|
Tahirpur
Tahirpur ( bn, তাহিরপুর) is an upazila of Sunamganj District in the Division of Sylhet, Bangladesh. Geography Tahirpur is located at . It has 21987 households and total area 313.7 km². History The territory of Tahirpur Upazila contains the historic village of Nabagram (in Badaghat Union), which served as the capital of the Laur Kingdom. After the Conquest of Sylhet in 1303, some disciples of warrior-saint Shah Jalal migrated and settled in present-day Tahirpur where they preached Islam to the local people. Most notably, Shah Rafiuddin migrated here and is buried in Sarping on the border with Meghalaya on top of Laur Hill. In the 18th century, Tahirpur became a part of Brajendra Kishore Roy Chowdhury's zamindari based in Gouripur House in Mymensingh. For most of its history, the lower caste Hindus formed the majority of the area's population. During the British Raj, the local council resolved a false accusation against a Bengali Muslim by the name of Tahir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahed Ali
Shahed Ali ( bn, শাহেদ আলী; 24 May 19256 November 2001) was a Bangladeshi litterateur and cultural activist. Aside from being an educationist and his journalism, he was one of the founders of the nationwide Tamaddun Majlish which initiated the Bengali language movement. He edited multiple magazines, was the founding secretary of the Islamic Academy (now Islamic Foundation Bangladesh), and is best known for his magnum opus, the short story ''Jibrailer Dana'' (Gabriel's Wings). Early life and education Ali was born in the village of Mahmudpur (presently in South Sripur Union) in Tahirpur Thana, Sunamganj Subdivision, Sylhet District to Bengali Muslim parents on 24 May 1925. He was the oldest of nine brothers and sisters. His first story, ''Ashru'' (Tears), was published in 1940 when he was a student at grade eight. In 1943, he completed his studies at the Government Jubilee High School and proceeded to study at the Murari Chand College in Sylhet. He received h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunamganj District
Sunamganj ( bn, সুনামগঞ্জ) is a district located in north-eastern Bangladesh within the Sylhet Division. History In the ancient period, Sunamganj was part of the Laur Kingdom. After the conquest of Sylhet (Kingdom of Gauiurh) in 1303 by Muslims under the spiritual guidance of Shah Jalal, Shah Kamal Quhafah established a capital in Shaharpara with the aid of his twelve disciples and his second son, Shah Muazzamuddin Qureshi, who also maintained a second sub-administration office at Nizgaon on the bank of the river Surma, present day Shologhar (there is now Shologhar Masjid and madrasa) in Sunamganj town, which was administered by one of his descendants. Between the latter part of 1300 CE and 1765 CE, the present-day Sunamganj district was a part of Iqlim-e-Muazzamabad, i.e. the state of Muazzamabad, which was an independent state until 1620 when it was conquered by the mighty Mughal of Delhi. The last sultan of Muazzamabad was Hamid Qureshi Khan, who was a desce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advaita Acharya
Advaita Acharya (; 1434–1559), (born Kamalaksha Bhattacharjee; কমলাক্ষ ভট্টাচার্য),"Shantipur parichoy"-Kalikrishna Bhattacharaya&"Samajer Pratichhabi Bises Shantipur Sankhya."-editor-Satya Narayan Goswami. p. 52 was a companion of the founder of the Gaudiya Vaishnava movement, Chaitanya Mahaprabhu, and guru of Haridasa Thakur. He was born in the village of Nabagram in Laud (in present-day Sunamganj District, Bangladesh), in 1434, some fifty years before Chaitanya, and spent most of his adult life in the town of Shantipur in Nadia with his wife and family. Advaita Acharya had six sons, Acyutananda Das (who also became a disciple of Chaitanya), Krisna Mishra, Gopala Das, Balarama Das Mishra (whose lineage became the zamindar of Krishna Chandra), Swarupa Das and Jagadisa Mishra. Advaita Acharya contributed in two Sanskrit literature, named ''Yogabashishta-Bhaishta'' and ''Geeta Bhaishya''. The ancestry and life of Advaita Acharya are na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of Sylhet
The Conquest of Sylhet ( bn, শ্রীহট্টের বিজয়, Srīhôtter Bijôy, Conquest of Srihatta) predominantly refers to an Islamic conquest of Srihatta (present-day Sylhet, Bangladesh) led by Sikandar Khan Ghazi, the military general of Sultan Shamsuddin Firoz Shah of the Lakhnauti Sultanate, against the Hindu king Gour Govinda. The conquest was aided by a Muslim saint known as Shah Jalal, who later ordered his disciples to scatter throughout eastern Bengal and propagate the religion of Islam. The Conquest of Sylhet may also include other minor incidents taking place after Govinda's defeat, such as the capture of nearby Taraf. Background The Greater Sylhet region historically consisted of many Hindu petty kingdoms such as Srihatta (Gour), Laur and Jaintia. Govinda was a conservative Hindu ruler of the Gour Kingdom, intolerant and harsh towards other faiths such as Islam, Buddhism and even certain denominations of Hinduism. It was known by his people tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laur Kingdom
The Kingdom of Laur was one of the many petty kingdoms of the Sylhet region. Others included the Gour Kingdom, Ita Kingdom, Taraf Kingdom, Pratapgarh Kingdom and Jaintia Kingdom. Location The kingdom was bounded by the Brahmaputra river in the west, the Jaintia Kingdom in the east, Kamarupa in the north and Brahmanbaria in the south. It is considered that in the 7th century, the kingdom consisted of the modern-day Sunamganj District as well as parts of Habiganj and Mymensingh. History Before the establishment of the Laur Kingdom, the area was a part of Jaintia in the greater Kamarupa Kingdom. When Guhak ascended the Jaintia throne, he married a princess from Kamarupa. Guhak had a deep interest in Hinduism and migration of Brahmins from the Kamrup region to this area took place. Guhak had three sons; Jayantak, Gurak and Ladduk, and two daughters; Sheela and Chatala. He split the Jaintia Kingdom into three for his three sons. He gave his eldest son, Jayantak, the northern hills whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
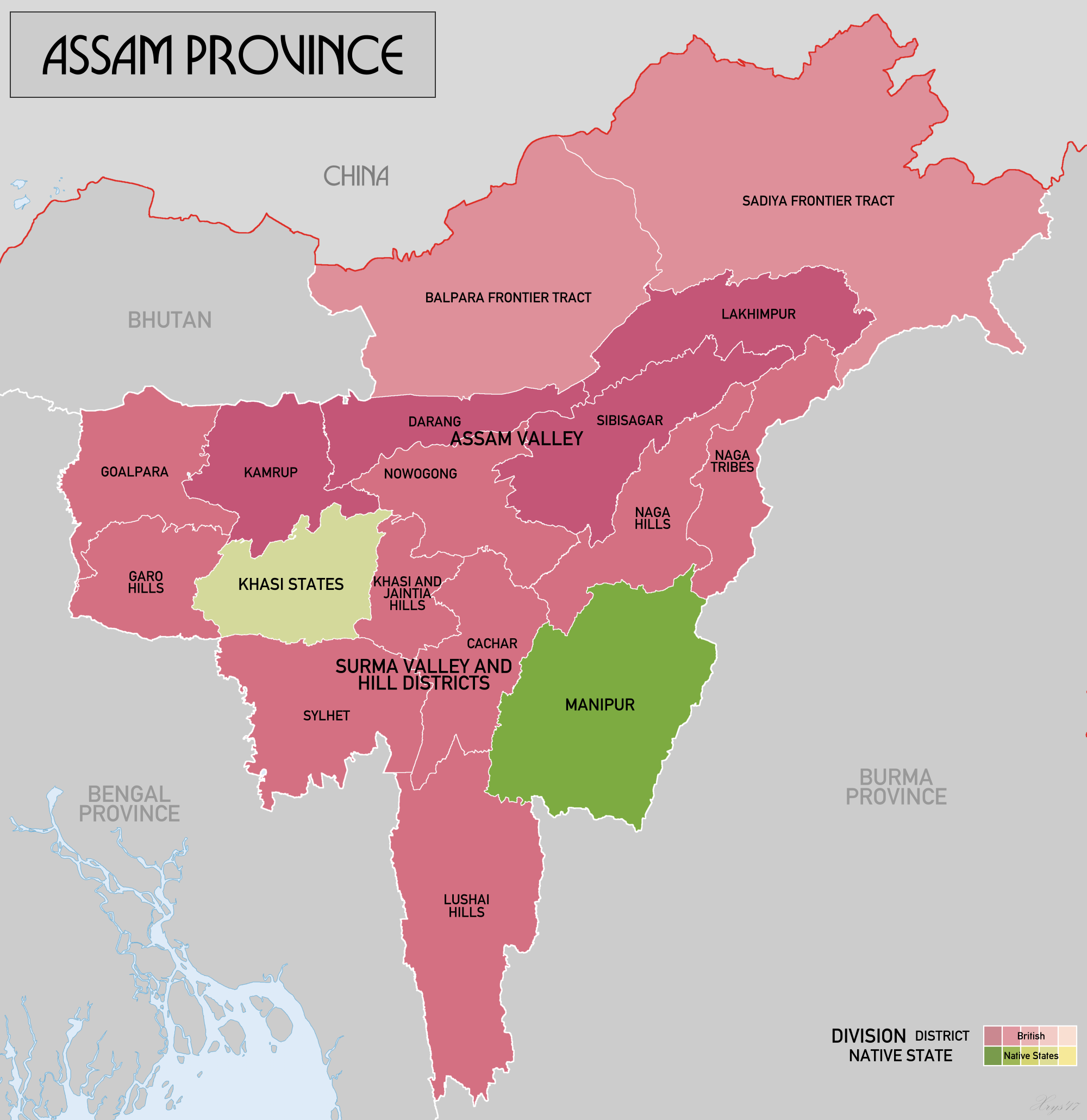
Sylhet Division
Sylhet Division ( bn, সিলেট বিভাগ) is the northeastern division of Bangladesh. It is bordered by the Indian states of Meghalaya, Assam and Tripura to the north, east and south respectively, and by the Bangladeshi divisions of Chittagong to the southwest and Dhaka and Mymensingh to the west. Prior to 1947, it included the subdivision of Karimganj (presently in Barak Valley, India). However, Karimganj (including the thanas of Badarpur, Patharkandi and Ratabari) was inexplicably severed from Sylhet by the Radcliffe Boundary Commission. According to Niharranjan Ray, it was partly due to a plea from a delegation led by Abdul Matlib Mazumdar. Etymology and names The name ''Sylhet'' is an anglicisation of ''Shilhot'' (শিলহট). Its origins seem to come from the Sanskrit words শিলা ''śilā'' (meaning 'stone') and হট্ট ''haṭṭa'' (meaning 'marketplace'). These words match the landscape and topography of the hilly region. The shila stones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meghalaya
Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a states and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: (a) the United Khasi Hills and Jaintia Hills and (b) the Garo Hills.History of Meghalaya State Government of India Meghalaya was previously part of Assam, but on 21 January 1972, the districts of Khasi, Garo and Jaintia Hills became the new state of Meghalaya. The population of Meghalaya as of 2014 is estimated to be 3,211,474. Meghalaya covers an area of approximately 22,430 square kilometres, with a length-to-breadth ratio of about 3:1.Meghal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taherpur
Taherpur is a town and a notified area in Ranaghat subdivision of Nadia district in the Indian state of West Bengal. History Taherpur has been named after a certain Pathan fief-holder Tahir Khan. Kamdev Bhatta, a Brahmin of shandilya gotra defeated the Pathan fief-holder Tahir Khan and laid the foundation of the Taherpur zamindari during the independent Sultanate period (1338-1538) of Bengal. Kamdev descendant Raja Kangshanarayan of Taherpur organized the first grand autumn Durga Puja in Bengal. Geography Location Taherpur is located at . Area overview Nadia district is mostly alluvial plains lying to the east of Hooghly River, locally known as Bhagirathi. The alluvial plains are cut across by such distributaries as Jalangi, Churni and Ichhamati. With these rivers getting silted up, floods are a recurring feature. The Ranaghat subdivision has the Bhagirathi on the west, with Purba Bardhaman and Hooghly districts lying across the river. Topographically, Ranaghat subdivision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upazila
An ''upazila'' ( bn, উপজেলা, upôzela, lit=sub-district pronounced: ), formerly called ''thana'', is an administrative region in Bangladesh, functioning as a sub-unit of a district. It can be seen as an analogous to a county or a borough of Western countries. Rural upazilas are further administratively divided into union council areas (union parishads). Bangladesh ha495 upazilas(as of 20 Oct 2022). The upazilas are the second lowest tier of regional administration in Bangladesh. The administrative structure consists of divisions (8), districts (64), upazilas (495) and union parishads (UPs). This system of devolution was introduced by the former military ruler and president of Bangladesh, Lieutenant General Hossain Mohammad Ershad, in an attempt to strengthen local government. Below UPs, villages (''gram'') and ''para'' exist, but these have no administrative power and elected members. The Local Government Ordinance of 1982 was amended a year later, redesignatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassan Shahriar
Hassan Shahriar (25 April 1946 – 10 April 2021) was a Bangladeshi journalist, columnist, and political analyst. Early life and career Shahriar was born on 25 April 1946 at Sunamganj, a district of Greater Sylhet region. Shahriar served ''The Daily Ittefaq'' as its executive editor. He was the first editor of the ''Daily Sun'' and Chief Editor of Chittagong-based ''Daily People's View''. He was Bangladesh correspondent of international news magazine ''Newsweek'', ''Khaleej Times'' of Dubai, India's Daily ''Deccan Herald'', ''The Indian Express'' and ''The Asian Age'', Pakistan's Morning News, ''Dawn'' and '' Evening Star''. Before the 1971 independence of Bangladesh, he worked as a staff reporter in Karachi, Pakistan. He was awarded the prestigious Harry Brittan Fellowship by the Commonwealth Press Union (CPU) in 1978. The five-month course included training on advance journalism, attachment to British newspaper Telegraph and Argus of Bradford and Oxford University's Elizabe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upazilas Of Bangladesh
An ''upazila'' ( bn, উপজেলা, upôzela, lit=sub-district pronounced: ), formerly called ''thana'', is an administrative region in Bangladesh, functioning as a sub-unit of a district. It can be seen as an analogous to a county or a borough of Western countries. Rural upazilas are further administratively divided into union council areas (union parishads). Bangladesh ha495 upazilas(as of 20 Oct 2022). The upazilas are the second lowest tier of regional administration in Bangladesh. The administrative structure consists of divisions (8), districts (64), upazilas (495) and union parishads (UPs). This system of devolution was introduced by the former military ruler and president of Bangladesh, Lieutenant General Hossain Mohammad Ershad, in an attempt to strengthen local government. Below UPs, villages (''gram'') and ''para'' exist, but these have no administrative power and elected members. The Local Government Ordinance of 1982 was amended a year later, redesignatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |