|
T Cell Receptor Revision
T-cell receptor revision (alternative term: antigen receptor editing) is a process in the peripheral immune system which is used by mature T cells to alter their original antigenic specificity based on rearranged T cell receptors (TCR). This process can lead either to continuous appearance of potentially self-reactive T cells in the body, not controlled by the central tolerance mechanism in the thymus or better eliminate such self-reactive T cells on the other hand and thus contributing to peripheral tolerance - the extent of each has not been completely understood yet. This process occurs during follicular helper T cell formation in lymph node germinal centers. T cell revision is achieved via reactivation of recombination enzymes RAG1 and/or RAG2 after T cell activation in the periphery and random recombination of their CDR sequences. Post-revision peripheral T cell repertoire is strengthening all essential features of self-tolerant and self- MHC-restricted T cell repertoir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-cell Receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding between TCR and antigen peptides is of relatively low affinity and is degenerate: that is, many TCRs recognize the same antigen peptide and many antigen peptides are recognized by the same TCR. The TCR is composed of two different protein chains (that is, it is a heterodimer). In humans, in 95% of T cells the TCR consists of an alpha (α) chain and a beta (β) chain (encoded by '' TRA'' and ''TRB'', respectively), whereas in 5% of T cells the TCR consists of gamma and delta (γ/δ) chains (encoded by '' TRG'' and '' TRD'', respectively). This ratio changes during ontogeny and in diseased states (such as leukemia). It also differs between species. Orthologues of the 4 loci have been mapped in various species. Each locus can produce a vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
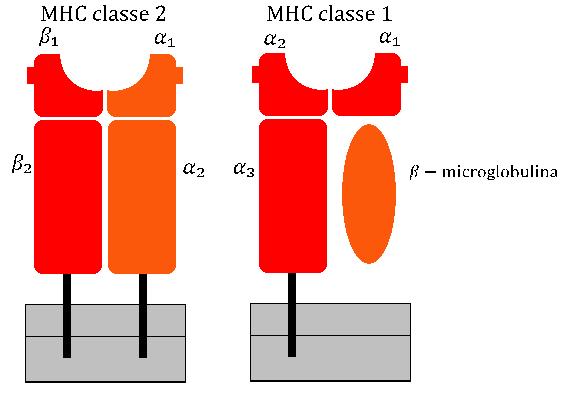
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Helper 17 Cell
T helper 17 cells (Th17) are a subset of pro-inflammatory T helper cells defined by their production of interleukin 17 (IL-17). They are related to T regulatory cells and the signals that cause Th17s to differentiate actually inhibit Treg differentiation. However, Th17s are developmentally distinct from Th1 and Th2 lineages. Th17 cells play an important role in maintaining mucosal barriers and contributing to pathogen clearance at mucosal surfaces; such protective and non-pathogenic Th17 cells have been termed as Treg17 cells. They have also been implicated in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. The loss of Th17 cell populations at mucosal surfaces has been linked to chronic inflammation and microbial translocation. These regulatory Th17 cells can be generated by TGF-beta plus IL-6 in vitro. Differentiation Like conventional regulatory T cells (Treg), induction of regulatory Treg17 cells could play an important role in modulating and preventing certain autoimmune diseases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory T Cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same lineage as naïve CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis. Mouse models have suggested that modulation of Treg cells can treat autoimmune disease and cancer and can facilitate orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Knock-in
In molecular cloning and biology, a gene knock-in (abbreviation: KI) refers to a genetic engineering method that involves the one-for-one substitution of DNA sequence information in a genetic locus or the insertion of sequence information not found within the locus. Typically, this is done in mice since the technology for this process is more refined and there is a high degree of shared sequence complexity between mice and humans. The difference between knock-in technology and traditional transgenic techniques is that a knock-in involves a gene inserted into a specific locus, and is thus a "targeted" insertion. It is the opposite of gene knockout. A common use of knock-in technology is for the creation of disease models. It is a technique by which scientific investigators may study the function of the regulatory machinery (e.g. promoters) that governs the expression of the natural gene being replaced. This is accomplished by observing the new phenotype of the organism in question. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetically Modified Organism
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, with the most common being an organism altered in a way that "does not occur naturally by mating and/or natural recombination". A wide variety of organisms have been genetically modified (GM), from animals to plants and microorganisms. Genes have been transferred within the same species, across species (creating transgenic organisms), and even across kingdoms. New genes can be introduced, or endogenous genes can be enhanced, altered, or knocked out. Creating a genetically modified organism is a multi-step process. Genetic engineers must isolate the gene they wish to insert into the host organism and combine it with other genetic elements, including a promoter and terminator region and often a selectable marker. A number of techniques are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Tolerance
In immunology, peripheral tolerance is the second branch of immunological tolerance, after central tolerance. It takes place in the immune periphery (after T and B cells egress from primary lymphoid organs). Its main purpose is to ensure that self-reactive T and B cells which escaped central tolerance do not cause autoimmune disease. Peripheral tolerance prevents immune response to harmless food antigens and allergens, too. Deletion of self-reactive T cells in the thymus is only 60-70% efficient, and naive T cell repertoire contains a significant portion of low-avidity self-reactive T cells. These cells can trigger an autoimmune response, and there are several mechanisms of peripheral tolerance to prevent their activation. Antigen-specific mechanisms of peripheral tolerance include persistent of T cell in quiescence, ignorance of antigen and direct inactivation of effector T cells by either clonal deletion, conversion to regulatory T cells (Tregs) or induction of anergy. Tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmunity
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease, post-infectious IBS, diabetes mellitus type 1, Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP) sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren syndrome, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Addison's disease, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis, polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), Alopecia Areata and multiple sclerosis (MS). Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids. Autoimmunity means presence of antibodies or T cells that react with self-protein and is present in all individuals, even in normal health state. It causes autoimmune diseases if self-reactivity can lead to tiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Conversion
Gene conversion is the process by which one DNA sequence replaces a homologous sequence such that the sequences become identical after the conversion event. Gene conversion can be either allelic, meaning that one allele of the same gene replaces another allele, or ectopic, meaning that one paralogous DNA sequence converts another. Allelic gene conversion Allelic gene conversion occurs during meiosis when homologous recombination between heterozygotic sites results in a mismatch in base pairing. This mismatch is then recognized and corrected by the cellular machinery causing one of the alleles to be converted to the other. This can cause non-Mendelian segregation of alleles in germ cells. Nonallelic/ectopic gene conversion Recombination occurs not only during meiosis, but also as a mechanism for repair of double-strand breaks (DSBs) caused by DNA damage. These DSBs are usually repaired using the sister chromatid of the broken duplex and not the homologous chromosome, so they wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V(D)J Recombination
V(D)J recombination is the mechanism of somatic recombination that occurs only in developing lymphocytes during the early stages of T and B cell maturation. It results in the highly diverse repertoire of antibodies/immunoglobulins and T cell receptors (TCRs) found in B cells and T cells, respectively. The process is a defining feature of the adaptive immune system. V(D)J recombination in mammals occurs in the primary lymphoid organs (bone marrow for B cells and thymus for T cells) and in a nearly random fashion rearranges variable (V), joining (J), and in some cases, diversity (D) gene segments. The process ultimately results in novel amino acid sequences in the antigen-binding regions of immunoglobulins and TCRs that allow for the recognition of antigens from nearly all pathogens including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and worms as well as "altered self cells" as seen in cancer. The recognition can also be allergic in nature (''e.g.'' to pollen or other allergens) or may match ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementarity-determining Region
Complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) are part of the variable chains in immunoglobulins (antibodies) and T cell receptors, generated by B-cells and T-cells respectively, where these molecules bind to their specific antigen. A set of CDRs constitutes a paratope. As the most variable parts of the molecules, CDRs are crucial to the diversity of antigen specificities generated by lymphocytes. Location and structure There are three CDRs (CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3), arranged non-consecutively, on the amino acid sequence of a variable domain of an antigen receptor. Since the antigen receptors are typically composed of two variable domains (on two different polypeptide chains, heavy and light chain), there are six CDRs for each antigen receptor that can collectively come into contact with the antigen. A single antibody molecule has two antigen receptors and therefore contains twelve CDRs total. There are three CDR loops per variable domain in antibodies. Sixty CDRs can be found on a pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Editing
Receptor editing is a process that occurs during the maturation of B cells, which are part of the adaptive immune system. This process forms part of central tolerance to attempt to change the specificity of the antigen receptor of self reactive immature B-cells, in order to rescue them from programmed cell death, called apoptosis. It is thought that 20-50% of all peripheral naive B cells have undergone receptor editing making it the most common method of removing self reactive B cells. During maturation in the bone marrow, B cells are tested for interaction with self antigens, which is called negative selection. If the maturing B cells strongly interact with these self antigens, they undergo death by apoptosis. Negative selection is important to avoid the production of B cells that could cause autoimmune diseases An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |