|
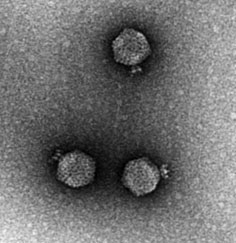
T7 Phage
Bacteriophage T7 (or the T7 phage) is a bacteriophage, a virus that infects bacteria. It infects most strains of ''Escherichia coli'' and relies on these hosts to propagate. Bacteriophage T7 has a lytic life cycle, meaning that it destroys the cell it infects. It also possesses several properties that make it an ideal phage for experimentation: its purification and concentration have produced consistent values in chemical analyses; it can be rendered noninfectious by exposure to UV light; and it can be used in phage display to clone RNA binding proteins. Discovery In a 1945 study by Demerec and Fano, T7 was used to describe one of the seven phage types (T1 to T7) that grow lytically on ''Escherichia coli;'' although all seven phages were numbered arbitrarily, phages with odd numbers, or T-odd phages, were later discovered to share morphological and biochemical features that distinguish them from T-even phages. Before being physically referred to as T7, the phage was used in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage T7 7-24-2021 Ps
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biomas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs ( guanine– cytosine and adenine– thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA into RNA. Many DNA-binding p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRISPR
CRISPR () (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bacteriophages that had previously infected the prokaryote. They are used to detect and destroy DNA from similar bacteriophages during subsequent infections. Hence these sequences play a key role in the antiviral (i.e. anti-phage) defense system of prokaryotes and provide a form of acquired immunity. CRISPR is found in approximately 50% of sequenced bacterial genomes and nearly 90% of sequenced archaea. Cas9 (or "CRISPR-associated protein 9") is an enzyme that uses CRISPR sequences as a guide to recognize and cleave specific strands of DNA that are complementary to the CRISPR sequence. Cas9 enzymes together with CRISPR sequences form the basis of a technology known as CRISPR-Cas9 that can be used to edit genes within organisms. This ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptidoglycan Layer
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid Cell wall#Bacterial_cell_walls, cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most bacteria (Domain (biology), domain ''Bacteria''). The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-Acetylmuramic acid, ''N''-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the ''N''-acetylmuramic acid is a oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. This repetitive linking results in a dense peptidoglycan layer which is critical for maintaining cell form and withstandi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysozyme
Lysozyme (EC 3.2.1.17, muramidase, ''N''-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase; systematic name peptidoglycan ''N''-acetylmuramoylhydrolase) is an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. It is a glycoside hydrolase that catalyzes the following process: : Hydrolysis of (1→4)-β-linkages between ''N''-acetylmuramic acid and ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitodextrins Peptidoglycan is the major component of gram-positive bacterial cell wall. This hydrolysis in turn compromises the integrity of bacterial cell walls causing lysis of the bacteria. Lysozyme is abundant in secretions including tears, saliva, human milk, and mucus. It is also present in cytoplasmic granules of the macrophages and the polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs). Large amounts of lysozyme can be found in egg white. C-type lysozymes are closely related to α-lactalbumin in sequence and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymatic Activity
Enzyme assays are laboratory methods for measuring enzymatic activity. They are vital for the study of enzyme kinetics and enzyme inhibition. Enzyme units The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with any other chemical, or in terms of activity in enzyme units. Enzyme activity Enzyme activity is a measure of the quantity of active enzyme present and is thus dependent on various physical conditions, ''which should be specified''. It is calculated using the following formula: :\operatorname=\operatorname=\operatorname\times\operatorname where :\operatorname= Enzyme activity :\operatorname= Moles of substrate converted per unit time :\operatorname= Rate of the reaction :\operatorname= Reaction volume The SI unit is the katal, 1 katal = 1 mol s−1 (mole per second), but this is an excessively large unit. A more practical and commonly used value is enzyme unit (U) = 1 μmol min−1 (micromole per minute). 1 U corresponds to 16.67 nano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-reactivity, cross-react and bind more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phage T7 Replication Machinery
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure Of T7 Phage
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building structures, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus Latency
Virus latency (or viral latency) is the ability of a pathogenic virus to lie dormant ( latent) within a cell, denoted as the lysogenic part of the viral life cycle. A latent viral infection is a type of persistent viral infection which is distinguished from a chronic viral infection. Latency is the phase in certain viruses' life cycles in which, after initial infection, proliferation of virus particles ceases. However, the viral genome is not eradicated. The virus can reactivate and begin producing large amounts of viral progeny (the lytic part of the viral life cycle) without the host becoming reinfected by new outside virus, and stays within the host indefinitely. Virus latency is not to be confused with clinical latency during the incubation period when a virus is ''not'' dormant. Mechanisms Episomal latency Episomal latency refers to the use of genetic episomes during latency. In this latency type, viral genes are stabilized, floating in the cytoplasm or nucleus as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |