|
Szyszkowski Equation
The Szyszkowski Equation has been used by Meissner and Michaels to describe the decrease in surface tension of aqueous solutions of carboxylic acids, alcohol (chemistry), alcohols and esters at varying mole fractions. It describes the exponential decrease of the surface tension at low concentrations reasonably but should be used only at concentrations below 1 mole%. Equation :\sigma_m =\sigma_w\left(1-0.411\log\left(1+\frac\right)\right) with: *σm is surface tension of the mixture *σw is surface tension of pure water *''a'' is component specific constant (see table below) *x is mole fraction of the solvated component The equation can be rearranged to be explicit in ''a'': :\begin a&=\frac\\ &=x10^ \end This allows the direct calculation of that component specific parameter ''a'' from experimental data. The equation can also be written as: :\gamma=\gamma_0-\frac\ln(1+K_c) with: *γ is surface tension of the mixture *γ0 is surface tension of pure water *R is ideal gas constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to float on a water surface without becoming even partly submerged. At liquid–air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of liquid molecules to each other (due to cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). There are two primary mechanisms in play. One is an inward force on the surface molecules causing the liquid to contract. Second is a tangential force parallel to the surface of the liquid. This ''tangential'' force is generally referred to as the surface tension. The net effect is the liquid behaves as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. But this analogy must not be taken too far as the tension in an elastic membrane is dependent on the amount of deformation of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters typically have a pleasant smell; those of low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and are found in essential oils and pheromones. They perform as high-grade solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, and are one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. Polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties. '' Nomenclature Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
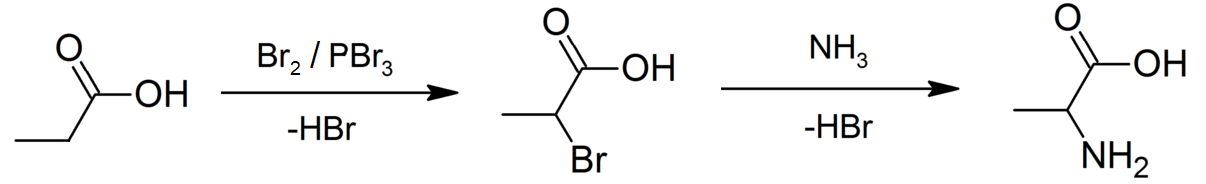
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion CH3CH2CO2− as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the same compound, which he called propionic acid, from the Greek words πρῶτος (prōtos), meaning ''first'', and πίων (piōn), meaning ''fat'', because it is the smallest H(CH2)''n''COOH acid that exhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Acetate
Ethyl acetate ( systematically ethyl ethanoate, commonly abbreviated EtOAc, ETAC or EA) is the organic compound with the formula , simplified to . This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and in the decaffeination process of tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent. Production and synthesis Ethyl acetate was first synthesized by the Count de Lauraguais in 1759 by distilling a mixture of ethanol and acetic acid. In 2004, an estimated 1.3 million tonnes were produced worldwide. The combined annual production in 1985 of Japan, North America, and Europe was about 400,000 tonnes. The global ethyl acetate market was valued at $3.3 billion in 2018. Ethyl acetate is synthesized in industry mainly via the classic Fischer esterification reaction of ethanol and acetic acid. This mixture converts to the ester in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Propionate
Methyl propionate, also known as methyl propanoate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CH2CO2CH3. It is a colorless liquid with a fruity, rum-like odor. Preparation Methyl propionate can be prepared by esterification of propionic acid with methanol. Industrially, it is prepared by carboalkoxylation, i.e., the reaction of ethylene with carbon monoxide and methanol in the presence of a catalyst: :C2H4 + CO + MeOH → MeO2CCH2CH3 The reaction is catalyzed by nickel carbonyl and palladium(0) complexes.(mayth and yafs)Scott D. Barnicki "Synthetic Organic Chemicals" in Handbook of Industrial Chemistry and Biotechnology edited by James A. Kent, New York : Springer, 2012. 12th ed. . Uses Condensation of Methyl propionate with formaldehyde followed by dehydration yields methyl methacrylate: :MeO2CCH2CH3 + CH2O → MeO2CCH(CH2OH)CH3 :MeO2CCH(CH2OH)CH3 → MeO2CC(=CH2)CH3 Methyl propionate is used as a solvent for cellulose nitrate and lacquers, and as a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Propionate
Ethyl propionate is an organic compound with formula C2H5O2CCH2CH3. It is the ethyl ester of propionic acid. It is a colorless volatile liquid with a pineapple-like odor. Some fruits such as kiwis and strawberries contain ethyl propionate in small amounts. Uses and reactions It is also used in the production of some antimalarial drugs including pyrimethamine. Ethyl propionate can be synthesized by the Fischer esterification of ethanol and propionic acid: :CH3CH2OH + CH3CH2CO2H → CH3CH2O2CCH2CH3 + H2O It participates in condensation reactions by virtue of the weakly acidic methylene group. See also *Methyl propionate Methyl propionate, also known as methyl propanoate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CH2CO2CH3. It is a colorless liquid with a fruity, rum-like odor. Preparation Methyl propionate can be prepared by esterification of propion ..., a similar compound References {{ester-stub Propionate esters Ethyl esters Flavors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propyl Acetate
Propyl acetate, also known as propyl ethanoate, is an organic compound. Nearly 20,000 tons are produced annually for use as a solvent. This colorless liquid is known by its characteristic odor of pears. Due to this fact, it is commonly used in fragrances and as a flavor additive. It is formed by the esterification of acetic acid and propan-1-ol, often via Fischer–Speier esterification Fischer esterification or Fischer–Speier esterification is a special type of esterification by refluxing a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. The reaction was first described by Emil Fischer and Arthur Speier ..., with sulfuric acid as a catalyst and water produced as a byproduct. References External links NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - Toxicity Data [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohdan Szyszkowski
Bohdan Szyszkowski (born June 20, 1873, in Trybuchy, Podolia, Russia (now village in Ukraine) – August 13, 1931 in Myślenice, Poland) was a Polish chemist and member of PAU. Szyszkowski published important papers on electrochemistry and surface chemistry. See also * Szyszkowski equation The Szyszkowski Equation has been used by Meissner and Michaels to describe the decrease in surface tension of aqueous solutions of carboxylic acids, alcohol (chemistry), alcohols and esters at varying mole fractions. It describes the exponential de ... References 1873 births 1931 deaths Polish chemists Chemists from the Russian Empire {{chemist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids ( liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them. It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, civil, chemical and biomedical engineering, geophysics, oceanography, meteorology, astrophysics, and biology. It can be divided into fluid statics, the study of fluids at rest; and fluid dynamics, the study of the effect of forces on fluid motion. It is a branch of continuum mechanics, a subject which models matter without using the information that it is made out of atoms; that is, it models matter from a ''macroscopic'' viewpoint rather than from ''microscopic''. Fluid mechanics, especially fluid dynamics, is an active field of research, typically mathematically complex. Many problems are partly or wholly unsolved and are best addressed by numerical methods, typically using computers. A modern discipline, called computational fluid dynamics (CFD), is dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |