|
TRML2D
The TRML (german: Telefunken Radar Mobil Luftraumüberwachung, or " Telefunken mobile airspace surveilance radar") is a family of air defense radars first developed by Telefunken and currently produced by Hensoldt. It is a development of the earlier TRMS (german: Telefunken Radar Mobil Such or "Telefunken mobile search radar"). Retractable mast versions are TRML-2D with a rotating parabolic antenna and TRML-3D with a rotating phased array antenna, designated as ''Nahbereichsradar'' (NBR) or "short range radar" by the Bundeswehr. The latest TRML-4D comes with non-retractable, rotating base active electronically scanned array (AESA) solid-state antenna. System description TRML-2D was designed as an autonomous mobile command system for air defense with an integrated search radar. It can detect, identifiy and track aircraft at low and medium altitude, designate targets for the connected launchers and send commands to the battle management network. The range of the radar is 60& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Warning Radar
An early-warning radar is any radar system used primarily for the long-range detection of its targets, i.e., allowing defences to be alerted as ''early'' as possible before the intruder reaches its target, giving the air defences the maximum time in which to operate. This contrasts with systems used primarily for tracking or gun laying, which tend to offer shorter ranges but offer much higher accuracy. EW radars tend to share a number of design features that improve their performance in the role. For instance, EW radar typically operates at lower frequencies, and thus longer wavelengths, than other types. This greatly reduces their interaction with rain and snow in the air, and therefore improves their performance in the long-range role where their coverage area will often include precipitation. This also has the side-effect of lowering their optical resolution, but this is not important in this role. Likewise, EW radars often use much lower pulse repetition frequency to maxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO Container
An intermodal container, often called a shipping container, is a large standardized shipping container, designed and built for intermodal freight transport, meaning these containers can be used across different modes of transport – from ship to rail to truck – without unloading and reloading their cargo. Intermodal containers are primarily used to store and transport materials and products efficiently and securely in the global containerized intermodal freight transport system, but smaller numbers are in regional use as well. These containers are known under a number of names. Based on size alone, up to 95% of intermodal containers comply with ISO standards, and can officially be called ISO containers. Many other names are simply: container, cargo or freight container, shipping, sea or ocean container, container van or sea van, sea can or C can, or MILVAN, SEAVAN, or RO/RO. The also used term CONEX (Box) is technically incorrect carry-over usage of the name of an importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-Doppler Radar
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics. The first operational Pulse Doppler radar was in the CIM-10 Bomarc, an American long range supersonic missile powered by ramjet engines, and which was armed with a W40 nuclear weapon to destroy entire formations of attacking enemy aircraft. Pulse-Doppler systems were first widely used on fighter aircraft starting in the 1960s. Earlier radars had used pulse-timing in order to determine range and the angle of the antenna (or similar means) to determine the bearing. However, this only worked when the radar antenna was not pointed down; in that case the reflection off the ground overwhelmed any returns from other objects. As the ground moves at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Beamforming
Beamforming or spatial filtering is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in an antenna array in such a way that signals at particular angles experience constructive interference while others experience destructive interference. Beamforming can be used at both the transmitting and receiving ends in order to achieve spatial selectivity. The improvement compared with omnidirectional reception/transmission is known as the directivity of the array. Beamforming can be used for radio or sound waves. It has found numerous applications in radar, sonar, seismology, wireless communications, radio astronomy, acoustics and biomedicine. Adaptive beamforming is used to detect and estimate the signal of interest at the output of a sensor array by means of optimal (e.g. least-squares) spatial filtering and interference rejection. Techniques To change the directionality of the array when transmit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Nitride
Gallium nitride () is a binary III/ V direct bandgap semiconductor commonly used in blue light-emitting diodes since the 1990s. The compound is a very hard material that has a Wurtzite crystal structure. Its wide band gap of 3.4 eV affords it special properties for applications in optoelectronic, high-power and high-frequency devices. For example, GaN is the substrate which makes violet (405 nm) laser diodes possible, without requiring nonlinear optical frequency-doubling. Its sensitivity to ionizing radiation is low (like other group III nitrides), making it a suitable material for solar cell arrays for satellites. Military and space applications could also benefit as devices have shown stability in high radiation environments. Because GaN transistors can operate at much higher temperatures and work at much higher voltages than gallium arsenide (GaAs) transistors, they make ideal power amplifiers at microwave frequencies. In addition, GaN offers promising charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Electronically Scanned Array
An active electronically scanned array (AESA) is a type of phased array antenna, which is a computer-controlled array antenna in which the beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antenna. In the AESA, each antenna element is connected to a small solid-state transmit/receive module (TRM) under the control of a computer, which performs the functions of a transmitter and/or receiver for the antenna. This contrasts with a passive electronically scanned array (PESA), in which all the antenna elements are connected to a single transmitter and/or receiver through phase shifters under the control of the computer. AESA's main use is in radar, and these are known as active phased array radar (APAR). The AESA is a more advanced, sophisticated, second-generation of the original PESA phased array technology. PESAs can only emit a single beam of radio waves at a single frequency at a time. The PESA must utilize a Butler matri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurosatory
Eurosatory is the largest international defence and security exhibition for land and airland that is held every two years in the Paris-Nord Villepinte Exhibition Centre, Paris, France. In 2022, it gathered over 1,700 exhibitors and over 62,000 visitors from 150 countries. It is organized by COGES The exhibition is reserved for professionals only. Description This exhibition presents products from the entire land and air-land defense and security industries, from raw materials to sub-assemblies and operational systems. It covers a wide range of products from vehicles (tanks, armored vehicles, trucks) to small arms (guns, missiles, knives) through communications systems, uniforms, logistics services, but also simulation, operational medicine and disaster responses, etc. Security has also been a major theme during last exhibitions, with monitoring, alert and emergency responses solutions as well as civil security with the presence of firemen, among other institutions. The exhibit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
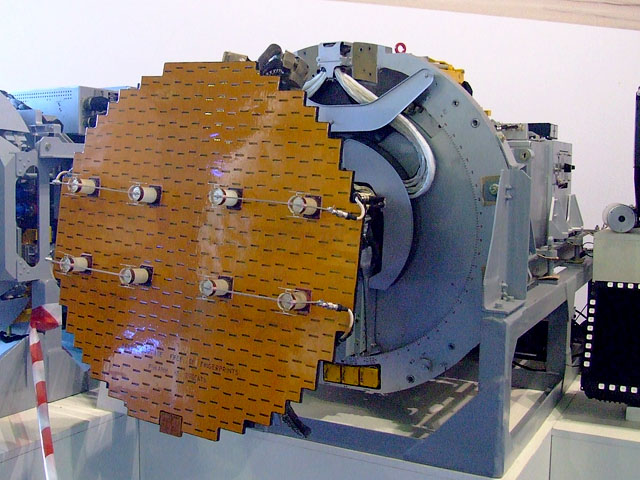
IRIS-T SLM Radar Unit TRML-4D ILA-2022
The IRIS-T (" InfraRed Imaging System Tail/ Thrust Vector-Controlled") is a medium range infrared homing missile available in both air-to-air and ground defence surface-to-air variants. The missile was developed in the late 1990s–early 2000s by a German-led program to develop a short to medium range infrared homing air-to-air missile to replace the AIM-9 Sidewinder in use by some NATO member countries at the time. A goal of the program was for any aircraft capable of firing the Sidewinder to also be capable of launching the IRIS-T. The air-to-air variant was fielded in 2005. Surface-to-air defence systems variants came later, with the short-range IRIS-T SLS fielded in 2015, and the medium-range IRIS-T SLM fielded in 2022. One IRIS-T SLM battery, as supplied by Germany to Ukraine, consists of three truck-mounted launchers, carrying eight missiles each (with a range of ), and a separate command vehicle that can be positioned up to away. The command vehicle integrates mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |