|
Stránská Skála
Stránská skála is a hill and a national nature monument in Brno in the Czech Republic. It refers to a Mid-Pleistocene- Cromerian interglacial most important paleontological site in Central Europe. Location Stránská skála is situated in the northern part of the Brno-Slatina district, in the eastern part of Brno. From the geomorphological point of view, Stránská skála belongs to the Dyje–Svratka Valley within the Outer Subcarpathia. Description Stránská skála is dating to approximately 600,000 BP, as supported by paleomagnetic dating. It is a long and wide hill, built from Jurassic limestone, especially Callovian- Oxfordian, built from light brown Caleidocrinus (Crinoid) mostly and Brachiopoddes and Coral and more other types of limestones rich of fossil fauna as well. Its northwestern slope is composed from karstified limestone cliffs in which numerous fossiliferous fissures and caves were found. Approximately 48 meter (157 ft) of this slope are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
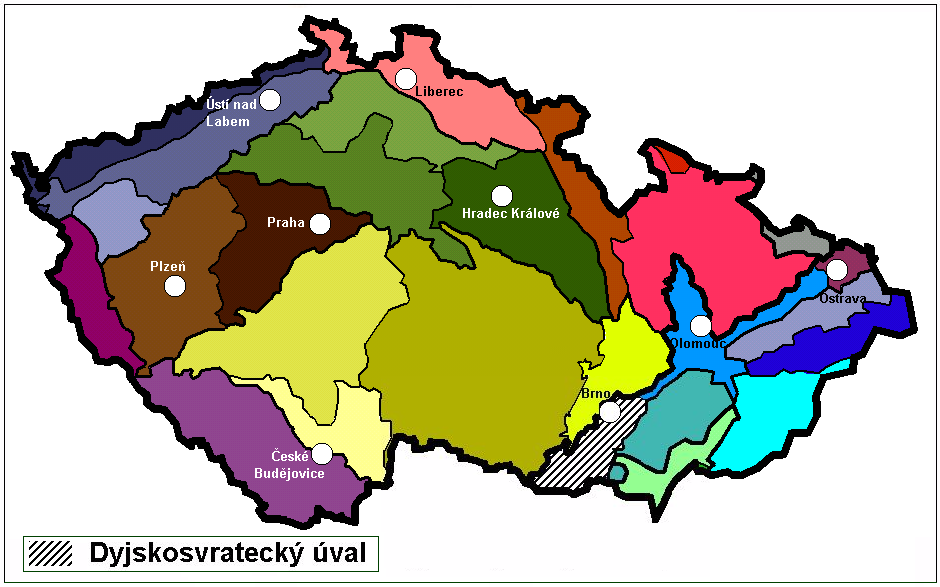
Dyje–Svratka Valley
The Dyje–Svratka Valley ( cs, Dyjsko-svratecký úval, german: Thaya-Schwarza Talsenke) is a geomorphological feature (a special type of vale) in South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. History The Dyje–Svratka Valley has been a natural pass between the Vienna Basin (Carpathians) and the Vyškov Gate, the Upper Morava Valley, Moravian Gate and later, the North European Plain (Poland - Lower Silesia - Galicia) since ancient times. It served as an arm of several important trade routes from southern Europe to the Baltic Sea such as the Amber Road, as well as routes from Moravia to Upper Silesia and Lesser Poland. The Emperor Ferdinand Northern Railway from Břeclav to Brno traverses the Dyje–Svratka Valley. Geography The floodplains of several rivers end in the Dyje–Svratka Valley, including Svratka, Jihlava, Svitava, Thaya, Jevišovka and Litava. Many towns are located within it, including the southern districts of Brno, Slavkov u Brna, Židlochovice, Pohořel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crinoid
Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or comatulids, which are members of the largest crinoid order, Comatulida. Crinoids are echinoderms in the phylum Echinodermata, which also includes the starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins and sea cucumbers. They live in both shallow water and in depths as great as . Adult crinoids are characterised by having the mouth located on the upper surface. This is surrounded by feeding arms, and is linked to a U-shaped gut, with the anus being located on the oral disc near the mouth. Although the basic echinoderm pattern of fivefold symmetry can be recognised, in most crinoids the five arms are subdivided into ten or more. These have feathery pinnules and are spread wide to gather planktonic particles from the water. At some stage in their lives, most crinoids have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Fish
Coastal fish, also called inshore fish or neritic fish, inhabit the sea between the shoreline and the edge of the continental shelf. Since the continental shelf is usually less than deep, it follows that pelagic coastal fish are generally epipelagic fish, inhabiting the sunlit epipelagic zone.Moyle and Cech, 2004, page 585 Coastal fish can be contrasted with ''oceanic fish'' or ''offshore fish'', which inhabit the deep seas beyond the continental shelves. Coastal fish are the most abundant in the world. They can be found in tidal pools, fjords and estuaries, near sandy shores and rocky coastlines, around coral reefs and on or above the continental shelf. Coastal fish include forage fish and the predator fish that feed on them. Forage fish thrive in inshore waters where high productivity results from upwelling and shoreline run off of nutrients. Some are partial residents that spawn in streams, estuaries and bays, but most complete their life cycles in the zone.Moyle and Cech, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalve
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. The shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances. The shell of a bivalve is composed of calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostracod
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 70,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant) have been identified, grouped into several orders. They are small crustaceans, typically around in size, but varying from in the case of ''Gigantocypris''. Their bodies are flattened from side to side and protected by a bivalve-like, chitinous or calcareous valve or "shell". The hinge of the two valves is in the upper (dorsal) region of the body. Ostracods are grouped together based on gross morphology. While early work indicated the group may not be monophyletic and early molecular phylogeny was ambiguous on this front, recent combined analyses of molecular and morphological data found support for monophyly in analyses with broadest taxon sampling. Ecologically, marine ostracods can be part of the zooplankton or (most commonly) are part of the benthos, living on or inside the upper layer of the sea floor. While Myodoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursus Deningeri
''Ursus deningeri'' (Deninger's bear) is an extinct species of bear, endemic to Eurasia during the Pleistocene for approximately 1.7 million years, from . The range of this bear has been found to encompass both Europe and Asia, demonstrating the ability of the species to adapt to many Pleistocene environments. ''U. deningeri'' is a descendant of ''U. savini'' and an ancestor of ''U. spelaeus''. Morphology ''Ursus deningeri'' has a combination of primitive and derived characters that distinguishes it from all other Pleistocene bears. Its mandible is slender like that of living brown bears and '' Ursus etruscus''. It also has derived characters of cave bears (''Ursus spelaeus'') and is considered to be the descendant of ''Ursus savini'' and very close to the common ancestor of brown bears. Fossil distribution Sites and specimen ages: *Nalaikha, Mongolia: ~1.8 Mya to 800,000 years ago *West Runton Freshwater Bed, Cromer Forest Bed Formation, Norfolk, England: ~800,000–100,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homotherium
''Homotherium'', also known as the scimitar-toothed cat or scimitar cat, is an extinct genus of machairodontine saber-toothed predator, often termed scimitar-toothed cats, that inhabited North America, South America, Eurasia, and Africa during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs (4 mya – 12,000 years ago), existing for approximately . It became extinct in Africa some 1.5 million years ago. The most recent Eurasian remains, recovered from what is now the North Sea, have been dated to around 28,000 years BP. In South America it is only known from a few remains in the northern region (Venezuela), from the mid-Pleistocene. Taxonomy and distribution The name ''Homotherium'' (Greek: (, 'same') and (, 'beast')) was proposed by Emilio Fabrini (1890), without further explanation, for a new subgenus of ''Machairodus'', whose main distinguishing feature was the presence of a large diastema between the two inferior premolars. The lineage of ''Homotherium'' is estimated (based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, ( gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavation (archaeology)
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be conducted over a few weeks to several years. Excavation involves the recovery of several types of data from a site. This data includes artifacts (portable objects made or modified by humans), features (non-portable modifications to the site itself such as post molds, burials, and hearths), ecofacts (evidence of human activity through organic remains such as animal bones, pollen, or charcoal), and archaeological context (relationships among the other types of data).Kelly&Thomas (2011). ''Archaeology: down to earth'' (4th ed.). Belmont, Calif.: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. Before excavating, the presence or absence of archaeological remains can often be suggested by, non-intrusive remote sensing, such as ground-penetrating radar. Basic informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fissure
A fissure is a long, narrow crack opening along the surface of Earth. The term is derived from the Latin word , which means 'cleft' or 'crack'. Fissures emerge in Earth's crust, on ice sheets and glaciers, and on volcanoes. Ground fissure A , also called an , is a long, narrow crack or linear opening in the Earth's crust. Ground fissures can form naturally, such as from tectonic faulting and earthquakes, or as a consequence of human activity, such as oil mining and groundwater pumping. Once formed, ground fissures can be extended and eroded by torrential rain. They can be hazardous to people and livestock living on the affected surfaces and damaging to property and infrastructure, such as roads, underground pipes, canals, and dams. In circumstances where there is the extensive withdrawal of groundwater, the earth above the water table can subside causing fissures to form at the surface. This typically occurs at the floor of arid valleys having rock formations and compacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossiliferous
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliff
In geography and geology, a cliff is an area of rock which has a general angle defined by the vertical, or nearly vertical. Cliffs are formed by the processes of weathering and erosion, with the effect of gravity. Cliffs are common on coasts, in mountainous areas, escarpments and along rivers. Cliffs are usually composed of rock that is resistant to weathering and erosion. The sedimentary rocks that are most likely to form cliffs include sandstone, limestone, chalk, and dolomite. Igneous rocks such as granite and basalt also often form cliffs. An escarpment (or scarp) is a type of cliff formed by the movement of a geologic fault, a landslide, or sometimes by rock slides or falling rocks which change the differential erosion of the rock layers. Most cliffs have some form of scree slope at their base. In arid areas or under high cliffs, they are generally exposed jumbles of fallen rock. In areas of higher moisture, a soil slope may obscure the talus. Many cliffs also fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |