|
Swiss Constitution
The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation (SR 10; german: Bundesverfassung der Schweizerischen Eidgenossenschaft (BV); french: Constitution fédérale de la Confédération suisse (Cst.); it, Costituzione federale della Confederazione Svizzera (Cost.); rm, ) of 18 April 1999 (SR 101) is the third and current federal constitution of Switzerland. It establishes the ''Swiss Confederation'' as a federal republic of 26 cantons (states). The document contains a catalogue of individual and popular rights (including the right to call for popular referendums on federal laws and constitutional amendments), delineates the responsibilities of the cantons and the Confederation and establishes the federal authorities of government. The Constitution was adopted by a referendum on 18 April 1999, in which a majority of the people and the Cantons voted in favour. It replaced the prior federal constitution of 1874, which it was intended to bring up to date without changing its s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1999 Swiss Referendums
Ten referendums were held in Switzerland during 1999. Nohlen, D & Stöver, P (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p1940 The first four were held on 7 February on changes to the eligibility for membership of the Federal Council (approved), constitutional regulations on organ transplantation (approved), a popular initiative "house ownership for everyone" (rejected) and an amendment to the federal law on spatial planning (approved). The fifth was held on 18 April on a new Swiss Federal Constitution, which was approved. The last five referendums were held on 13 June on the asylum law (approved), on a federal resolution on asylum and foreigners (approved), a federal resolution on the medical prescription of heroin (approved), federal laws on disability and maternity insurance (both rejected). Background New constitution The proposed new constitution would sever the link between gold and the Swiss franc, which had been required by the old constitution. The Swiss National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
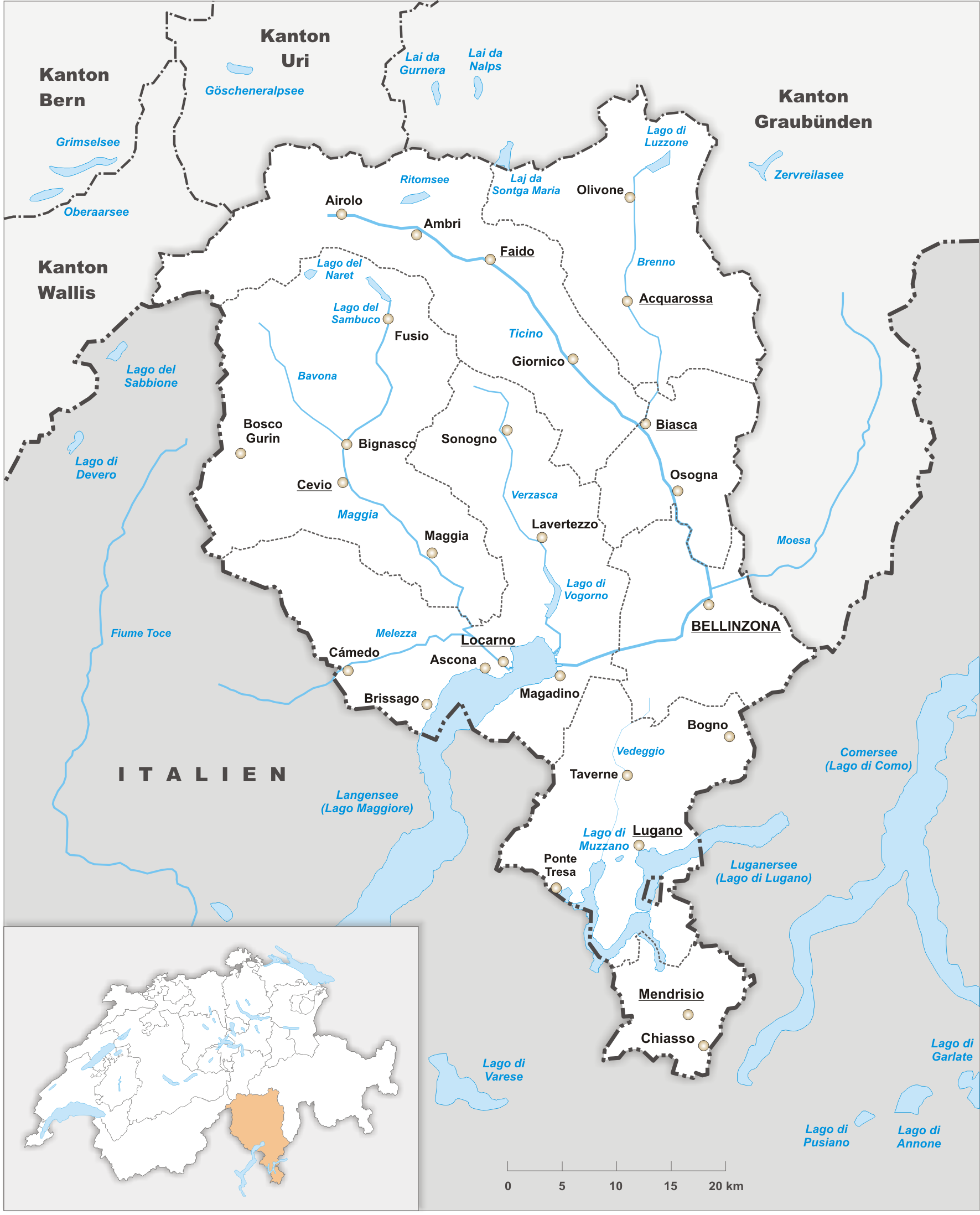
Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts and its capital city is Bellinzona. It is also traditionally divided into the Sopraceneri and the Sottoceneri, respectively north and south of Monte Ceneri. Red and blue are the colours of its flag. Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. It is one of the three large southern Alpine cantons, along with Valais and the Grisons. However, unlike all other cantons, it lies almost entirely south of the Alps, and has no natural access to the Swiss Plateau. Through the main crest of the Gotthard and adjacent mountain ranges, it borders the canton of Valais to the northwest, the canton of Uri to the north and the canton of Grisons to the northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thurgau
Thurgau (; french: Thurgovie; it, Turgovia), anglicized as Thurgovia, more formally the Canton of Thurgau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts and its capital is Frauenfeld. Thurgau is part of Eastern Switzerland. It is named for the river Thur, and the name ''Thurgovia'' was historically used for a larger area, including part of this river's basin upstream of the modern canton. The area of what is now Thurgau was acquired as subject territories by the cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy from the mid 15th century. Thurgau was first declared a canton in its own right at the formation of the Helvetic Republic in 1798. The population, , is . In 2007, there were a total of 47,390 (or 19.9% of the population) who were resident foreigners. History In prehistoric times the lands of the canton were inhabited by people of the Pfyn culture along Lake Constance. During Roman times the canton was part of the province ''Raetia'' unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
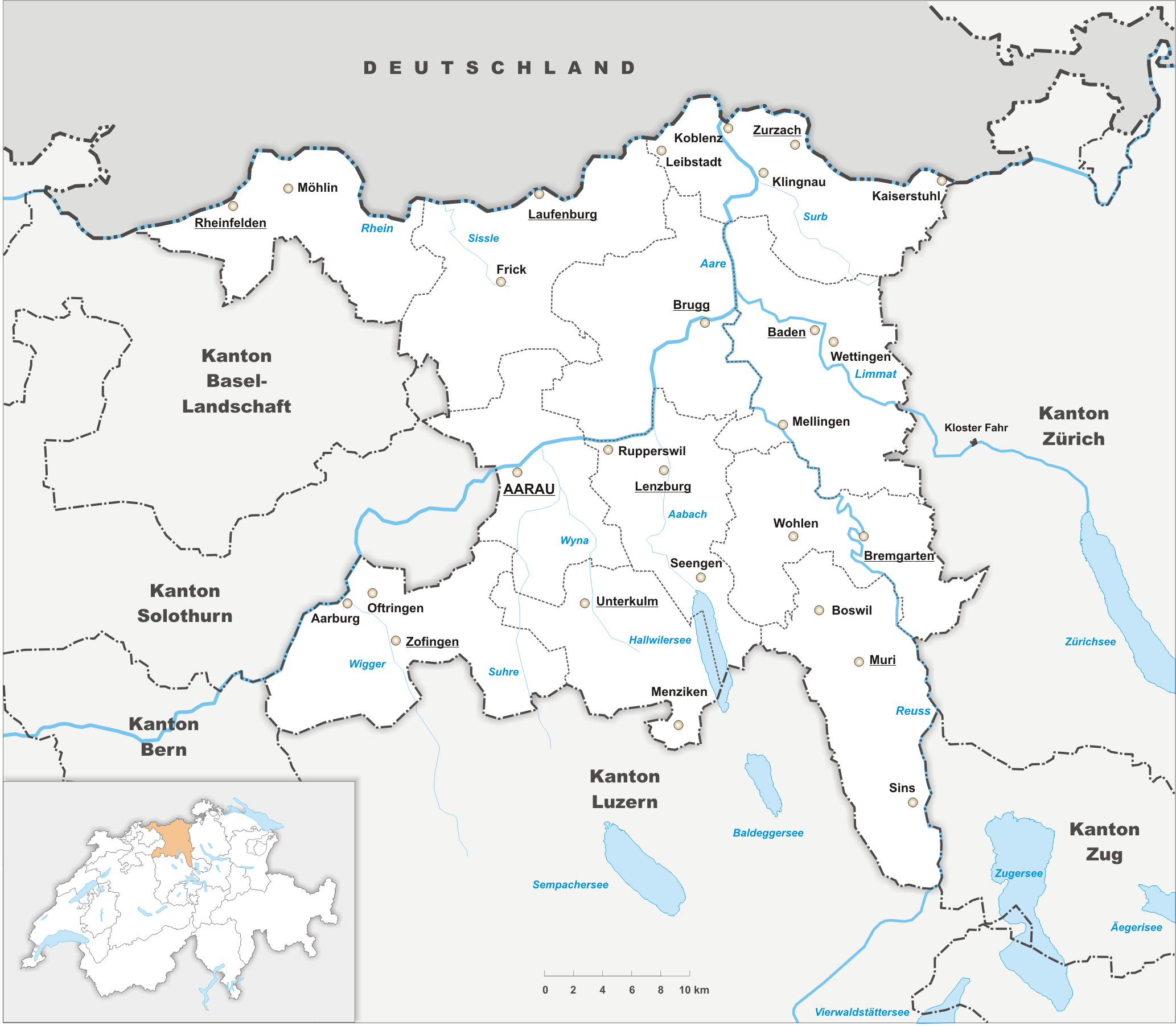
Aargau
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau. Aargau is one of the most northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare River, which is why the canton is called ''Aar- gau'' (meaning "Aare province"). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland. History Early history The area of Aargau and the surrounding areas were controlled by the Helvetians, a member of the Celts, as far back as 200 BC. It was eventually occupied by the Romans and then by the 6th century, the Franks. The Romans built a major settlement called Vindonissa, near the present location of Brugg. Medieval Aargau The reconstructed Old High German name of Aargau is ''Argowe'', first unambiguously attested (in the spelling ''Argue'') in 795. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of St
Canton may refer to: Administrative division terminology * Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland * Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French Arts and entertainment * Canton (band), an Italian synth pop group * "Canton" (song) by Japan * Canton, a fictional town in " Jaynestown", an episode of ''Firefly'' Design * Canton (building), a corner pilaster * Canton (flag), an emblem placed in the top left quarter of a flag * Canton (heraldry), a square or other charge (symbol) occupying the upper left corner of a coat of arms * Canton porcelain, Chinese ceramic ware People * Canton (surname), and list of people with the surname * Canton Jones, American Christian music/hip-hop artist Places Canada * Canton, New Brunswick, a community in Drummond Parish, New Brunswick * Canton, Ontario China * Guangdong (Canton Province), province in southern China * Guangzhou (Canton City), capita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Switzerland
The early modern history of the Old Swiss Confederacy (''Eidgenossenschaft'', also known as the "Swiss Republic" or ''Republica Helvetiorum'') and its constituent Thirteen Cantons encompasses the time of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) until the French invasion of 1798. The early modern period was characterized by an increasingly aristocratic and oligarchic ruling class as well as frequent economic or religious revolts. This period came to be referred to as the ''Ancien Régime'' retrospectively, in post-Napoleonic Switzerland. The loosely organized Confederation remained generally disorganized and crippled by the religious divisions created by the Swiss Reformation. During this period the Confederation gained formal independence from the Holy Roman Empire with support from France, and had very close relations with France. The early modern period also saw the growth of French-Swiss literature, and notable authors of the Age of Enlightenment such as the mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to * the French word for "ancient, old" ** Société des anciens textes français * the French for "former, senior" ** Virelai ancien ** Ancien Régime ** Ancien Régime in France {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
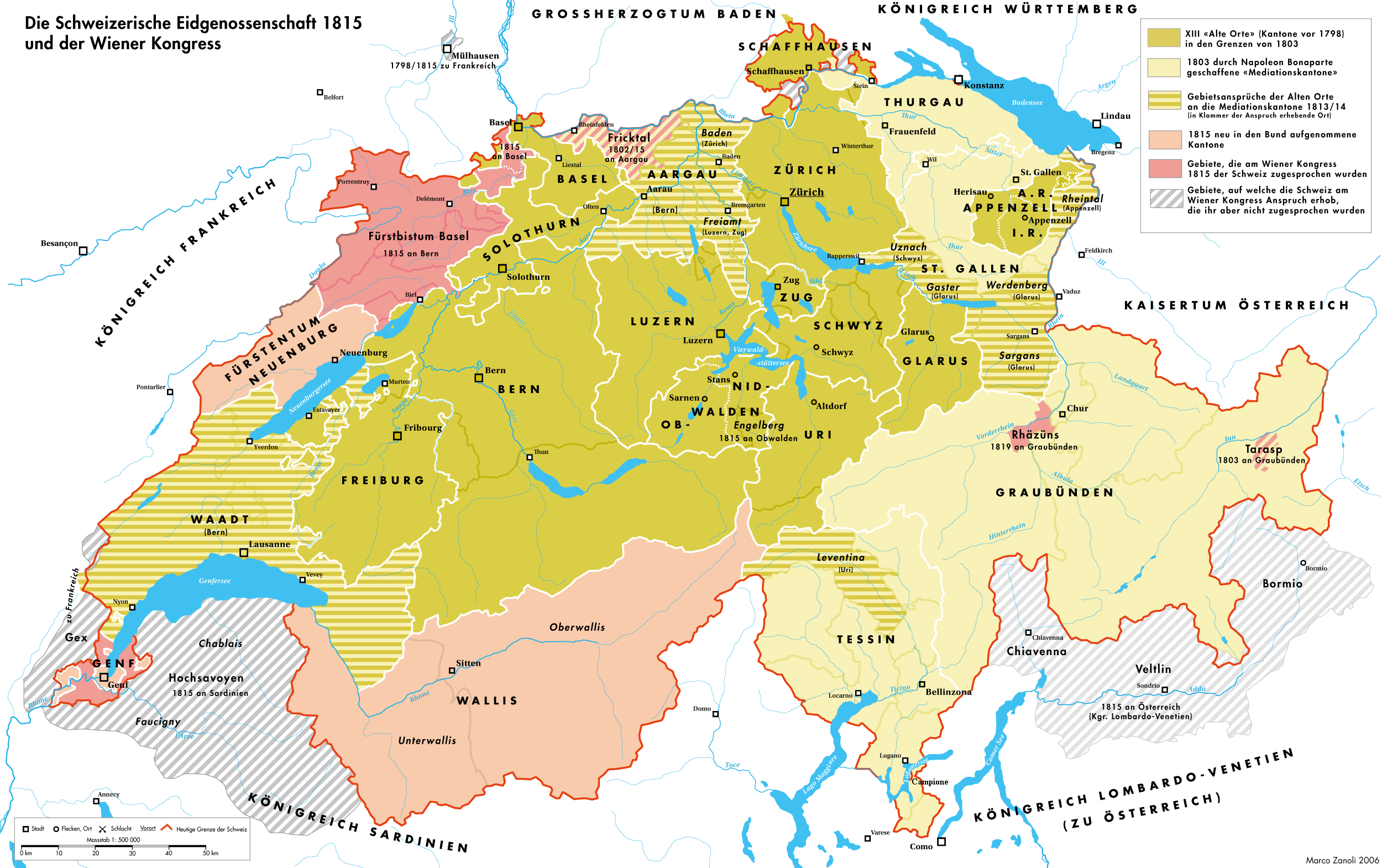
Restoration And Regeneration In Switzerland
The periods of Restoration and Regeneration in Swiss history lasted from 1814 to 1847. "Restoration" is the period of 1814 to 1830, the restoration of the ''Ancien Régime'' (federalism), reverting the changes imposed by Napoleon Bonaparte on the centralist Helvetic Republic from 1798 and the partial reversion to the old system with the Act of Mediation of 1803. "Regeneration" is the period of 1830 to 1848, when in the wake of the July Revolution the "restored" ''Ancien Régime'' was countered by the liberal movement. In the Protestant cantons, the rural population enforced liberal cantonal constitutions, partly in armed marches on the cities. This resulted in a conservative backlash in the Catholic cantons in the 1830s, raising the conflict to the point of civil war by 1847. Restoration When Napoleon's fall appeared imminent, the Act of Mediation was suspended in late December 1813, and lengthy discussions about future constitutions were initiated in all cantons of Switzerla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Treaty
The Federal Treaty (German: ''Bundesvertrag'', French: ''Pacte fédéral'', Italian: ''Patto federale'') was the legal foundation for the new Swiss Confederacy of 1815. It came about after interventions by the great powers of the Sixth Coalition that defeated Napoleon. The Federal Treaty defined a confederation between 22 independent Cantons. From 1815 until the Swiss Federal Constitution of 1848, it acted as the Restorationist Constitution of Switzerland. Historical development When the anti-French troops marched into Switzerland in 1813, the Act of Mediation imposed by Napoleon in 1803 lost meaning and was repealed by 10 of the 19 cantons, who simultaneously founded the Confederate Convention in Zürich with the goal of establishing a new "Federal Union" (''Bundesverein'') with the Old Swiss Confederacy in mind. 9 old and 5 new cantons were represented. From February 1814 on, a new constitution was being negotiated to replace the Act of Mediation. At the same time, the Reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 establishing the Swiss Confederation. The act also abolished the previous Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasion of Switzerland by French troops in 1798. After the withdrawal of French troops in July 1802, the Republic collapsed (in the '' Stecklikrieg'' civil war). The Act of Mediation was Napoleon's attempt at a compromise between the ''Ancien Régime'' and a republic. This intermediary stage of Swiss history lasted until the Restoration of 1815. The Act also destroyed the statehood of Tarasp and gave it to Graubunden. End of the Helvetic Republic Following the French invasion of 1798, the decentralized and aristocratic Old Swiss Confederation was replaced with the highly centralized and republican Helvetic Republic. However the changes were too abrupt and sweeping and ignored the strong sense of identity that most Swiss had with their canton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Ochs
Peter Ochs (20 August 1752, Nantes, France – 19 June 1821, Basel, Switzerland) was a Swiss politician who is best known for drawing up the first constitution of the short-lived Helvetic Republic. Biography Born in France of a family that claimed roots in the Basel aristocracy, Ochs himself settled in Basel in 1769. In 1776 he obtained a doctorate of laws, became a magistrate and took up politics, making many useful contacts through his marriage.''Histoire de la Suisse'', Éditions Fragnière, Fribourg, Switzerland At the time Switzerland was a confederacy of self-governing cantons held together by a loose military alliance. There was little in terms of actual union and no central government. Like most of Europe, Switzerland was deemed feudal in nature since the wealthiest members of society benefited from privileges that others were denied. There was much resentment over this which led to many conspiracies and uprisings, such as that led by Major Abraham Davel who protested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |