|
Sulfolane
Sulfolane (also ''tetramethylene sulfone'', systematic name: 1λ6-thiolane-1,1-dione) is an organosulfur compound, formally a cyclic sulfone, with the formula (CH2)4SO2. It is a colorless liquid commonly used in the chemical industry as a solvent for extractive distillation and chemical reactions. Sulfolane was originally developed by the Shell Oil Company in the 1960s as a solvent to purify butadiene. Sulfolane is a polar aprotic solvent, and it is readily soluble in water. Properties Sulfolane is classified as a sulfone, a group of organosulfur compounds containing a sulfonyl functional group. The sulfone group is a sulfur atom doubly bonded to two oxygen atoms and singly bonded to two carbon centers. The sulfur-oxygen double bond is polar, conferring good solubility in water, while the four carbon ring provides non-polar stability. These properties allow it to be miscible in both water and hydrocarbons, resulting in its widespread use as a solvent for purifying hydrocarbon mixtu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfolene
Sulfolene, or butadiene sulfone is a cyclic organic chemical with a sulfone functional group. It is a white, odorless, crystalline, indefinitely storable solid, which dissolves in water and many organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of butadiene. Production Sulfolene is formed by the cheletropic reaction between butadiene and sulfur dioxide. The reaction is typically conducted in an autoclave. Small amounts of hydroquinone or pyrogallol are added to inhibit polymerization of the diene. The reaction proceeds at room temperature over the course of days. At 130 °C, only 30 minutes are required. An analogous procedure gives the isoprene-derived sulfone. Reactions Acid-base reactivity The compound is unaffected by acids. It can even be recrystallized from conc. HNO3. The protons in the 2- and 5-positions rapidly exchange with deuterium oxide under alkaline conditions. Sodium cyanide catalyzes this reaction. : Isomerization to 2-sulfolene In the presence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfolene
Sulfolene, or butadiene sulfone is a cyclic organic chemical with a sulfone functional group. It is a white, odorless, crystalline, indefinitely storable solid, which dissolves in water and many organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of butadiene. Production Sulfolene is formed by the cheletropic reaction between butadiene and sulfur dioxide. The reaction is typically conducted in an autoclave. Small amounts of hydroquinone or pyrogallol are added to inhibit polymerization of the diene. The reaction proceeds at room temperature over the course of days. At 130 °C, only 30 minutes are required. An analogous procedure gives the isoprene-derived sulfone. Reactions Acid-base reactivity The compound is unaffected by acids. It can even be recrystallized from conc. HNO3. The protons in the 2- and 5-positions rapidly exchange with deuterium oxide under alkaline conditions. Sodium cyanide catalyzes this reaction. : Isomerization to 2-sulfolene In the presence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
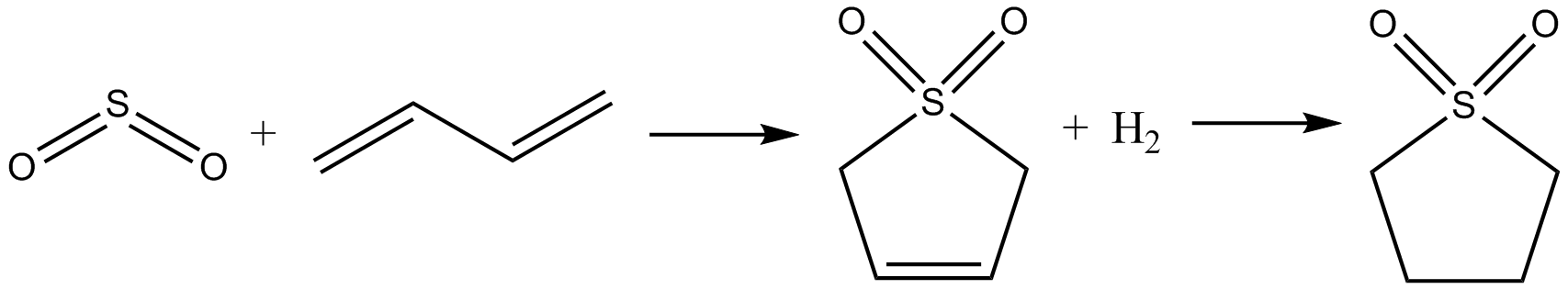
Sulfone
In organic chemistry, a sulfone is a organosulfur compound containing a sulfonyl () functional group attached to two carbon atoms. The central hexavalent sulfur atom is double-bonded to each of two oxygen atoms and has a single bond to each of two carbon atoms, usually in two separate hydrocarbon substituents. Synthesis and reactions By oxidation of thioethers and sulfoxides Sulfones are typically prepared by organic oxidation of thioethers, often referred to as sulfides. Sulfoxides are intermediates in this route. For example, dimethyl sulfide oxidizes to dimethyl sulfoxide and then to dimethyl sulfone. From SO2 : Sulfur dioxide is a convenient and widely used source of the sulfonyl functional group. Specifically, Sulfur dioxide participates in cycloaddition reactions with dienes. The industrially useful solvent sulfolane is prepared by addition of sulfur dioxide to buta-1,3-diene followed by hydrogenation of the resulting sulfolene. From sulfonyl and sulfuryl halides Sulfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula (CH2=CH)2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene. Although butadiene breaks down quickly in the atmosphere, it is nevertheless found in ambient air in urban and suburban areas as a consequence of its constant emission from motor vehicles. The name butadiene can also refer to the isomer, 1,2-butadiene, which is a cumulated diene with structure H2C=C=CH−CH3. This allene has no industrial significance. History In 1863, the French chemist E. Caventou isolated butadiene from the pyrolysis of amyl alcohol. This hydrocarbon was identified as butadiene in 1886, after Henry Edward Armstrong isolated it from among the pyrolysis products of petroleum. In 1910, the Russian chemist Sergei Lebedev polymerized butadiene and obtained a material wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylsulfonylmethane
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2SO2. It is also known by several other names including methyl sulfone and dimethyl sulfone (DMSO2). This colorless solid features the sulfonyl functional group and is the simplest of the sulfones. It is considered relatively inert chemically and is able to resist decomposition at elevated temperatures. It occurs naturally in some primitive plants, is present in small amounts in many foods and beverages, and is marketed as a dietary supplement. It is sometimes used as a cutting agent for illicitly manufactured methamphetamine. It is also commonly found in the atmosphere above marine areas, where it is used as a carbon source by the airborne bacteria ''Afipia''. Oxidation of dimethyl sulfoxide produces the sulfone, both under laboratory conditions and metabolically. Use as a solvent Because of its polarity and thermal stability, MSM has been used industrially as a high-temperature solvent. For example, di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrothiophene
Tetrahydrothiophene is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH2)4S. The molecule consists of a five-membered saturated ring with four methylene groups and a sulfur atom. It is the saturated analog of thiophene. It is a volatile, colorless liquid with an intensely unpleasant odor. It is also known as thiophane, thiolane, or THT. While THT is not particularly common, the vitamin biotin is essential for life in aerobic organisms. Synthesis and reactions Tetrahydrothiophene is prepared by the reaction of tetrahydrofuran with hydrogen sulfide. This vapor-phase reaction is catalyzed by alumina and other heterogenous acid catalysts. This compound is a ligand in coordination chemistry, an example being the complex chloro(tetrahydrothiophene)gold(I). Oxidation of THT gives the sulfone sulfolane, which is of interest as a polar, odorless solvent: : Sulfolane is, however, more conventionally prepared from butadiene. Natural occurrence Both unsubstituted and substituted tetra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of copper extraction and the burning of sulfur- bearing fossil fuels. Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support for this simple approach that does not invoke ''d'' orbital participation. In terms of electron-counting formalism, the sulfur atom has an oxidation state of +4 and a formal charge of +1. Occurrence Sulfur dioxide is found on Earth and exists in very small concentrations and in the atmosphere at about 1 ppm. On other planets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrothiophene
Tetrahydrothiophene is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH2)4S. The molecule consists of a five-membered saturated ring with four methylene groups and a sulfur atom. It is the saturated analog of thiophene. It is a volatile, colorless liquid with an intensely unpleasant odor. It is also known as thiophane, thiolane, or THT. While THT is not particularly common, the vitamin biotin is essential for life in aerobic organisms. Synthesis and reactions Tetrahydrothiophene is prepared by the reaction of tetrahydrofuran with hydrogen sulfide. This vapor-phase reaction is catalyzed by alumina and other heterogenous acid catalysts. This compound is a ligand in coordination chemistry, an example being the complex chloro(tetrahydrothiophene)gold(I). Oxidation of THT gives the sulfone sulfolane, which is of interest as a polar, odorless solvent: : Sulfolane is, however, more conventionally prepared from butadiene. Natural occurrence Both unsubstituted and substituted tetra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Aprotic Solvent
A polar aprotic solvent is a solvent that lacks an acidic proton and is polar. Such solvents lack hydroxyl and amine groups. In contrast to protic solvents, these solvents do not serve as proton donors in hydrogen bonding In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a l ..., although they can be proton acceptors. Many solvents, including chlorocarbons and hydrocarbons, are classifiable as aprotic, but polar aprotic solvents are of particular interest for their ability to dissolve salts. Methods for purification of common solvents are available. References {{Chemical solutions Solvents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |