|
Table Of Nuclides (segmented, Wide)
These isotope tables show all of the known isotopes of the chemical elements, arranged with increasing atomic number from left to right and increasing neutron number from top to bottom. half-life, Half lives are indicated by the color of each isotope's cell (see color chart in each section). Colored borders indicate half lives of the most stable nuclear isomer states. The data for these tables came from Brookhaven National Laboratory which has an interactivTable of Nuclideswith data on ~3000 nuclides. Recent discoveries are sourced from M. Thoennessen's "Discovery of Nuclides Project" websit Isotopes for elements 0-29 , #Isotopes_for_elements_30-59, Next → Isotopes for elements 30-59 #Isotopes_for_elements_0-29, ← Previous , #Isotopes_for_elements_60-89, Next → Isotopes for elements 60-89 #Isotopes_for_elements_30-59, ← Previous , #Isotopes_for_elements_90-118, Next → Isotopes for elements 90-118 #Isotopes_for_elements_60-89, ← Previous , #Periodic_tab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Of Nuclides
A table or chart of nuclides is a two-dimensional graph of isotopes of the elements, in which one axis represents the number of neutrons (symbol ''N'') and the other represents the number of protons (atomic number, symbol ''Z'') in the atomic nucleus. Each point plotted on the graph thus represents a nuclide of a known or hypothetical chemical element. This system of ordering nuclides can offer a greater insight into the characteristics of isotopes than the better-known periodic table, which shows only elements and not their isotopes. The chart of the nuclides is also known as the Segrè chart, after the Italian physicist Emilio Segrè. Description and utility A chart or table of nuclides maps the nuclear, or radioactive, behavior of nuclides, as it distinguishes the isotopes of an element. It contrasts with a periodic table, which only maps their chemical behavior, since isotopes (nuclides which are variants of the same element) do not differ chemically to any significant deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
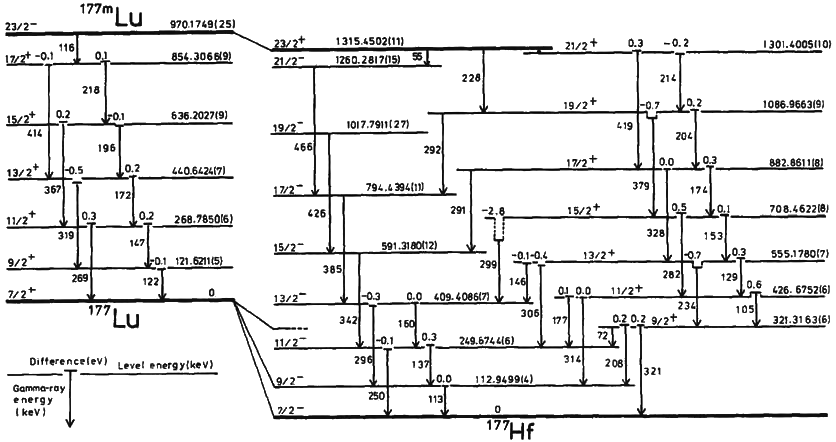
Isotopes For Elements 90-118
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in 1913 in a suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes For Elements 60-89
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in 1913 in a suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes For Elements 0-29
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in 1913 in a suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Table (complete)
A table or chart of nuclides is a two-dimensional graph of isotopes of the elements, in which one axis represents the number of neutrons (symbol ''N'') and the other represents the number of protons (atomic number, symbol ''Z'') in the atomic nucleus. Each point plotted on the graph thus represents a nuclide of a known or hypothetical chemical element. This system of ordering nuclides can offer a greater insight into the characteristics of isotopes than the better-known periodic table, which shows only elements and not their isotopes. The chart of the nuclides is also known as the Segrè chart, after the Italian physicist Emilio Segrè. Description and utility A chart or table of nuclides maps the nuclear, or radioactive, behavior of nuclides, as it distinguishes the isotopes of an element. It contrasts with a periodic table, which only maps their chemical behavior, since isotopes (nuclides which are variants of the same element) do not differ chemically to any significant degr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotones
Two nuclides are isotones if they have the same neutron number ''N'', but different proton number ''Z''. For example, boron-12 and carbon-13 nuclei both contain 7 neutrons, and so are isotones. Similarly, 36S, 37Cl, 38Ar, 39K, and 40Ca nuclei are all isotones of 20 because they all contain 20 neutrons. Despite its similarity to the Greek for "same stretching", the term was formed by the German physicist K. Guggenheimer by changing the "p" in "isotope" from "p" for "proton" to "n" for "neutron". The largest numbers of observationally stable nuclides exist for isotones 50 (five: 86Kr, 88Sr, 89Y, 90Zr, 92Mo) and 82 (six: 138Ba, 139La, 140Ce, 141Pr, 142Nd, 144Sm). Neutron numbers for which there are no stable isotones are 19, 21, 35, 39, 45, 61, 89, 115, 123, and 127 or more. In contrast, the proton numbers for which there are no stable isotopes are 43, 61, and 83 or more.via :File:NuclideMap_stitched.png; note also Isotopes of bismuth This is related to nuclear magic number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry. It is a graphic formulation of the periodic law, which states that the properties of the chemical elements exhibit an approximate periodic dependence on their atomic numbers. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. The rows of the table are called periods, and the columns are called groups. Elements from the same group of the periodic table show similar chemical characteristics. Trends run through the periodic table, with nonmetallic character (keeping their own electrons) increasing from left to right across a period, and from down to up across a group, and metallic character (surrendering electrons to other atoms) increasing in the opposite direction. The underlying reason for these trends is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes For Elements 30-59
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in 1913 in a suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Periodic Table Chart-blocks
Simple or SIMPLE may refer to: *Simplicity, the state or quality of being simple Arts and entertainment * Simple (album), ''Simple'' (album), by Andy Yorke, 2008, and its title track * Simple (Florida Georgia Line song), "Simple" (Florida Georgia Line song), 2018 * "Simple", a song by Johnny Mathis from the 1984 album ''A Special Part of Me'' * "Simple", a song by Collective Soul from the 1995 album ''Collective Soul (1995 album), Collective Soul'' * "Simple", a song by Katy Perry from the 2005 soundtrack to ''The Sisterhood of the Traveling Pants (film), The Sisterhood of the Traveling Pants'' * "Simple", a song by Khalil from the 2017 album ''Prove It All'' * "Simple", a song by Kreesha Turner from the 2008 album ''Passion (Kreesha Turner album), Passion'' * "Simple", a song by Ty Dolla Sign from the 2017 album ''Beach House 3'' deluxe version * Simple (video game series), ''Simple'' (video game series), budget-priced console games Businesses and organisations * Simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base and Japanese internment camp. Its name stems from its location within the Town of Brookhaven, approximately 60 miles east of New York City. It is managed by Stony Brook University and Battelle Memorial Institute. Research at BNL includes nuclear and high energy physics, energy science and technology, environmental and bioscience, nanoscience, and national security. The 5,300 acre campus contains several large research facilities, including the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider and National Synchrotron Light Source II. Seven Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work conducted at Brookhaven Lab. Overview BNL is staffed by approximately 2,750 scientists, engineers, technicians, and support personnel, and hosts 4,000 guest investigators every year. The laboratory has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state, higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have Half-life, half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" Induced gamma emission, gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the Isotopes of tantalum#Tantalum-180m, nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |