|
Svein Heglund
Svein Heglund (10 December 1918 – 18 June 1998) was a Norwegian engineer and RAF officer. He was the leading Norwegian pilot ace during the Second World War shooting down 16 German planes. He was awarded the Norwegian War Cross with two Swords and the British Distinguished Service Order and Distinguished Flying Cross. He served as head of ''Luftforsvarets forsyningskommando'' (LFK), with the rank of major general, from 1974 until his retirement in 1982. His memoir of his career in the RAF - ''Høk over høk'' (''Hawk Over Hawk'') - was published in 1995. Biography Heglund was born in Kristiania on 10 December 1918, to engineer Otto Hjalmar Heglund and photographer Anna Margaretha Klinkenberg. Second World War Heglund had tried to enlist with the Norwegian army flight school in the autumn of 1939 but the admission deadline had already expired. When he completed his period of national service conscription he travelled to Zurich to study engineering. He was in Switzerland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of in 2019, and the metropolitan area had an estimated population of in 2021. During the Viking Age the area was part of Viken. Oslo was founded as a city at the end of the Viking Age in 1040 under the name Ánslo, and established as a ''kaupstad'' or trading place in 1048 by Harald Hardrada. The city was elevated to a bishopric in 1070 and a capital under Haakon V of Norway around 1300. Personal unions with Denmark from 1397 to 1523 and again from 1536 to 1814 reduced its influence. After being destroyed by a fire in 1624, during the reign of King Christian IV, a new city was built closer to Akershus Fortress and named Christiania in honour of the king. It became a municipality ('' formannskapsdistrikt'') on 1 January 1838. The city fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernt Balchen
Bernt Balchen (23 October 1899 – 17 October 1973) was a Norwegian pioneer polar aviator, navigator, aircraft mechanical engineer and military leader. A Norwegian native, he later became an American citizen and was a recipient of the Distinguished Flying Cross. His service in the U.S. Army Air Forces during World War II made use of his Arctic exploration expertise to help the Allies over Scandinavia and Northern Europe. After the war, Balchen continued to be an influential leader with the U.S. Air Force, as well as a highly regarded private consultant in projects involving the Arctic and aviation. Early years The son of a country doctor, Balchen was born at the farm Myren in Tveit, just outside Kristiansand, Norway. After having finished Norwegian middle school in 1916, he attended a Forestry School from 1917 to 1918. Next he enrolled in the French Foreign Legion, and his unit was assigned to the Verdun front in World War I. In 1918, before seeing action, Balchen was recalle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
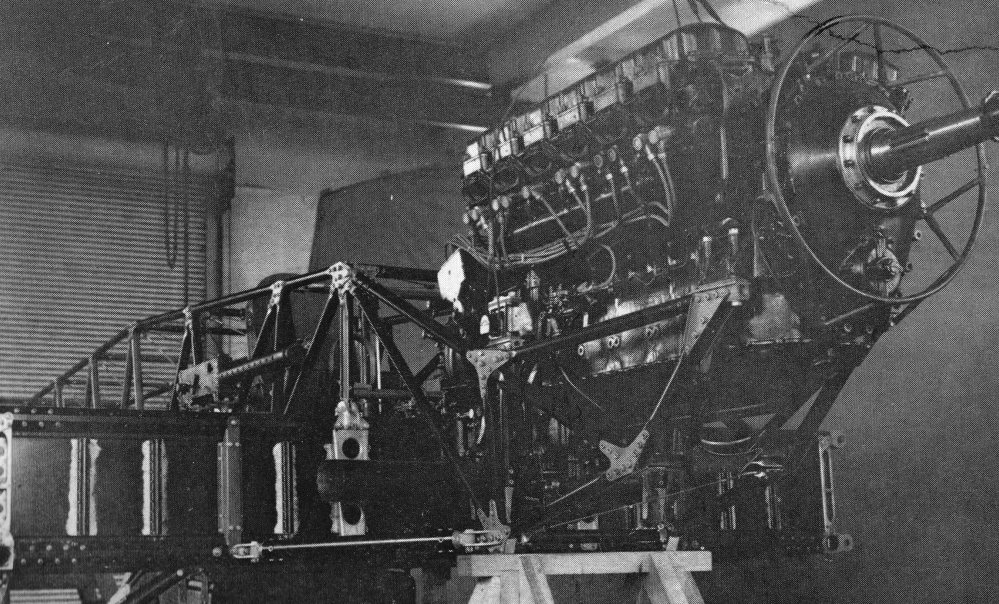
De Havilland Mosquito
The de Havilland DH.98 Mosquito is a British twin-engined, shoulder-winged, multirole combat aircraft, introduced during the Second World War. Unusual in that its frame was constructed mostly of wood, it was nicknamed the "Wooden Wonder", or "Mossie". Lord Beaverbrook, Minister of Aircraft Production, nicknamed it "Freeman's Folly", alluding to Air Chief Marshal Sir Wilfrid Freeman, who defended Geoffrey de Havilland and his design concept against orders to scrap the project. In 1941, it was one of the fastest operational aircraft in the world.Bowman 2005, p. 21. Originally conceived as an unarmed fast bomber, the Mosquito's use evolved during the war into many roles, including low- to medium-altitude daytime tactical bomber, high-altitude night bomber, pathfinder, day or night fighter, fighter-bomber, intruder, maritime strike, and photo-reconnaissance aircraft. It was also used by the British Overseas Airways Corporation as a fast transport to carry small, high-value c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cunningham (RAF Officer)
John "Cat's Eyes" Cunningham (27 July 1917 – 21 July 2002) was a Royal Air Force (RAF) night fighter ace during the Second World War and a test pilot. During the war he was nicknamed "Cat's Eyes" by the British press to explain his successes and to avoid communicating the existence of airborne radar to the enemy. Cunningham was born in Croydon, and as a teenager was keen on entering the aviation industry. Temporarily abiding by his father's wishes for him to avoid the military, he approached the de Havilland company and was accepted as an engineering candidate. Concurrently, he joined the Royal Auxiliary Air Force and became a member of No. 604 (County of Middlesex) Squadron. Cunningham began his training in August 1935, flew solo in March 1936 and received his wings in 1937. He gradually became an established test pilot, gaining considerable flying time on different types of aircraft. In August 1939 Cunningham rejoined his squadron, now equipped with a version of the Brist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Ferry Command
RAF Ferry Command was the secretive Royal Air Force command formed on 20 July 1941 to ferry urgently needed aircraft from their place of manufacture in the United States and Canada, to the front line operational units in Britain, Europe, North Africa and the Middle East during the Second World War. It was later subsumed into the new Transport Command on 25 March 1943 by being reduced to Group status. History The practice of ferrying aircraft from US manufacturers to the UK was begun by the Ministry of Aircraft Production. Its minister, Lord Beaverbrook, a Canadian by origin, reached an agreement with Sir Edward Beatty, a friend and chairman of the Canadian Pacific Railway Company, to provide ground facilities and support. MAP would discretely provide civilian crews and management. Previously, aircraft were being assembled then disassembled and then transported by ship across the Atlantic, and were subject to long delays and frequent attacks by German U-Boats. Former RAF off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF North Weald
North Weald Airfield is an operational general aviation aerodrome, in the civil parish of North Weald Bassett in Epping Forest, Essex, England. It was an important fighter station during the Battle of Britain, when it was known as the RAF Station RAF North Weald. It is the home of North Weald Airfield Museum. It is home to many private aircraft and historic types, Essex & Herts Air Ambulance helicopter and is an active flight training airfield. History Royal Flying Corps Station North Weald Bassett aerodrome was established in the summer of 1916 during the First World War by the Royal Flying Corps. Later it became Royal Air Force with effect from Monday 1 April 1918. Its military functions continued to develop during the interwar period, with the building of large hangars and accommodation for Royal Air Force (RAF) personnel. The airfield played an important part in the air defence strategy of the United Kingdom during the Second World War. Initially Hawker Hurricanes were de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft used by the Royal Air Force and other Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. Many variants of the Spitfire were built, from the Mk 1 to the Rolls-Royce Griffon engined Mk 24 using several wing configurations and guns. It was the only British fighter produced continuously throughout the war. The Spitfire remains popular among enthusiasts; around 70 remain airworthy, and many more are static exhibits in aviation museums throughout the world. The Spitfire was designed as a short-range, high-performance interceptor aircraft by R. J. Mitchell, chief designer at Supermarine Aviation Works, which operated as a subsidiary of Vickers-Armstrong from 1928. Mitchell developed the Spitfire's distinctive elliptical wing with innovative sunken rivets (designed by Beverley Shenstone) to have the thinnest possible cross-section, achieving a potential top speed greater than that of several contemporary figh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapa Flow
Scapa Flow viewed from its eastern end in June 2009 Scapa Flow (; ) is a body of water in the Orkney Islands, Scotland, sheltered by the islands of Mainland, Graemsay, Burray,S. C. George, ''Jutland to Junkyard'', 1973. South Ronaldsay and Hoy. Its sheltered waters have played an important role in travel, trade and conflict throughout the centuries. Vikings anchored their longships in Scapa Flow more than a thousand years ago. It was the United Kingdom's chief naval base during the First and Second World Wars, but the facility was closed in 1956. Scapa Flow has a shallow sandy bottom not deeper than and most of it is about deep; it is one of the great natural harbours and anchorages of the world, with sufficient space to hold a number of navies. The harbour has an area of and contains just under 1 billion cubic metres of water. Since the scuttling of the German fleet after World War I, its wrecks and their marine habitats form an internationally acclaimed diving lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Skeabrae
Royal Air Force Skeabrae or more simply RAF Skeabrae is a former Royal Air Force Royal Air Force station, station located in Orkney, Mainland, Orkney, Mainland, United Kingdom. History The following units were here at some point: ;Squadrons ;Units * Advanced Ship Recognition Flight RAF (January - February 1943) became No. 1476 (Advanced Ship Recognition) Flight RAF (February - June 1943 & June - January 1944) * No. 1491 (Fighter Gunnery) Flight RAF (November 1942 - August 1943) * 1841 Naval Air Squadron * No. 2714 Squadron RAF Regiment * No. 2745 Squadron RAF Regiment * No. 2766 Squadron RAF Regiment * No. 2824 Squadron RAF Regiment ;Royal Navy Current use The site is currently open land. See also * List of former Royal Air Force stations References Citations Bibliography * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Skeabrae, RAF Royal Air Force stations in Scotland Buildings and structures in Orkney Royal Air Force stations of World War II in the United Kingdom Military airbases establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north of the coast of Caithness and has about 70 islands, of which 20 are inhabited. The largest island, the Mainland, Orkney, Mainland, has an area of , making it the List of islands of Scotland, sixth-largest Scottish island and the List of islands of the British Isles, tenth-largest island in the British Isles. Orkney’s largest settlement, and also its administrative centre, is Kirkwall. Orkney is one of the 32 Subdivisions of Scotland, council areas of Scotland, as well as a Orkney (Scottish Parliament constituency), constituency of the Scottish Parliament, a Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area, and an counties of Scotland, historic county. The local council is Orkney Islands Council, one of only three councils in Scotland with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miles Master
The Miles M.9 Master was a British two-seat monoplane advanced trainer designed and built by aviation company Miles Aircraft Ltd. It was inducted in large numbers into both the Royal Air Force (RAF) and Fleet Air Arm (FAA) during the Second World War. The Master can trace its origins back to the earlier M.9 Kestrel demonstrator aircraft. Following the failure of the rival de Havilland Don as a satisfactory trainer aircraft, the RAF ordered 500 ''M9A Master'' advanced trainers to meet its needs. Once in service, it provided a fast, strong and fully aerobatic aircraft that functioned as an excellent introduction to the high performance British fighter aircraft of the day: the Spitfire and Hurricane. Throughout its production life, thousands of aircraft and various variants of the Master were produced, the latter being largely influenced by engine availability. Numerous Masters were modified to enable their use as glider tows. The Master also served as the basis for the Miles M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)