|
Subdwarf O Star
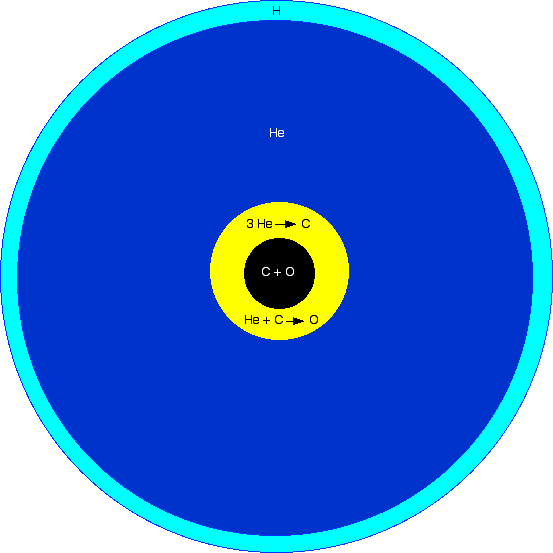
A subdwarf O star (sdO) is a type of hot, but low-mass star. O-type subdwarfs are much dimmer than regular O-type main-sequence stars, but with a brightness about 10 to 100 times that of the Sun, and have a mass approximately half that of the Sun. Their temperature ranges from 40,000 to 100,000 K. Ionized helium is prominent in their spectra. Their surface gravity (typically given as the gravity's logarithm), log ''g'' is usually between 4.0 and 6.5. Many sdO stars are moving at high velocity through the Milky Way and are found at high galactic latitudes. Structure The structure of a subdwarf O star is believed to be a carbon and oxygen core surrounded by a helium burning shell. The spectrum shows that the content is from 50 to 100% helium. History In the early 1970s Greenstein and Sargent measured temperatures and gravity strengths and were able to plot their correct position on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. The Palomar-Green survey, Hamburg surveys, Sloan Digital Sky Surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subdwarf O Star Schematic Cross Section
A subdwarf, sometimes denoted by "sd", is a star with luminosity class VI under the stellar classification#Yerkes spectral classification, Yerkes spectral classification system. They are defined as stars with luminosity 1.5 to 2 Absolute magnitude, magnitudes lower than that of main-sequence stars of the same spectral type. On a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram subdwarfs appear to lie below the main sequence. The term "subdwarf" was coined by Gerard Kuiper in 1939, to refer to a series of stars with anomalous spectra that were previously labeled as "intermediate white dwarfs". Since Gerard Kuiper, Kuiper coined the term, the subdwarf type has been extended to lower-mass stars than were known at the time. Astronomers have also discovered an entirely different group of blue-white subdwarfs, making two distinct categories: * #cool_subdwarf_anchor, Cool subdwarfs * #hot_subdwarf_anchor, Hot subdwarfs Like ordinary main sequence, main-sequence stars, cool subdwarfs (of spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
HD 49798
HD 49798 is a binary star in the constellation Puppis about from Earth. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.3, making it one of the brightest known O class subdwarf stars. HD 49798 was discovered in 1964 to be a rare hydrogen-deficient O class subdwarf, and was the brightest known at the time. This was identified as a binary star, but the companion could not be detected visually or spectroscopically. The X-ray source RX J0648.0-4418 was discovered close to HD 49798's location in the sky. Only the space telescope XMM-Newton was able to identify the source. It is a white dwarf with about 1.3 solar masses, in orbit about HD 49798 and rotating once every 13 seconds; this rotation is speeding up by per year. This is detected from the 13-second X-ray pulse, which results from the stellar wind accreting onto the compact object. It has been proposed that the white dwarf is surrounded by a debris disk. In this model, the material of the disk would be funneled onto the pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
White Dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place in a white dwarf; what light it radiates is from its residual heat. The nearest known white dwarf is Sirius B, at 8.6 light years, the smaller component of the Sirius binary star. There are currently thought to be eight white dwarfs among the hundred star systems nearest the Sun. The unusual faintness of white dwarfs was first recognized in 1910. The name ''white dwarf'' was coined by Willem Jacob Luyten in 1922. White dwarfs are thought to be the final stellar evolution, evolutionary state of stars whose mass is not high enough to become a neutron star or black hole. This includes over 97% of the stars in the Milky Way. After the hydrogen-stellar nucleosynthesis, fusing period of a main sequence, main-sequence star of Stellar mass, lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
B-type Subdwarf
A B-type subdwarf (sdB) is a kind of subdwarf star with spectral type B. They differ from the typical subdwarf by being much hotter and brighter. They are situated at the "extreme horizontal branch" of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. Masses of these stars are around 0.5 solar masses, and they contain only about 1% hydrogen, with the rest being helium. Their radius is from 0.15 to 0.25 solar radii, and their surface temperature is from . Formation and evolution These stars represent a late stage in the evolution of some stars, caused when a red giant star loses its outer hydrogen layers before the core begins to fuse helium. The reasons why this premature mass loss occurs are unclear, but the interaction of stars in a binary star system is thought to be one of the main mechanisms. Single subdwarfs may be the result of a merger of two white dwarfs. The sdB stars are expected to become white dwarfs without going through any more giant stages. Subdwarf B stars, being more lumin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Planetary Nebula
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives. The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to planets. The term originates from the planet-like round shape of these nebulae observed by astronomers through early telescopes. The first usage may have occurred during the 1780s with the English astronomer William Herschel who described these nebulae as resembling planets; however, as early as January 1779, the French astronomer Antoine Darquier de Pellepoix described in his observations of the Ring Nebula, "very dim but perfectly outlined; it is as large as Jupiter and resembles a fading planet". Though the modern interpretation is different, the old term is still used. All planetary nebulae form at the end of the life of a star of intermediate mass, about 1-8 solar masses. It is expected that the Sun will form a planetary nebula at the end of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Extended Horizontal Branch
Extension, extend or extended may refer to: Mathematics Logic or set theory * Axiom of extensionality * Extensible cardinal * Extension (model theory) * Extension (proof theory) * Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values that satisfy the predicate * Extension (semantics), the set of things to which a property applies * Extension (simplicial set) * Extension by definitions * Extensional definition, a definition that enumerates every individual a term applies to * Extensionality Other uses * Extension of a function, defined on a larger domain * Extension of a polyhedron, in geometry * Extension of a line segment (finite) into an infinite line (e.g., extended base) * Exterior algebra, Grassmann's theory of extension, in geometry * Field extension, in Galois theory * Group extension, in abstract algebra and homological algebra * Homotopy extension property, in topology * Kolmogorov extension theorem, in probability theory * Linear extension, in order theory * Shea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Asymptotic Giant Branch
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) late in their lives. Observationally, an asymptotic-giant-branch star will appear as a bright red giant with a luminosity ranging up to thousands of times greater than the Sun. Its interior structure is characterized by a central and largely inert core of carbon and oxygen, a shell where helium is undergoing fusion to form carbon (known as helium burning), another shell where hydrogen is undergoing fusion forming helium (known as hydrogen burning), and a very large envelope of material of composition similar to main-sequence stars (except in the case of carbon stars). Stellar evolution When a star exhausts the supply of hydrogen by nuclear fusion processes in its core, the core contracts and its temperature increases, causing the oute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram
The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (abbreviated as H–R diagram, HR diagram or HRD) is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities and their stellar classifications or effective temperatures. The diagram was created independently in 1911 by Ejnar Hertzsprung and by Henry Norris Russell in 1913, and represented a major step towards an understanding of stellar evolution. Historical background In the nineteenth century large-scale photographic spectroscopic surveys of stars were performed at Harvard College Observatory, producing spectral classifications for tens of thousands of stars, culminating ultimately in the Henry Draper Catalogue. In one segment of this work Antonia Maury included divisions of the stars by the width of their spectral lines. Hertzsprung noted that stars described with narrow lines tended to have smaller proper motions than the others of the same spectral classification. He took this as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
A Fleeting Moment In Time - Planetary Nebula ESO 577-24
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
US 708
US 708 is a hyper-velocity class O subdwarf in Ursa Major, in the halo of the Milky Way Galaxy. One of the fastest-moving stars in the galaxy, the star was first surveyed in 1982. Discovery US 708 was first discovered in 1982 by Peter Usher and colleagues of Pennsylvania State University as a faint blue object in the Milky Way halo. Sloan Digital Sky Survey measured the star again in 2005. Research In 2015, Stephan Geier of the European Southern Observatory led a team that reported in ''Science'' that the velocity of the star was , the highest ever recorded in the galaxy at that time. The star's high velocity was originally suspected to be caused by the massive black hole at the center of the galaxy. But now it is found out that the star must have crossed the galactic disk about 14 million years ago and thus it did not come from the center of the galaxy; hence the speed now possessed by the star may not be attributed to the black hole. However, closer study sug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
HIP 52181
In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) (: ''coxae'') in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint on the outer (lateral) side of the pelvis. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest, and lateral to the obturator foramen, with muscle tendons and soft tissues overlying the greater trochanter of the femur. In adults, the three pelvic bones ( ilium, ischium and pubis) have fused into one hip bone, which forms the superomedial/deep wall of the hip region. The hip joint, scientifically referred to as the acetabulofemoral joint (''art. coxae''), is the ball-and-socket joint between the pelvic acetabulum and the femoral head. Its primary function is to support the weight of the torso in both static (e.g. standing) and dynamic (e.g. walking or running) postures. The hip joints have very i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subdwarf
A subdwarf, sometimes denoted by "sd", is a star with luminosity class VI under the Yerkes spectral classification system. They are defined as stars with luminosity 1.5 to 2 magnitudes lower than that of main-sequence stars of the same spectral type. On a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram subdwarfs appear to lie below the main sequence. The term "subdwarf" was coined by Gerard Kuiper in 1939, to refer to a series of stars with anomalous spectra that were previously labeled as "intermediate white dwarfs". Since Kuiper coined the term, the subdwarf type has been extended to lower-mass stars than were known at the time. Astronomers have also discovered an entirely different group of blue-white subdwarfs, making two distinct categories: * Cool subdwarfs * Hot subdwarfs Like ordinary main-sequence stars, cool subdwarfs (of spectral types G to M) produce their energy from hydrogen fusion. The explanation of their underluminosity lies in their low metallicity: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |