|
Søren Løvtrup
Soren Løvtrup (1922–2002) was a Danish embryologist and historian of science in the Department of Animal Physiology at the Umeå University, Sweden. Løvtrup was known for his macromutation theory of evolution, which was in opposition to traditional neo-Darwinism. In 1987, Løvtrup published his controversial book ''Darwinism: The Refutation of a Myth'' which challenged Charles Darwin's role as the intellectual founder of evolutionary theory and accused Darwin of plagiarism. Career Løvtrup was born in Copenhagen. In 1945, he enrolled at University of Copenhagen, where he obtained a master's degree in biochemistry. He worked at Carlsberg Laboratory, until 1953 when he received a PhD in embryology. He also worked at University of Gothenburg. From 1965, he worked at Umeå University in Sweden as professor of animal physiology. Research ''Darwinism: The Refutation of a Myth'' Løvtrup is best known for his book ''Darwinism: The Refutation of a Myth'' (1987). In this controv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark
) , song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast") , song_type = National and royal anthem , image_map = EU-Denmark.svg , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark , established_title = History of Denmark#Middle ages, Consolidation , established_date = 8th century , established_title2 = Christianization , established_date2 = 965 , established_title3 = , established_date3 = 5 June 1849 , established_title4 = Faroese home rule , established_date4 = 24 March 1948 , established_title5 = European Economic Community, EEC 1973 enlargement of the European Communities, accession , established_date5 = 1 January 1973 , established_title6 = Greenlandic home rule , established_date6 = 1 May 1979 , official_languages = Danish language, Danish , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = German language, GermanGerman is recognised as a protected minority language in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with selective breeding, artificial selection, which in his view is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Genetic diversity, Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and their offspring can inherit such mutations. Throughout the lives of the individuals, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the Cell (biology), cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment. Because individuals with certain variants of the trait tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltationism
In biology, saltation () is a sudden and large mutational change from one generation to the next, potentially causing single-step speciation. This was historically offered as an alternative to Darwinism. Some forms of mutationism were effectively saltationist, implying large discontinuous jumps. Speciation, such as by polyploidy in plants, can sometimes be achieved in a single and in evolutionary terms sudden step. Evidence exists for various forms of saltation in a variety of organisms. History Prior to Charles Darwin most evolutionary scientists had been saltationists. Jean-Baptiste Lamarck was a gradualist but similar to other scientists of the period had written that saltational evolution was possible. Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire endorsed a theory of saltational evolution that "monstrosities could become the founding fathers (or mothers) of new species by instantaneous transition from one form to the next." Geoffroy wrote that environmental pressures could produce sudden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Synthesis (20th Century)
The modern synthesis was the early 20th-century synthesis of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution and Gregor Mendel's ideas on heredity into a joint mathematical framework. Julian Huxley coined the term in his 1942 book, ''Evolution: The Modern Synthesis''. The synthesis combined the ideas of natural selection, Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian genetics, and population genetics. It also related the broad-scale macroevolution seen by paleontology, palaeontologists to the small-scale microevolution of local population, populations. The synthesis was defined differently by its founders, with Ernst Mayr in 1959, G. Ledyard Stebbins in 1966, and Theodosius Dobzhansky in 1974 offering differing basic postulates, though they all include natural selection, working on heritable variation supplied by mutation. Other major figures in the synthesis included E. B. Ford, Bernhard Rensch, Ivan Schmalhausen, and George Gaylord Simpson. An early event in the modern synthesis was R. A. Fisher's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
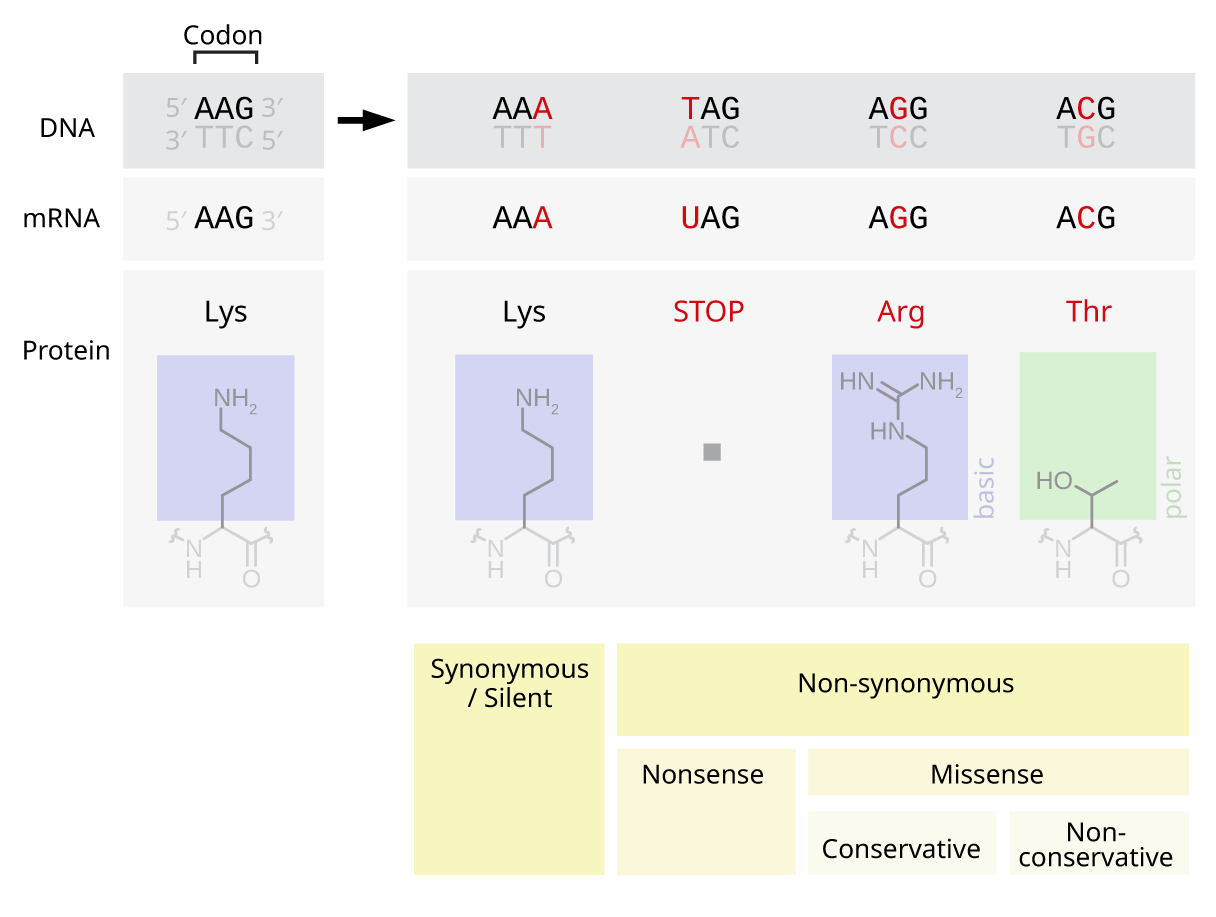
Point Mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function. Causes Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the nucleotides code for. Point mutations may arise from spontaneous mutations that occur during DNA replication. The rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publishes a monthly Dutch-language edition. First published on 22 November 1956, ''New Scientist'' has been available in online form since 1996. Sold in retail outlets (paper edition) and on subscription (paper and/or online), the magazine covers news, features, reviews and commentary on science, technology and their implications. ''New Scientist'' also publishes speculative articles, ranging from the technical to the philosophical. ''New Scientist'' was acquired by Daily Mail and General Trust (DMGT) in March 2021. History Ownership The magazine was founded in 1956 by Tom Margerison, Max Raison and Nicholas Harrison as ''The New Scientist'', with Issue 1 on 22 November 1956, priced at one shilling (a twentieth of a pound in pre-decimal UK cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punctuated Equilibrium
In evolutionary biology, punctuated equilibrium (also called punctuated equilibria) is a Scientific theory, theory that proposes that once a species appears in the fossil record, the population will become stable, showing little evolution, evolutionary change for most of its geological history. : ''Reprinted in'' * * This state of little or no morphological change is called ''stasis''. When significant evolutionary change occurs, the theory proposes that it is generally restricted to rare and geologic time scale, geologically rapid events of branching speciation called cladogenesis. Cladogenesis is the process by which a species splits into two distinct species, rather than one species gradually transforming into another. Punctuated equilibrium is commonly contrasted with phyletic gradualism, the idea that evolution generally occurs uniformly by the steady and gradual transformation of whole lineages (anagenesis). In 1972, paleontologists Niles Eldredge and Stephen Jay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gradualism
Gradualism, from the Latin ''gradus'' ("step"), is a hypothesis, a theory or a tenet assuming that change comes about gradually or that variation is gradual in nature and happens over time as opposed to in large steps. Uniformitarianism, incrementalism, and reformism are similar concepts. Geology and biology In the natural sciences, gradualism is the theory which holds that profound change is the cumulative product of slow but continuous processes, often contrasted with catastrophism. The theory was proposed in 1795 by James Hutton, a Scottish geologist, and was later incorporated into Charles Lyell's theory of uniformitarianism. Tenets from both theories were applied to biology and formed the basis of early evolutionary theory. Charles Darwin was influenced by Lyell's ''Principles of Geology'', which explained both uniformitarian methodology and theory. Using uniformitarianism, which states that one cannot make an appeal to any force or phenomenon which cannot presently be obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution (journal)
''Evolution: International Journal of Organic Evolution'', is a monthly scientific journal that publishes significant new results of empirical or theoretical investigations concerning facts, processes, mechanics, or concepts of evolutionary phenomena and events. ''Evolution'' is published by the Society for the Study of Evolution. Its current editor-in-chief is Tracey Chapman. Former editors-in-chief The journal was founded soon after the Second World War. Its first editor was the evolutionary geneticist Ernst Mayr. * Ruth Geyer Shaw, July 2013 – 2017 * Daphne Fairbairn Daphne (; ; el, Δάφνη, , ), a minor figure in Greek mythology, is a naiad, a variety of female nymph associated with fountains, wells, springs, streams, brooks and other bodies of freshwater. There are several versions of the myth in whi ..., 2010- June 2013 References External linksOfficial website Evolutionary biology journals Publications established in 1947 Academic journals published by l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Studies
''Victorian Studies'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Indiana University Press. It covers research on nineteenth-century Britain during the reign of Queen Victoria (1837–1901) and publishes essays, forums, and reviews on a variety of topics concerning Victorianism, including literature, social and political history, philosophy, fine arts, science, economics, and law. It is the official journal of the North American Victorian Studies Association. ''Victorian Studies'' was established in 1956 at Indiana University by Philip Appleman, William A. Madden, and Michael Wolff. The journal is hosted by the university's Victorian Studies Program, in conjunction with the English department. The current editors-in-chief are Ivan Kreilkamp, Rae Greiner, Monique Morgan, and Lara Kriegel. Recent issues of the journal have focused on a variety of topics, ranging from science, including "Darwin and the Evolution of Victorian Studies", to the more subjective sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Scientist
__NOTOC__ ''American Scientist'' (informally abbreviated ''AmSci'') is an American bimonthly science and technology magazine published since 1913 by Sigma Xi, The Scientific Research Society. In the beginning of 2000s the headquarters was in New Haven, CT. Each issue includes feature articles written by prominent scientists and engineers who review research in fields from molecular biology to computer engineering. Each issue also includes the work of cartoonists, including those of Sidney Harris, Benita Epstein Benita L. Epstein is a prolific gag cartoonist for magazines, greeting cards, websites and newspapers. She was a regular contributor to the comic strip ''Six Chix'', distributed by King Features Syndicate. Before becoming a cartoonist, Epstein ea ..., and Mark Heath. Also included is the ''Scientists' Nightstand'' that reviews a vast range of science-related books and novels. ''American Scientist Online'' () was launched in May 2003. References External links * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire
Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire (15 April 177219 June 1844) was a French naturalist who established the principle of "unity of composition". He was a colleague of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and expanded and defended Lamarck's evolutionary theories. Geoffroy's scientific views had a transcendental flavor (unlike Lamarck's materialistic views) and were similar to those of German morphologists like Lorenz Oken. He believed in the underlying unity of organismal design, and the possibility of the transmutation of species in time, amassing evidence for his claims through research in comparative anatomy, paleontology, and embryology. He is considered as a predecessor of the evo-devo evolutionary concept. Life and early career Geoffroy was born at Étampes (in present-day Essonne), and studied at the Collège de Navarre, in Paris, where he studied natural philosophy under M. J. Brisson. He then attended the lectures of Daubenton at the College de France and Fourcroy at the Jardin des Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |