious holidays of Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, traditionally from the minaret. It is the first call summoning Muslims to enter the mosque for obligatory (''fard'') prayer (''salah''). A second call, known as the ''iqamah'', summons those within the mosque to line up for the beginning of the prayers. Only in Turkey, Ezan is voiced in five different styles at different times; saba, uşşak, hicaz, rast, segah. Terminology Adhān, Arabic for "announcement", from root ''ʾadhina'' meaning "to listen, to hear, be informed about", is variously transliterated in different cultures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muezzin
The muezzin ( ar, مُؤَذِّن) is the person who proclaims the call to the daily prayer ( ṣalāt) five times a day (Fajr prayer, Zuhr prayer, Asr prayer, Maghrib prayer and Isha prayer) at a mosque. The muezzin plays an important role in ensuring an accurate prayer schedule for the Muslim community. Etymology The English word ''muezzin'' is derived from the ar, مُؤَذِّن, , simplified ''mu'azzin''. The word means "one by the ear", since the word stems from the word for "ear" in Arabic is ''ʾudhun'' (أُذُن). As the ''muʾadh·dhin'' will place both hands on his ears to recite the call to prayer. Roles and responsibilities The professional muezzin is chosen for his good character, voice and skills to serve at the mosque. However, the muezzin is not considered a cleric, but in a position comparable to a Christian verger. He is responsible for keeping the mosque clean, for rolling the carpets, for cleaning the toilets and the place where people wash the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nafl Prayer
In Islam, a nafl prayer, (pl. Nawafil) ( ar, صلاة النفل, ''ṣalāt al-nafl'') or supererogatory prayer, is a type of optional Muslim ''salah'' (formal worship). As with sunnah prayer, they are not considered obligatory but are thought to confer extra benefit on the person performing them. An example is the offering of four raka'ahs of ''"nafl"'' before the compulsory ''Zuhr'' prayers. According to the following Hadith, ''"nafl"'' not only draws a person closer to Allah but also helps one attain the better success in the Afterworld i.e. Jannah (Paradise). Tahiyatul Wudu ''Tahiyatul wudu'' is the nafl prayer after doing wudhu. Abu Hureyrah (RA) narrates that once the Islamic prophet Muhammad asked Bilal at Fajr salah: Bilal replied: Abu Hureyrah narrated that Muhammad said to Bilal Bilal said : There are 6 rakats in Tahiyatul Wudhu. It should not be performed during the improper (''makruh'') times; when the sun rises, when it is at zenith and when it s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Cry
A battle cry or war cry is a yell or chant taken up in battle, usually by members of the same combatant group. Battle cries are not necessarily articulate (e.g. "Eulaliaaaa!", "Alala"..), although they often aim to invoke patriotic or religious sentiment. Their purpose is a combination of arousing aggression and esprit de corps on one's own side and causing intimidation on the hostile side. Battle cries are a universal form of display behaviour (i.e., threat display) aiming at competitive advantage, ideally by overstating one's own aggressive potential to a point where the enemy prefers to avoid confrontation altogether and opts to flee. In order to overstate one's potential for aggression, battle cries need to be as loud as possible, and have historically often been amplified by acoustic devices such as horns, drums, conches, carnyxes, bagpipes, bugles, etc. (see also martial music). Battle cries are closely related to other behavioral patterns of human aggression, such as wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilah
' ( ar, إله; plural: ') is an Arabic term meaning "god". In Arabic, ilah refers to anyone or anything that is worshipped. The feminine is ' (, meaning "goddess"); with the article, it appears as ' (). The Arabic word for God (') is thought to be derived from it (in a proposed earlier form ''al-Lāh'') though this is disputed. is cognate to Northwest Semitic '' '' and Akkadian ''ilum''. The word is from a Proto-Semitic archaic biliteral ' meaning "god" (possibly with a wider meaning of "strong"), which was extended to a regular triliteral by the addition of a '' h'' (as in Hebrew '' , ''). The word is spelled either with an optional diacritic alif to mark the ' only in Qur'anic texts or (more rarely) with a full alif, . The term is used throughout the Quran in passages discussing the existence of God or the beliefs in other divinities by non-Muslims. Notably, the first statement of the ' (the Muslim confession of faith) is "There is no god (') except the God (')." See als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |