|
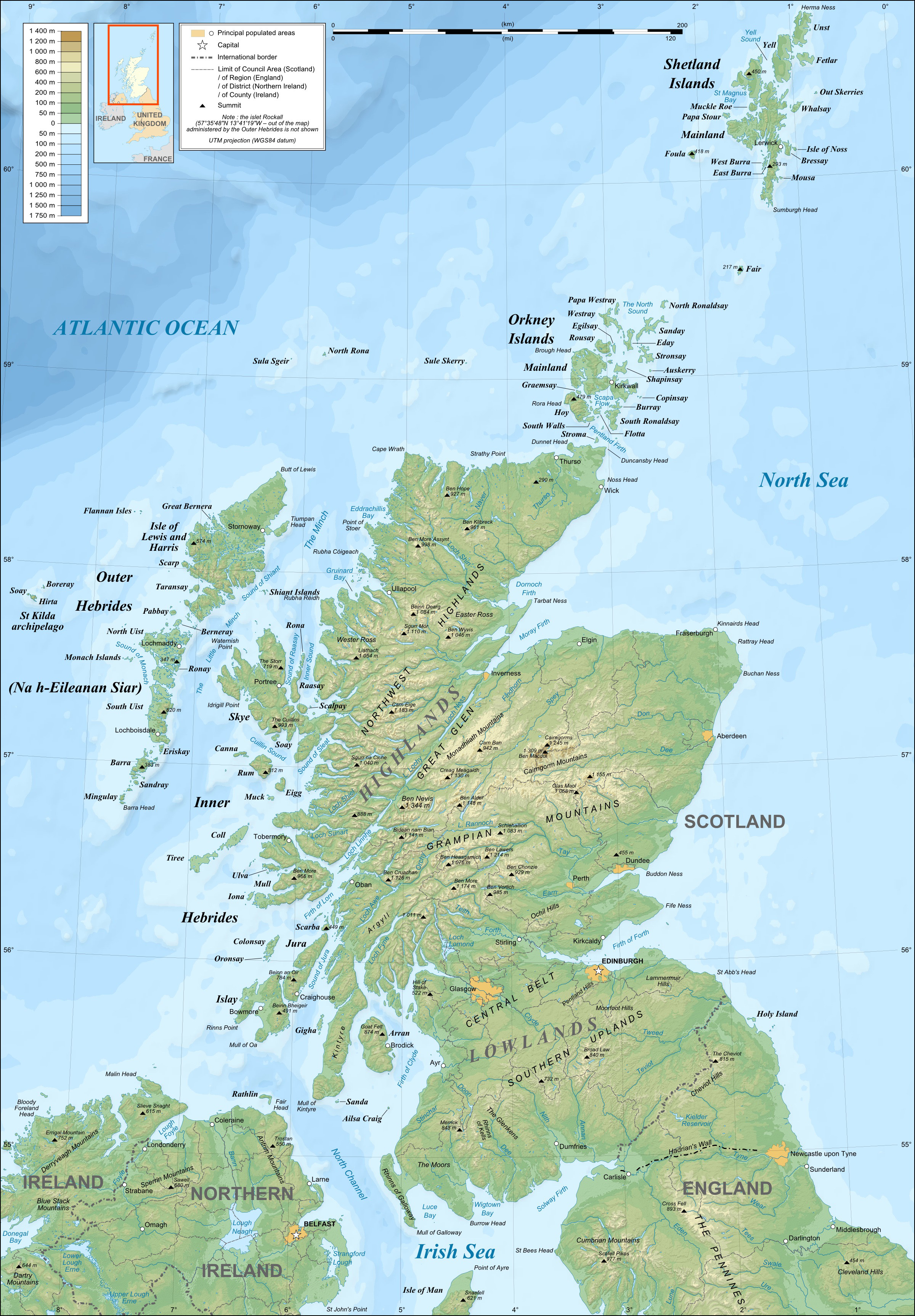
Sule Stack
Sule Stack or Stack Skerry is an extremely remote island or stack in the North Atlantic off the north coast of Scotland. It is formed of Lewisian gneiss. Sule Stack lies north of the Scottish mainland, and west of the Orkney mainland, at . Sule Stack's sole neighbour, Sule Skerry, lies northeast and the remote islands of Rona and Sula Sgeir lie further to the west. Sule Stack and Sule Skerry are home to thousands of gannets and as a result are listed as a special protection area; the island falls within the administrative region of the Orkney Islands. Bird species nesting on the stack include: *Razorbill ''Alca torda'' *Atlantic puffin ''Fratercula arctica'' *Fulmar ''Fulmarus glacialis'' *Great black-backed gull ''Larus marinus'' * Common shag '' Phalacrocorax aristotelis'' *Black-legged kittiwake ''Rissa tridactyla'' *Arctic tern ''Sterna paradisaea'' *Northern gannet ''Morus bassanus'' *Common guillemot ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulmar
The fulmars are tubenosed seabirds of the family Procellariidae. The family consists of two extant species and two extinct fossil species from the Miocene. Fulmars superficially resemble gulls, but are readily distinguished by their flight on stiff wings, and their tube noses. They breed on cliffs, laying one or rarely two eggs on a ledge of bare rock or on a grassy cliff. Outside the breeding season, they are pelagic, feeding on fish, squid and shrimp in the open ocean. They are long-lived for birds, living for up to 40 years. Historically, the northern fulmar lived on the Isle of St Kilda, where it was extensively hunted. The species has expanded its breeding range southwards to the coasts of England and northern France. Taxonomy The genus ''Fulmarus'' was introduced in 1826 by the English naturalist James Stephens. The name comes from the Old Norse ''Fúlmár'' meaning "foul-mew" or "foul-gull" because of the birds' habit of ejecting a foul-smelling oil. The type species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sites Of Special Scientific Interest In Orkney
Site most often refers to: * Archaeological site * Campsite, a place used for overnight stay in an outdoor area * Construction site * Location, a point or an area on the Earth's surface or elsewhere * Website, a set of related web pages, typically with a common domain name It may also refer to: * Site, a National Register of Historic Places property type * SITE (originally known as ''Sculpture in the Environment''), an American architecture and design firm * Site (mathematics), a category C together with a Grothendieck topology on C * ''The Site'', a 1990s TV series that aired on MSNBC * SITE Intelligence Group, a for-profit organization tracking jihadist and white supremacist organizations * SITE Institute, a terrorism-tracking organization, precursor to the SITE Intelligence Group * Sindh Industrial and Trading Estate, a company in Sindh, Pakistan * SITE Centers, American commercial real estate company * SITE Town, a densely populated town in Karachi, Pakistan * S.I.T.E Indust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Protection Areas In Scotland
This is a list of Special Protection Areas (SPAs) in Scotland. {, class="wikitable" summary="Table of classified and potential SPAs in Scotland" , - ! style="width:42%;" , Site name ! style="width:10%;" , Site code ! style="width:8%;" , Country ! style="width:10%;" , Area (ha) ! Coordinates ! style="width:10%;" , Status , - style="vertical-align:top;" , Abernethy Forest , UK9002561 , S , 5793.46 , , Classified , - style="vertical-align:top;" , Achanalt Marshes , UK9001701 , S , 208.25 , , Classified , - style="vertical-align:top;" , Ailsa Craig , UK9003091 , S , 99.94 , , Classified , - style="vertical-align:top;" , Aird and Borve, Benbecula , UK9001751 , S , 361 , , Classified , - style="vertical-align:top;" , Anagach Wood , UK9020297 , S , , , Potential , - style="vertical-align:top;" , Arran Moors , UK9003341 , S , 10736.51 , , Classified , - style="vertical-align:top;" , Assynt Lochs , UK9001591 , S , 1156.43 , , Class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Birds (magazine)
''British Birds'' is a monthly ornithology magazine that was established in 1907. It is now published by BB 2000 Ltd, which is wholly owned by The British Birds Charitable Trust (registered charity number 1089422), established for the benefit of British ornithology. Its circulation in 2000 was 5,250 copies; its circulation peaked at 11,000 in the late 1980s. The current editor is Stephen Menzie. ''British Birds'' is aimed at serious birdwatchers and ornithologists, rather than the more casual birdwatchers catered for by some other magazines on the subject. It publishes the findings of the British Birds Rarities Committee. Its mascot, and later logo, the red grouse, was chosen because at the time it was thought to be an endemic British species (although it is now considered a subspecies of the willow grouse). In 1916, ''British Birds'' magazine absorbed ''The Zoologist'', due to the latter's shortage of subscribers. Editors The current editor of ''British Birds'' is Stephen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Outlying Islands Of Scotland
The outlying islands of Scotland are not part of the larger archipelagos and island groups of Scotland—the Hebrides, the Northern Isles or the Islands of the Forth and Clyde estuaries. None of these islands are currently inhabited and few of them ever were, although Hirta was occupied from the Neolithic age until 1930 and Stroma was permanently occupied until the 1970s and thereafter by lighthouse keepers and their families until 1996. Several other outlying islands have lighthouses, none of which is still staffed. In this list, an island is defined as "land that is surrounded by seawater on a daily basis, but not necessarily at all stages of the tide, excluding human devices such as bridges and causeways". A complication relating to membership of this list is that there are various descriptions of the scope of the Hebrides, the large group of islands that lie off Scotland's west coast. The '' Collins Encyclopedia of Scotland'' describes the Inner Hebrides as lying "east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Guillemot
The common murre or common guillemot (''Uria aalge'') is a large auk. It has a circumpolar distribution, occurring in low-Arctic and boreal waters in the North Atlantic and North Pacific. It spends most of its time at sea, only coming to land to breed on rocky cliff shores or islands. Common murres have fast direct flight but are not very agile. They are more maneuverable underwater, typically diving to depths of . Depths of up to have been recorded. Common murres breed in colonies at high densities. Nesting pairs may be in bodily contact with their neighbours. They make no nest; their single egg is incubated on a bare rock ledge on a cliff face. Eggs hatch after ~30 days incubation. The chick is born downy and can regulate its body temperature after 10 days. Some 20 days after hatching the chick leaves its nesting ledge and heads for the sea, unable to fly, but gliding for some distance with fluttering wings, accompanied by its male parent. Male guillemots spend more time divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Gannet
The northern gannet (''Morus bassanus'') is a seabird, the largest species of the gannet family, Sulidae. It is native to the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean, breeding in Western Europe and Northeastern North America. It is the largest seabird in the northern Atlantic. The sexes are similar in appearance. The adult northern gannet has a mainly white streamlined body with a long neck, and long and slender wings. It is long with a wingspan. The head and nape have a buff tinge that is more prominent in breeding season, and the wings are edged with dark brown-black feathers. The long, pointed bill is blue-grey, contrasting with black, bare skin around the mouth and eyes. Juveniles are mostly grey-brown, becoming increasingly white in the five years it takes them to reach maturity. Nesting takes place in colonies on both sides of the North Atlantic, the largest of which are at Bass Rock (75,000 pairs as of 2014), St. Kilda (60,000 pairs as of 2013) and Ailsa Craig (33,000 pairs as of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Tern
The Arctic tern (''Sterna paradisaea'') is a tern in the family Laridae. This bird has a circumpolar breeding distribution covering the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions of Europe (as far south as Brittany), Asia, and North America (as far south as Massachusetts). The species is strongly migratory, seeing two summers each year as it migrates along a convoluted route from its northern breeding grounds to the Antarctic coast for the southern summer and back again about six months later. Recent studies have shown average annual round-trip lengths of about for birds nesting in Iceland and Greenland and about for birds nesting in the Netherlands. These are by far the longest migrations known in the animal kingdom. The Arctic tern nests once every one to three years (depending on its mating cycle). Arctic terns are medium-sized birds. They have a length of and a wingspan of . They are mainly grey and white plumaged, with a red/orange beak and feet, white forehead, a black nape and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-legged Kittiwake
The black-legged kittiwake (''Rissa tridactyla'') is a seabird species in the gull family Laridae. This species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' as ''Larus tridactylus''. The English name is derived from its call, a shrill 'kittee-wa-aaake, kitte-wa-aaake'. The genus name ''Rissa'' is from the Icelandic name ''rita'' for this bird, and the specific ''tridactyla'' is from Ancient Greek ''tridaktulos'', "three-toed", from ''tri-'', "three-" and ''daktulos'', "toe". In North America, this species is known as the black-legged kittiwake to differentiate it from the red-legged kittiwake, but in Europe, where it is the only member of the genus, it is often known just as kittiwake. Range and distribution The black-legged kittiwake is a coastal bird of the arctic to subarctic regions of the world.del Hoyo, J; Elliott, A; Sargatal, J (1996). ''Handbook of the Birds of the World Vol. 3''. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. pp. 622–62 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Shag
The European shag or common shag (''Gulosus aristotelis'') is a species of cormorant. It is the only member of the monotypic genus ''Gulosus''. It breeds around the rocky coasts of western and southern Europe, southwest Asia and north Africa, mainly wintering in its breeding range except for the northernmost birds. In Britain this seabird is usually referred to as simply the shag. The scientific genus name derives from the Latin for glutton. The species name ''aristotelis'' commemorates the Greek philosopher Aristotle. Taxonomy The European shag was formerly classified within the genus ''Phalacrocorax'', but a 2014 study found it to be significantly more diverged than the clade containing ''Phalacrocorax'' and ''Urile'', but basal to the clade containing ''Nannopterum'' and ''Leucocarbo'', and thus classified it in its own genus, ''Gulosus''. The IOC followed this classification in 2021. ''Gulosus'' is thought to have split from the ''Nannopterum''-''Leucocarbo'' clade between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Black-backed Gull
The great black-backed gull (''Larus marinus'') is the largest member of the gull family. Described by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology as "the king of the Atlantic waterfront", it is a very aggressive hunter, pirate, and scavenger. It breeds on the European and North American coasts and islands of the North Atlantic and is fairly sedentary, though some move farther south or inland to large lakes or reservoirs. The adult great black-backed gull has a white head, neck and underparts, dark grey wings and back, pink legs and yellow bill. Taxonomy The great black-backed gull was one of the many species originally described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'', and it still bears its original name of ''Larus marinus''. The scientific name is from Latin. ''Larus'' appears to have referred to a gull or other large seabird. The specific name ''marinus'' means "marine", or when taken together, "sea gull". This predates Linnean taxonomy, as it had been called ''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |