|
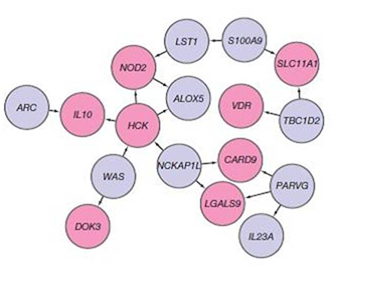
TTC7A
Tetratricopeptide repeat domain 7A (TTC7A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TTC7A'' gene. Function TPR domain-containing proteins, such as TTC7A, have diverse functions in cell cycle control, protein transport, phosphate turnover, and protein trafficking or secretion, and they can act as chaperones or scaffolding proteins. Clinical significance TTC7A deficiency disrupts epithelial cell differentiation and polarization in the intestinal tract, thymus, and lungs. TTC7A deficiency is very rare with less than 80 cases described in the literature to date. Mutations in this gene are known to cause intestinal atresia, severe infantile or very early onset inflammatory bowel disease, extensive enteropathy, combined immunodeficiencies, thyroid dysfunction, alopecia, and lung disease. There is a broad spectrum of severity and variety of symptoms, although quality of life is generally very poor for these children with few surviving beyond the first year or two of li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Atresia
Intestinal atresia is any congenital malformation of the structure of the intestine that causes bowel obstruction. The malformation can be a narrowing (stenosis), absence or malrotation of a portion of the intestine. These defects can either occur in the small or large intestine. Symptoms and signs The most prominent symptom of intestinal atresia is bilious vomiting soon after birth. This is most common in jejunal atresia. Other features include abdominal distension and failure to pass meconium. The distension is more generalised the further down the bowel the atresia is located and is thus most prominent with ileal atresia. Inability to pass stool is most common with duodenal or jejunal atresia; if stool is passed, it may be small, mucus-like and grey. Occasionally, there may be jaundice, which is most common in jejunal atresia. Abdominal tenderness or an abdominal mass are not generally seen as symptoms of intestinal atresia. Rather, abdominal tenderness is a symptom of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammation, inflammatory conditions of the colon (anatomy), colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and the rectum. IBD also occurs in dogs and is thought to arise from a combination of host genetics, intestinal microenvironment, environmental components and the immune system. There is an ongoing discussion, however, that the term "chronic enteropathy" might be better to use than "inflammatory bowel disease" in dogs because it differs from IBD in humans in how the dogs respond to treatment. For example, many dogs respond to only dietary changes compared to humans with IBD, who often need Immunosuppression, immunosuppressive treatment. Some dogs may also need immunosuppressant or antibiotic treatment when dieta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteropathy
Enteropathy refers to any pathology of the intestine. Although enteritis specifically refers to an inflammation of the intestine, and is thus a more specific term than "enteropathy", the two phrases are sometimes used interchangeably. __TOC__ Types Specific types of enteropathy include: * Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma * Environmental enteropathy, also known as tropical enteropathy :An incompletely defined syndrome of inflammation related to the quality of the environment. Signs and symptoms include reduced absorptive capacity and reduced intestinal barrier function of the small intestine. It is widespread among children and adults in low- and middle-income countries. * Eosinophilic enteropathy :A condition in which eosinophils (a type of white blood cell) accumulate in the gastrointestinal tract and in the blood. Eosinophil build up in the gastrointestinal tract can result in polyp formation, tissue break down, inflammation, and ulcers. * Coeliac disease :A malabsorptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combined Immunodeficiencies
Combined immunodeficiencies (or combined immunity deficiency) are immunodeficiency disorders that involve multiple components of the immune system, including both humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity. This category includes conditions such as bare lymphocyte syndrome, as well as severe combined immunodeficiency. Combined immunodeficiencies are commonly distinguished from SCID by low but not absent T-cell function. ICD-9 The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is a globally used diagnostic tool for epidemiology, health management and clinical purposes. The ICD is maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO), which is the directing and coordinatin ... divides immune deficiencies into three categories: humoral (279.0), cell-mediated (279.1), and combined (279.2). However, ICD-10 does not include a category for cell-mediated immune dysfunction (antibody is D80, and combined is D81), thus grouping T-cell mediated conditions with combined conditions. Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
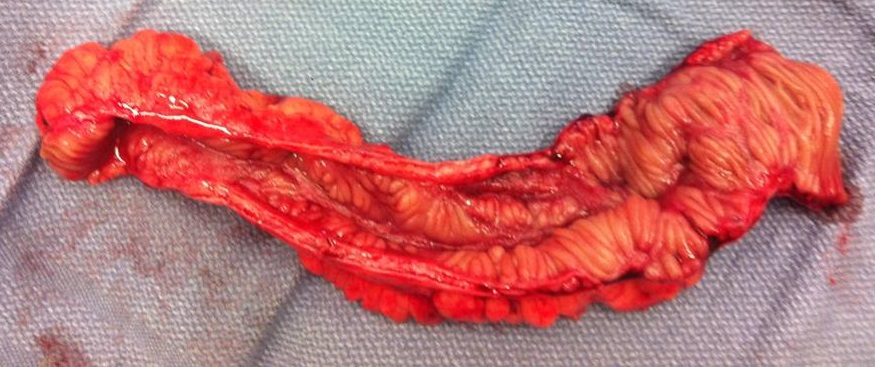
Bowel Resection
A bowel resection or enterectomy ('' enter-'' + '' -ectomy'') is a surgical procedure in which a part of an intestine (bowel) is removed, from either the small intestine or large intestine. Often the word ''enterectomy'' is reserved for the sense of small bowel resection, in distinction from colectomy, which covers the sense of large bowel resection. Bowel resection may be performed to treat gastrointestinal cancer, bowel necrosis, severe enteritis, diverticular disease, Crohn's disease, endometriosis, ulcerative colitis, or bowel obstruction due to scar tissue. Other reasons to perform bowel resection include traumatic injuries and to remove polyps when polypectomy is insufficient, either to prevent polyps from ever becoming cancerous or because they are causing or threatening bowel obstruction, such as in familial adenomatous polyposis, Peutz–Jeghers syndrome, or other polyposis syndromes. Some patients require ileostomy or colostomy after this procedure as alternative means o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce additional normal blood cells. It may be autologous (the patient's own stem cells are used), allogeneic (the stem cells come from a donor) or syngeneic (from an identical twin). It is most often performed for patients with certain cancers of the blood or bone marrow, such as multiple myeloma or leukemia. In these cases, the recipient's immune system is usually destroyed with radiation or chemotherapy before the transplantation. Infection and graft-versus-host disease are major complications of allogeneic HSCT. HSCT remains a dangerous procedure with many possible complications; it is reserved for patients with life-threatening diseases. As survival following the procedure has increased, its use has expanded beyond cancer to autoimmun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce additional normal blood cells. It may be autologous (the patient's own stem cells are used), allogeneic (the stem cells come from a donor) or syngeneic (from an identical twin). It is most often performed for patients with certain cancers of the blood or bone marrow, such as multiple myeloma or leukemia. In these cases, the recipient's immune system is usually destroyed with radiation or chemotherapy before the transplantation. Infection and graft-versus-host disease are major complications of allogeneic HSCT. HSCT remains a dangerous procedure with many possible complications; it is reserved for patients with life-threatening diseases. As survival following the procedure has increased, its use has expanded beyond cancer to autoimmun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestine Transplantation
Intestine transplantation (intestinal transplantation, or small bowel transplantation) is the surgical replacement of the small intestine for chronic and acute cases of intestinal failure. While intestinal failure can oftentimes be treated with alternative therapies such as parenteral nutrition (PN), complications such as PN-associated liver disease and short bowel syndrome may make transplantation the only viable option. One of the rarest type of organ transplantation performed, intestine transplantation is becoming increasingly prevalent as a therapeutic option due to improvements in immunosuppressive regimens, surgical technique, PN, and the clinical management of pre and post-transplant patients. History Intestine transplantation dates back to 1959, when a team of surgeons at the University of Minnesota led by Richard C. Lillehei reported successful transplantation of the small intestine in dogs. Five years later in 1964, Ralph Deterling in Boston attempted the first human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Kinase
Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) is a kinase belonging to the AGC (PKA/ PKG/PKC) family of serine-threonine specific protein kinases. It is involved mainly in regulating the shape and movement of cells by acting on the cytoskeleton. ROCKs (ROCK1 and ROCK2) occur in mammals (human, rat, mouse, cow), zebrafish, ''Xenopus'', invertebrates (''C. elegans'', mosquito, ''Drosophila'') and chicken. Human ROCK1 has a molecular mass of 158 kDa and is a major downstream effector of the small GTPase RhoA. Mammalian ROCK consists of a kinase domain, a coiled-coil region and a Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, which reduces the kinase activity of ROCKs by an autoinhibitory intramolecular fold if RhoA-GTP is not present. Rat ROCKs were discovered as the first effectors of Rho and they induce the formation of stress fibers and focal adhesions by phosphorylating MLC (myosin light chain). Due to this phosphorylation, the actin binding of myosin II and, thus, the contractility increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Kinase Inhibitor
Rho-kinase inhibitors (rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor or ROCK inhibitor) are a series of compounds that target rho kinase (ROCK) and inhibit the ROCK pathway. Clinical trials have found that inhibition of the ROCK pathway contributes to the cardiovascular benefits of statin therapy. Furthermore, ROCK inhibitors may have clinical applications for anti-erectile dysfunction, antihypertension, and tumor metastasis inhibition. More recently they have been studied for the treatment of glaucoma and as a therapeutic target for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, including ischemic stroke. While statin therapy has been demonstrated to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events, including ischemic stroke, the interplay between the ROCK pathway and statin therapy to treat and prevent strokes in older adults has not yet been proven. On a cellular level, ROCK has multiple functions, including regulation of smooth muscle cell contraction, cell migration, and maintenance of cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |