|
Supercomputing In Pakistan
The high performance supercomputing program started in mid-to-late 1980s in Pakistan. Supercomputing is a recent area of Computer science in which Pakistan has made progress, driven in part by the growth of the information technology age in the country. Developing on the ingenious supercomputer program started in 1980s when the deployment of the Cray supercomputers was initially denied. The fastest supercomputer currently in use in Pakistan is developed and hosted by the National University of Sciences and Technology at its modeling and simulation research centre. As of November 2012, there are no supercomputers from Pakistan on the Top500 list. Background The initial interests of Pakistan in the research and development of supercomputing began during the early 1980s, at several high-powered institutions of the country. During this time, senior scientists at the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC) were the first to engage in research on high performance computing, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
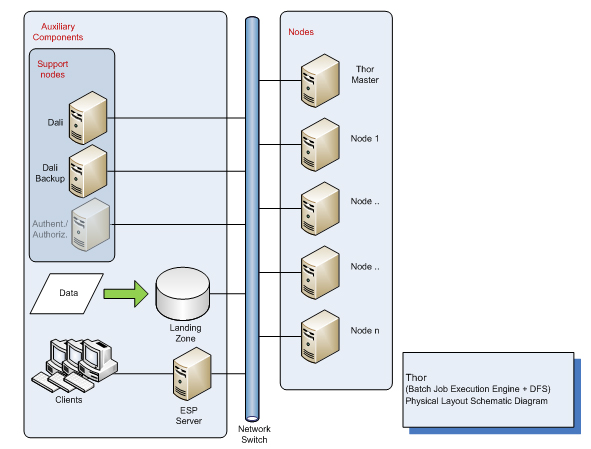
High Performance Computing Cluster
HPCC (High-Performance Computing Cluster), also known as DAS (Data Analytics Supercomputer), is an open source, data-intensive computing system platform developed by LexisNexis Risk Solutions. The HPCC platform incorporates a software architecture implemented on commodity computing clusters to provide high-performance, data-parallel processing for applications utilizing big data. The HPCC platform includes system configurations to support both parallel batch data processing (Thor) and high-performance online query applications using indexed data files (Roxie). The HPCC platform also includes a data-centric declarative programming language for parallel data processing called ECL. The public release of HPCC waannouncedin 2011, after ten years of in-house development (according to LexisNexis). It is an alternative to Hadoop and other Big data platforms. System architecture The HPCC system architecture includes two distinct cluster processing environments Thor and Roxie, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan And Weapons Of Mass Destruction
Pakistan is one of nine states to possess nuclear weapons. Pakistan began development of nuclear weapons in January 1972 under Prime Minister Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, who delegated the program to the Chairman of the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC) Munir Ahmad Khan with a commitment to having the device ready by the end of 1976. Since PAEC, which consisted of over twenty laboratories and projects under reactor physicist Munir Ahmad Khan, was falling behind schedule and having considerable difficulty producing fissile material, Abdul Qadeer Khan, a metallurgist working on centrifuge enrichment for Urenco, joined the program at the behest of the Bhutto administration by the end of 1974. As pointed out by Houston Wood, "The most difficult step in building a nuclear weapon is the production of fissile material"; as such, this work in producing fissile material as head of the Kahuta Project was pivotal to Pakistan developing the capability to detonate a nuclear weapon by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLOPS
In computing, floating point operations per second (FLOPS, flops or flop/s) is a measure of computer performance, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations. For such cases, it is a more accurate measure than measuring instructions per second. Floating-point arithmetic Floating-point arithmetic is needed for very large or very small real numbers, or computations that require a large dynamic range. Floating-point representation is similar to scientific notation, except everything is carried out in base two, rather than base ten. The encoding scheme stores the sign, the exponent (in base two for Cray and VAX, base two or ten for IEEE floating point formats, and base 16 for IBM Floating Point Architecture) and the significand (number after the radix point). While several similar formats are in use, the most common is ANSI/IEEE Std. 754-1985. This standard defines the format for 32-bit numbers called ''single precision'', as well as 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operations Per Second
In computing, floating point operations per second (FLOPS, flops or flop/s) is a measure of computer performance, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations. For such cases, it is a more accurate measure than measuring instructions per second. Floating-point arithmetic Floating-point arithmetic is needed for very large or very small real numbers, or computations that require a large dynamic range. Floating-point representation is similar to scientific notation, except everything is carried out in base two, rather than base ten. The encoding scheme stores the sign, the exponent (in base two for Cray and VAX, base two or ten for IEEE floating point formats, and base 16 for IBM Floating Point Architecture) and the significand (number after the radix point). While several similar formats are in use, the most common is ANSI/IEEE Std. 754-1985. This standard defines the format for 32-bit numbers called ''single precision'', as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first test of a fission ("atomic") bomb released an amount of energy approximately equal to . The first thermonuclear ("hydrogen") bomb test released energy approximately equal to . Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons TNT (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than . A nuclear device no larger than a conventional bomb can devastate an entire city by blast, fire, and radiation. Since they are weapons of mass destruction, the proliferation of nuclear weapons is a focus of international relations policy. Nuclear weapons have been d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monte Carlo Method
Monte Carlo methods, or Monte Carlo experiments, are a broad class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. The underlying concept is to use randomness to solve problems that might be deterministic in principle. They are often used in physical and mathematical problems and are most useful when it is difficult or impossible to use other approaches. Monte Carlo methods are mainly used in three problem classes: optimization, numerical integration, and generating draws from a probability distribution. In physics-related problems, Monte Carlo methods are useful for simulating systems with many coupled degrees of freedom, such as fluids, disordered materials, strongly coupled solids, and cellular structures (see cellular Potts model, interacting particle systems, McKean–Vlasov processes, kinetic models of gases). Other examples include modeling phenomena with significant uncertainty in inputs such as the calculation of ris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monte Carlo Method In Statistical Physics
Monte Carlo in statistical physics refers to the application of the Monte Carlo method to problems in statistical physics, or statistical mechanics. Overview The general motivation to use the Monte Carlo method in statistical physics is to evaluate a multivariable integral. The typical problem begins with a system for which the Hamiltonian is known, it is at a given temperature and it follows the Boltzmann statistics. To obtain the mean value of some macroscopic variable, say A, the general approach is to compute, over all the phase space, PS for simplicity, the mean value of A using the Boltzmann distribution: :\langle A\rangle=\int_ A_ \frac d\vec. where E(\vec)=E_ is the energy of the system for a given state defined by \vec - a vector with all the degrees of freedom (for instance, for a mechanical system, \vec = \left(\vec, \vec \right) ), \beta\equiv 1/k_bT and :Z= \int_ e^d\vec is the partition function. One possible approach to solve this multivariable integral is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Physics
Statistical physics is a branch of physics that evolved from a foundation of statistical mechanics, which uses methods of probability theory and statistics, and particularly the Mathematics, mathematical tools for dealing with large populations and approximations, in solving physical problems. It can describe a wide variety of fields with an inherently stochastic nature. Its applications include many problems in the fields of physics, biology, chemistry, and neuroscience. Its main purpose is to clarify the properties of matter in aggregate, in terms of physical laws governing atomic motion. Statistical mechanics develop the Phenomenology (particle physics), phenomenological results of thermodynamics from a probabilistic examination of the underlying microscopic systems. Historically, one of the first topics in physics where statistical methods were applied was the field of classical mechanics, which is concerned with the motion of particles or objects when subjected to a force. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Mathematics
Computational mathematics is an area of mathematics devoted to the interaction between mathematics and computer computation.National Science Foundation, Division of Mathematical ScienceProgram description PD 06-888 Computational Mathematics 2006. Retrieved April 2007. A large part of computational mathematics consists roughly of using mathematics for allowing and improving computer computation in areas of science and engineering where mathematics are useful. This involves in particular algorithm design, computational complexity, numerical methods and computer algebra. Computational mathematics refers also to the use of computers for mathematics itself. This includes mathematical experimentation for establishing conjectures (particularly in number theory), the use of computers for proving theorems (for example the four color theorem), and the design and use of proof assistants. Areas of computational mathematics Computational mathematics emerged as a distinct part of applied ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Additive Function
In number theory, an additive function is an arithmetic function ''f''(''n'') of the positive integer variable ''n'' such that whenever ''a'' and ''b'' are coprime, the function applied to the product ''ab'' is the sum of the values of the function applied to ''a'' and ''b'':Erdös, P., and M. Kac. On the Gaussian Law of Errors in the Theory of Additive Functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1939 April; 25(4): 206–207online/ref> f(a b) = f(a) + f(b). Completely additive An additive function ''f''(''n'') is said to be completely additive if f(a b) = f(a) + f(b) holds ''for all'' positive integers ''a'' and ''b'', even when they are not coprime. Totally additive is also used in this sense by analogy with totally multiplicative functions. If ''f'' is a completely additive function then ''f''(1) = 0. Every completely additive function is additive, but not vice versa. Examples Examples of arithmetic functions which are completely additive are: * The restriction of the Logarithm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kahuta Research Laboratories
The Dr. A. Q. Khan Research Laboratories, ( ur, ) or KRL for short, is a federally funded, multi-program national research institute and national laboratory site primarily dedicated to uranium enrichment, supercomputing and fluid mechanics. It is managed by the Ministry of Energy for the Government of Pakistan. The laboratory is located in Kahuta, a short distance north-east of Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan. The site was organized to produce weapons-grade nuclear material, primarily weapons-grade uranium, as part of Pakistan's secretive atomic bomb program in the years after the Indo-Pakistani war of 1971. Chosen to be a top-secret location, it was built in secrecy by the Pakistan Army Corps of Engineers. It was commissioned under the Army engineers with civilian scientists joining the site in late 1976. During the midst of the 1970s, the site was the cornerstone of the first stage of Pakistan's atomic bomb program, and is one of the many sites where classified scientific resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasneem M
Tasneem or Tasnim may refer to: A well of water in according to Islam. Tasnim: a spring of water in heaven,high in stature, descending from a height, mixing with it the nectar for the companions of the right and the rest of the people of Paradise. And it is the most honorable drink in heaven. And Tasneem in origin: height and altitude. Given name * Tasneem Essop, South African politician * Tasneem Motara (born 1982), South African politician * Tasneem Roc, Australian television and film actress of Burmese and Scottish descent * Tasneem Sheikh, Indian actress * Tasneem Zehra Husain, Pakistani theoretical physicist * Tasneem Qureishi, a fictional character from the American TV series ''Homeland'' Surname * Ahmed Tasnim, Pakistan Navy admiral See also * '' Tasneem Tafsir'', a Tafsir (interpretation) of the Quran by Javadi Amoli * Tasnim News Agency Tasnim News Agency ( fa, خبرگزاری تسنیم) is a semi-official news agency in Iran. It has links to the Islamic Revol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |